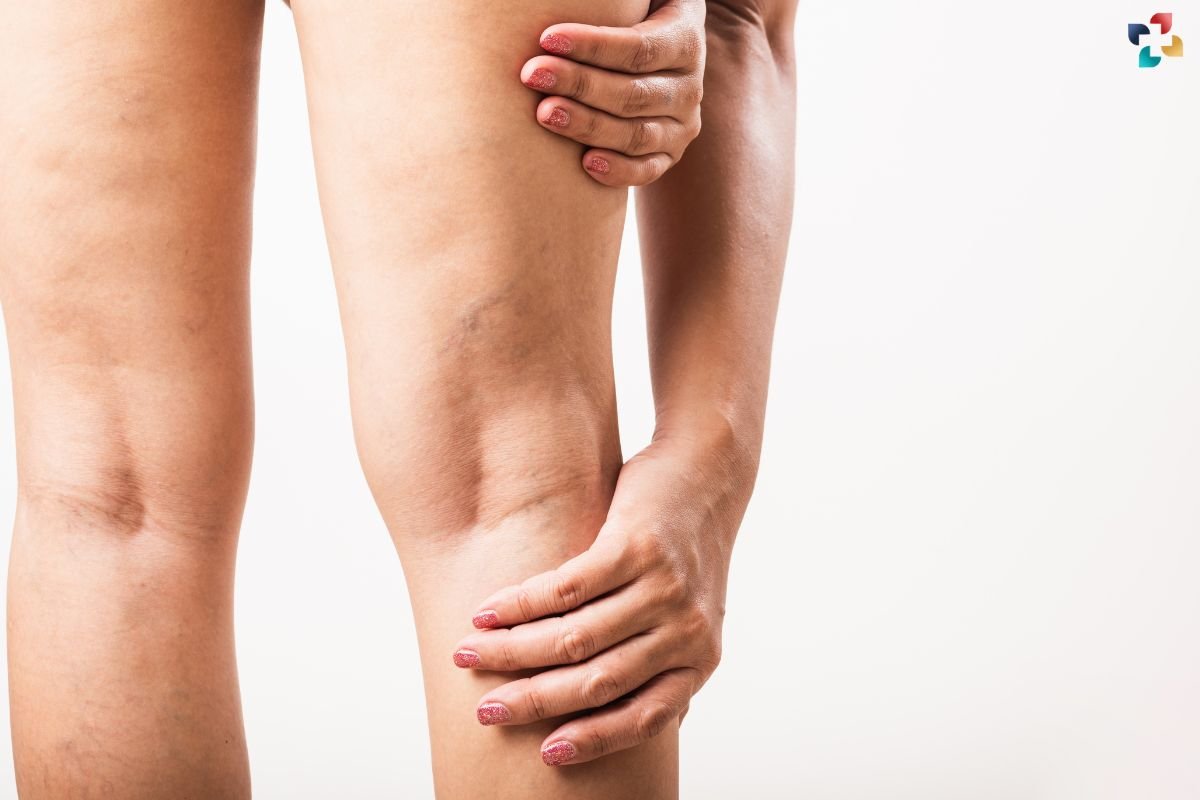
Deep Leg Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a condition that often lurks in the shadows, undetected until it strikes with potentially fatal consequences. Despite its silent nature, DVT poses a significant threat to individuals worldwide, affecting millions annually. In this article, we delve deep into the intricacies of DVT, exploring its causes, symptoms, risk factors, and crucial preventative measures.
Understanding Deep Leg Vein Thrombosis:
Deep Leg Vein Thrombosis occurs when a blood clot forms in one or more of the deep veins in the legs. These clots can impede blood flow, leading to severe complications such as pulmonary embolism if they dislodge and travel to the lungs. While DVT primarily affects the lower limbs, it can occur in other parts of the body as well, albeit less frequently.
Causes and Risk Factors:
Several factors contribute to the development of DVT, including prolonged immobility, injury or surgery, hormone therapy, pregnancy, obesity, and genetic predisposition. Individuals with a history of DVT or a family history of blood clotting disorders are at heightened risk. Additionally, long-distance travel, especially by air, increases the likelihood of DVT due to extended periods of immobility.
Symptoms and Diagnosis:
Recognizing the symptoms of Deep Leg Vein Thrombosis is crucial for early intervention and prevention of complications. Common signs include swelling, pain, warmth, and redness in the affected leg. However, in some cases, DVT may present asymptomatically, making diagnosis challenging. Medical professionals utilize various diagnostic tools, such as ultrasound imaging and blood tests, to confirm the presence of DVT accurately.
