Source – Petz Park
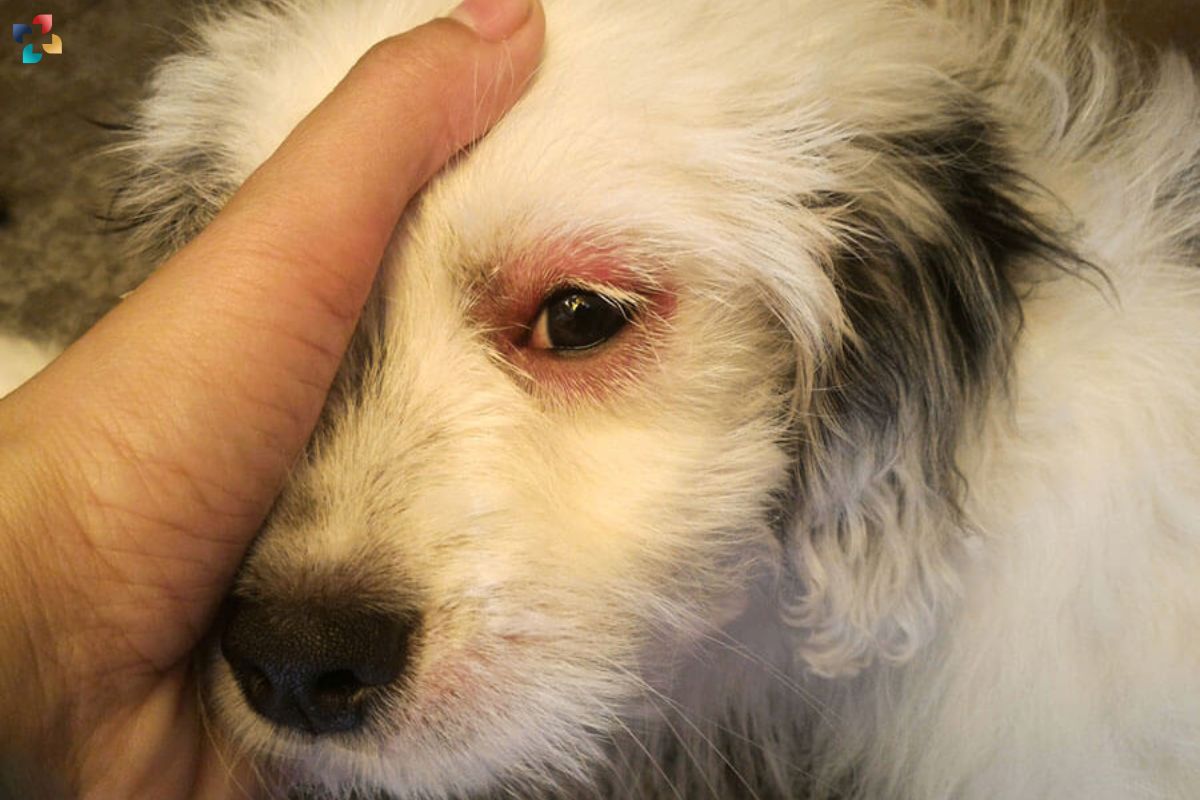
Dog eye infections are a common concern among pet owners and can affect dogs of all breeds and ages. These infections, if left untreated, can cause discomfort and potentially lead to more serious complications. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for dog eye infections, as well as preventive measures to keep your canine companion’s eyes healthy.
Understanding Dog Eye Infections
Dog eye infections, also known as canine conjunctivitis or dog pink eye, occur when the tissues lining the eye become inflamed or infected. This inflammation can be caused by bacteria, viruses, allergies, foreign objects, or underlying health conditions. Identifying the underlying cause of the infection is crucial for effective treatment and management.
Common Causes of Dog Eye Infections
Dog eye infections can be caused by various factors, including:
- Bacterial Infections: Bacteria such as Staphylococcus or Streptococcus can infect the eyes, leading to conjunctivitis or other forms of bacterial eye infections.