Complications and Treatment:
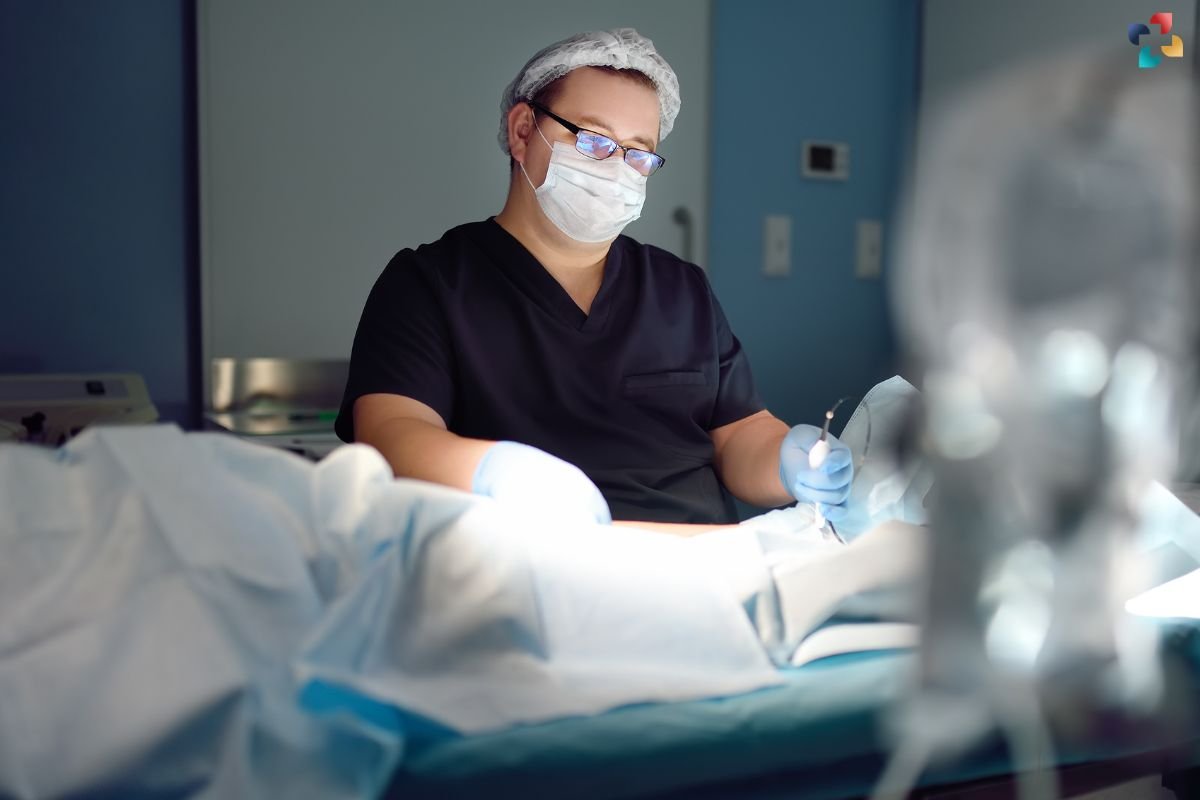
If left untreated, DVT can lead to serious complications, including pulmonary embolism, post-thrombotic syndrome, and chronic venous insufficiency. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent these adverse outcomes. Anticoagulant medications, such as heparin and warfarin, are commonly prescribed to prevent clot expansion and recurrence. In severe cases, thrombolytic therapy or surgical intervention may be necessary to dissolve or remove the clot.
Preventative Measures:
Prevention is key in mitigating the risk of Deep Leg Vein Thrombosis, particularly in high-risk individuals. Simple lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise, avoiding prolonged periods of immobility, and maintaining a healthy weight, can significantly reduce the likelihood of DVT occurrence. For individuals at increased risk, especially during long flights or following surgery, prophylactic measures such as compression stockings or blood-thinning medications may be recommended.
Raising Awareness:
Despite its potentially life-threatening consequences, DVT often remains overlooked or underestimated. Raising awareness about the risk factors, symptoms, and preventative strategies associated with Deep Leg Vein Thrombosis is paramount in combating this silent menace. Educational initiatives targeting both healthcare professionals and the general public can facilitate early detection and intervention, ultimately saving lives.