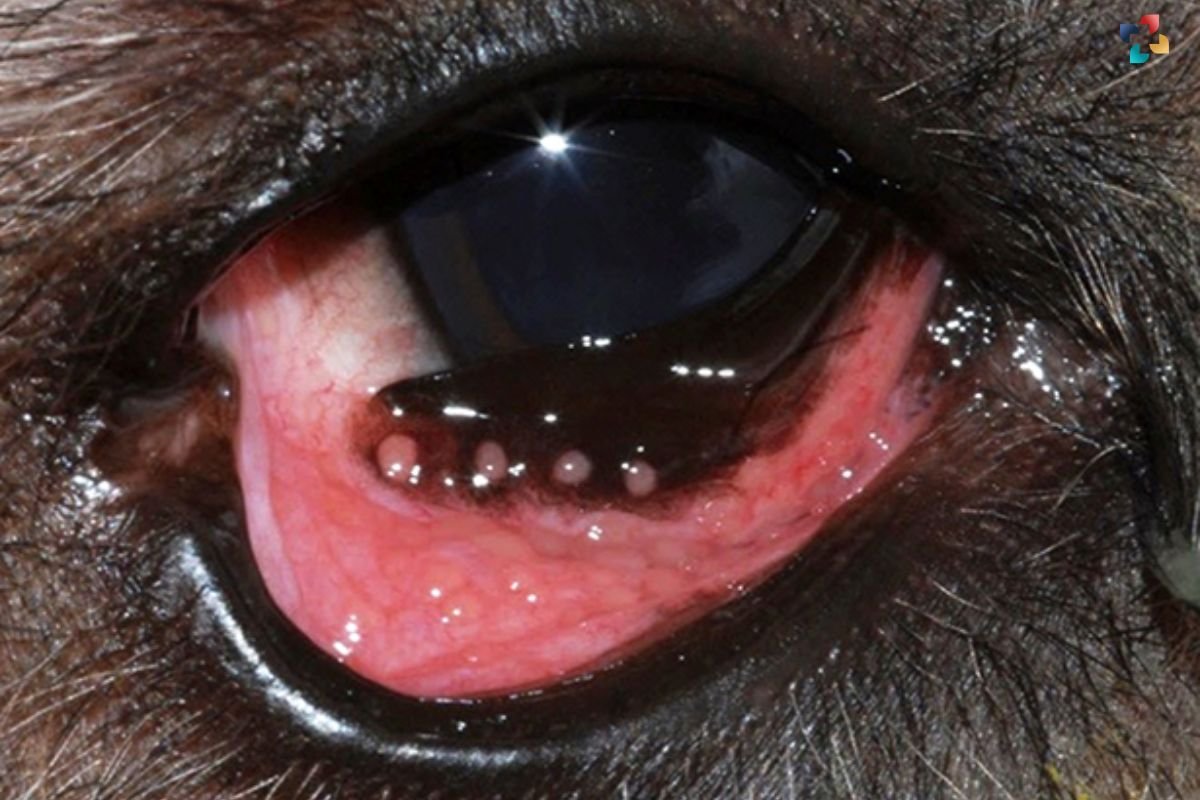
- Viral Infections: Viruses such as canine distemper virus or canine adenovirus can cause viral conjunctivitis in dogs.
- Allergies: Allergens such as pollen, dust, or certain chemicals can trigger allergic reactions in dogs, leading to red, itchy eyes.
- Foreign Objects: Particles such as dirt, dust, or plant material can irritate the eyes and potentially cause infections if not removed promptly.
- Genetic Predisposition: Certain dog breeds may be more prone to eye infections due to their anatomy or genetics.
- Environmental Factors: Environmental factors such as dry air, smoke, or pollutants can irritate the eyes and increase the risk of infections.
Symptoms of Dog Eye Infections
Recognizing the symptoms of dog eye infections is essential for prompt intervention and treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Redness: Redness in one or both eyes is a hallmark symptom of dog eye infections and indicates inflammation.
- Swelling: Swelling of the eyelids or tissues around the eyes may occur due to inflammation or fluid buildup.
- Discharge: Dogs with eye infections may have discharge from the eyes, which can be clear, watery, mucous-like, or purulent (containing pus).
- Tearing: Excessive tearing or watery eyes can occur as a result of irritation or inflammation.
- Squinting or Blinking: Dogs may squint or blink frequently to alleviate discomfort or pain associated with eye infections.
- Rubbing or Scratching: Dogs may rub or scratch at their eyes in an attempt to relieve itching or irritation.
- Cloudiness or Haze: Cloudiness or a hazy appearance in the eyes may indicate the presence of infection or other underlying issues.
Diagnosing Dog Eye Infections
Diagnosing dog eye infections involves a thorough examination by a veterinarian, including:
- Physical Examination: A veterinarian will examine the dog’s eyes for signs of inflammation, discharge, swelling, or other abnormalities.
- Medical History: A detailed medical history, including any previous eye problems or recent changes in the dog’s environment, helps identify potential causes of the infection.
- Eye Tests: Specialized eye tests, such as fluorescein staining or Schirmer tear tests, may be performed to evaluate the integrity of the eye’s surface and tear production.
- Additional Testing: In some cases, additional tests such as bacterial culture, viral PCR testing, or allergy testing may be recommended to identify the specific cause of the infection.
Treatment Options for Dog Eye Infections
The treatment approach for dog eye infections depends on the underlying cause and severity of the infection. Common treatment options include:
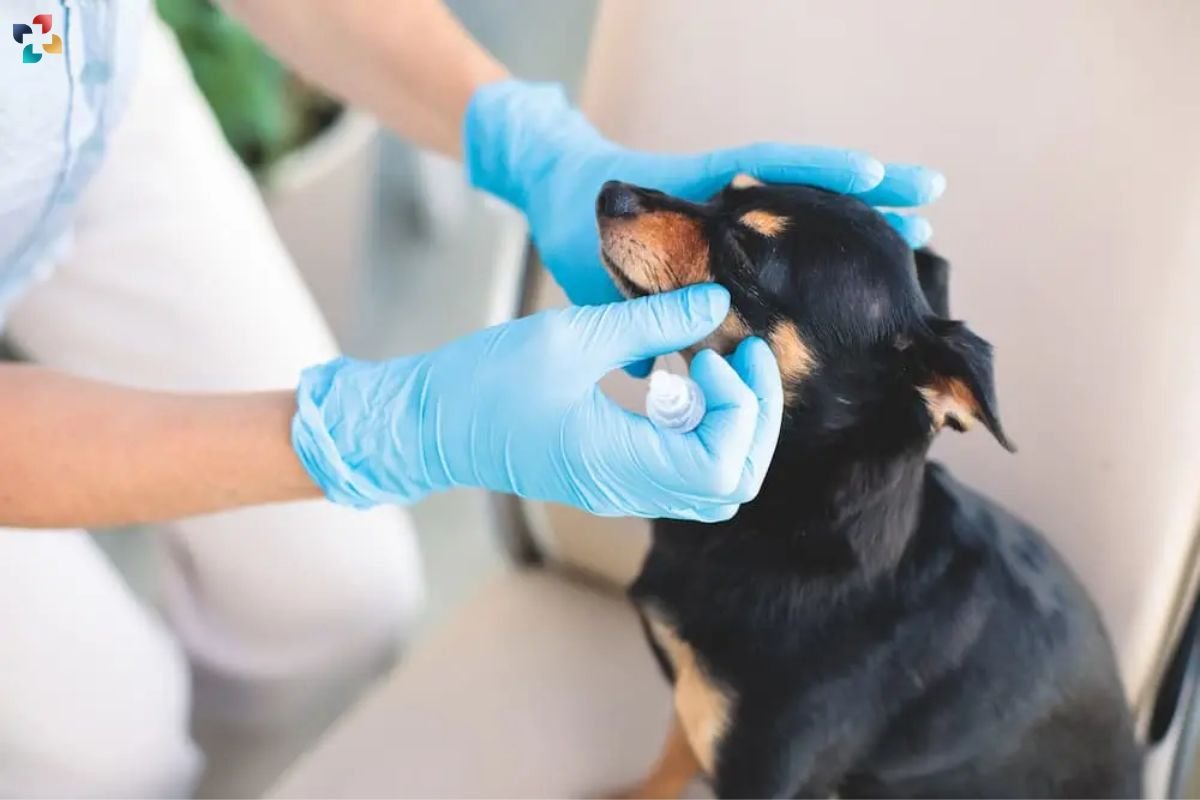
- Topical Antibiotics: Antibiotic eye drops or ointments are often prescribed to treat bacterial eye infections and prevent secondary complications.
- Antiviral Medications: In cases of viral conjunctivitis, antiviral medications may be prescribed to help control the infection and reduce symptoms.
- Anti-inflammatory Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroids may be used to reduce inflammation and alleviate discomfort.
- Artificial Tears: Lubricating eye drops or ointments can help soothe dry, irritated eyes and promote healing.
- Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to the eyes can help loosen debris, reduce swelling, and promote drainage of discharge.
- Eye Irrigation: Flushing the eyes with saline solution or sterile water can help remove foreign objects or irritants and cleanse the eye.
- Oral Medications: In severe or systemic infections, oral medications such as antibiotics or antivirals may be prescribed.
- Surgical Intervention: In rare cases of severe or chronic eye infections, surgical procedures such as eyelid surgery or corneal debridement may be necessary.
Preventing Dog Eye Infections
Preventing dog eye infections involves implementing preventive measures to minimize the risk of exposure to potential irritants or pathogens. Here are some tips for preventing dog eye infections:
- Regular Eye Examinations: Schedule regular veterinary check-ups to monitor your dog’s eye health and address any concerns promptly.
- Good Hygiene Practices: Keep your dog’s eyes clean by gently wiping away discharge or debris with a damp cloth or cotton ball.
- Environmental Management: Minimize exposure to potential allergens, pollutants, or irritants in your dog’s environment.
- Proper Nutrition: Provide a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients to support your dog’s overall health and immune function.

- Avoiding Trauma: Take precautions to prevent eye injuries, such as using protective eyewear during outdoor activities or avoiding rough play.
- Regular Grooming: Keep your dog’s facial hair trimmed to prevent irritation and reduce the risk of debris getting trapped around the eyes.
- Avoiding Contaminated Water: Prevent your dog from swimming in or drinking from contaminated water sources, as this can increase the risk of eye infections.
Conclusion
Dog eye infections are a common health concern for pet owners, but with proper understanding, early detection, and prompt treatment, most infections can be effectively managed. By recognizing the symptoms of dog eye infections, seeking timely veterinary care, and implementing preventive measures, you can help protect your canine companion’s vision and overall well-being.
Remember to consult your veterinarian if you notice any signs of eye irritation or infection in your dog, as prompt intervention can help prevent complications and promote faster recovery. With attentive care and proactive management, you can ensure that your dog enjoys healthy, happy eyes for years to come.

Top 10 Most Common Health Problems For Dogs
Your dog is a devoted friend, but he can’t tell you how he’s feeling. As his owner, it is your responsibility to understand his suffering and provide for his well-being. There are several Common Health Problems For Dogs must deal with.