Empowering Patients and Healthcare Providers:
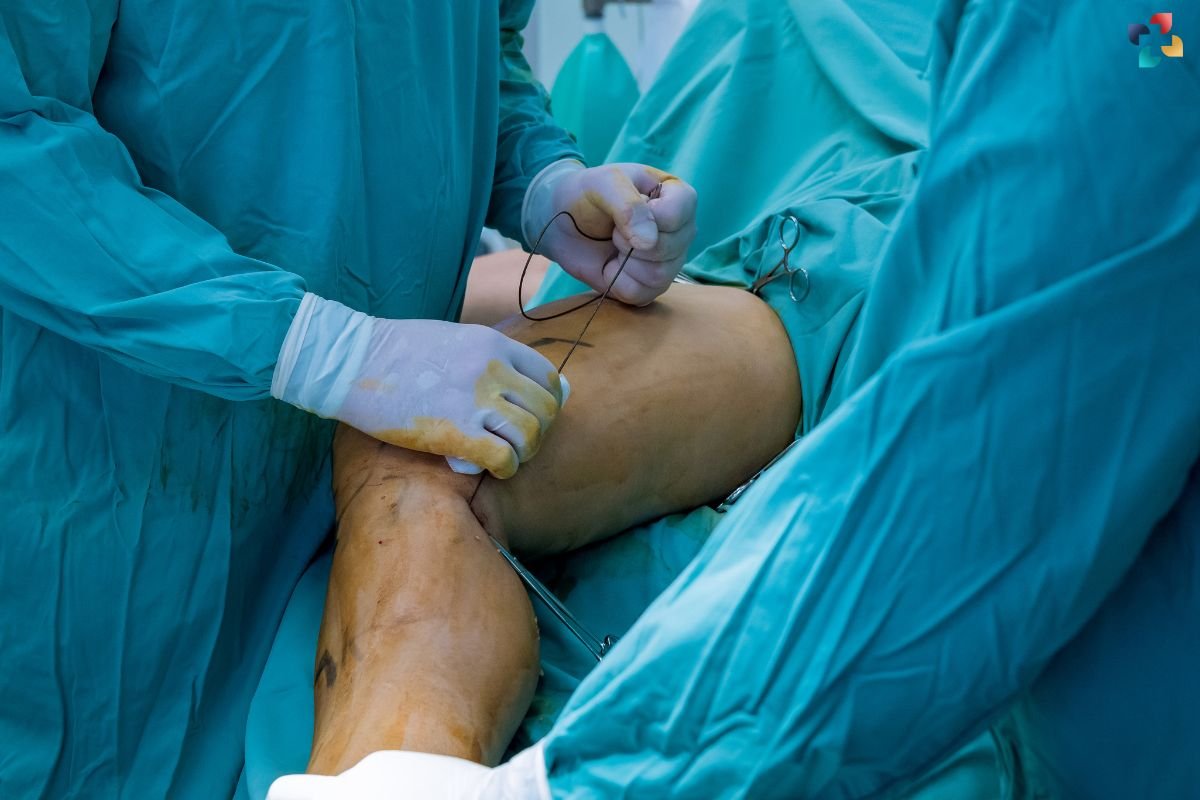
One of the most effective ways to combat deep leg vein thrombosis (DVT) is through empowerment—both of patients and healthcare providers. Patients need to be informed about the signs and symptoms of DVT, particularly if they fall into high-risk categories. Healthcare providers must stay updated with the latest guidelines and advancements in DVT management, ensuring that they can provide the best possible care to their patients.
Educational campaigns can play a significant role here. For instance, distributing informational brochures in clinics, hospitals, and community centers can help raise awareness. Additionally, leveraging digital platforms such as social media, websites, and mobile applications can disseminate information to a broader audience. These platforms can offer valuable resources, including interactive tools that help individuals assess their risk of DVT and prompt them to seek medical advice if necessary.
The Role of Technology in DVT Prevention and Management:
Advancements in technology have paved the way for innovative approaches to Deep Leg Vein Thrombosis prevention and management. Wearable devices, for example, can monitor a patient’s physical activity and provide reminders to move or perform leg exercises during prolonged periods of immobility. These devices can be particularly beneficial for individuals who travel frequently or have sedentary jobs.
Telemedicine is another promising avenue, allowing healthcare providers to monitor and manage patients remotely. This can be particularly useful for individuals who have been diagnosed with DVT or are at high risk. Through regular virtual check-ins, healthcare providers can ensure that patients are adhering to their treatment plans and making necessary lifestyle adjustments to prevent DVT recurrence.
Research and Future Directions:
Ongoing research into the pathophysiology of DVT and the development of new therapeutic strategies is crucial for improving patient outcomes. Studies exploring the genetic factors associated with DVT can provide insights into why certain individuals are more predisposed to the condition, leading to more personalized approaches to prevention and treatment.
Furthermore, advancements in pharmacology are continually enhancing the efficacy and safety of anticoagulant therapies. Newer anticoagulants that require less frequent monitoring and have fewer dietary restrictions offer improved convenience for patients. Additionally, research into alternative therapies, such as anti-inflammatory agents and targeted molecular treatments, holds promise for the future of DVT management.
Patient Stories: Personalizing the Impact of DVT:
Sharing real-life patient stories can humanize the impact of DVT and underscore the importance of awareness and prevention. For instance, consider the story of Sarah, a young professional who developed DVT after a long-haul flight. Despite experiencing mild discomfort in her leg, she initially dismissed it as muscle soreness. However, when the pain intensified and her leg began to swell, she sought medical attention and was diagnosed with DVT. Thanks to prompt treatment, Sarah recovered fully, but her experience highlights the need for greater awareness about the risks of DVT, especially among frequent travelers.
Similarly, the story of John, a retiree with a family history of blood clots, emphasizes the importance of genetic factors in DVT risk. John’s proactive approach, including regular check-ups and lifestyle modifications, helped him manage his risk effectively. His story serves as a reminder that understanding one’s personal risk factors and taking preventive measures can make a significant difference.
The Importance of Support Systems:
Support systems, including family, friends, and support groups, play a vital role in the management of DVT. Emotional and psychological support can help patients cope with the anxiety and uncertainty that often accompany a DVT diagnosis. Support groups, whether in-person or online, provide a platform for individuals to share their experiences, exchange information, and offer encouragement to one another.
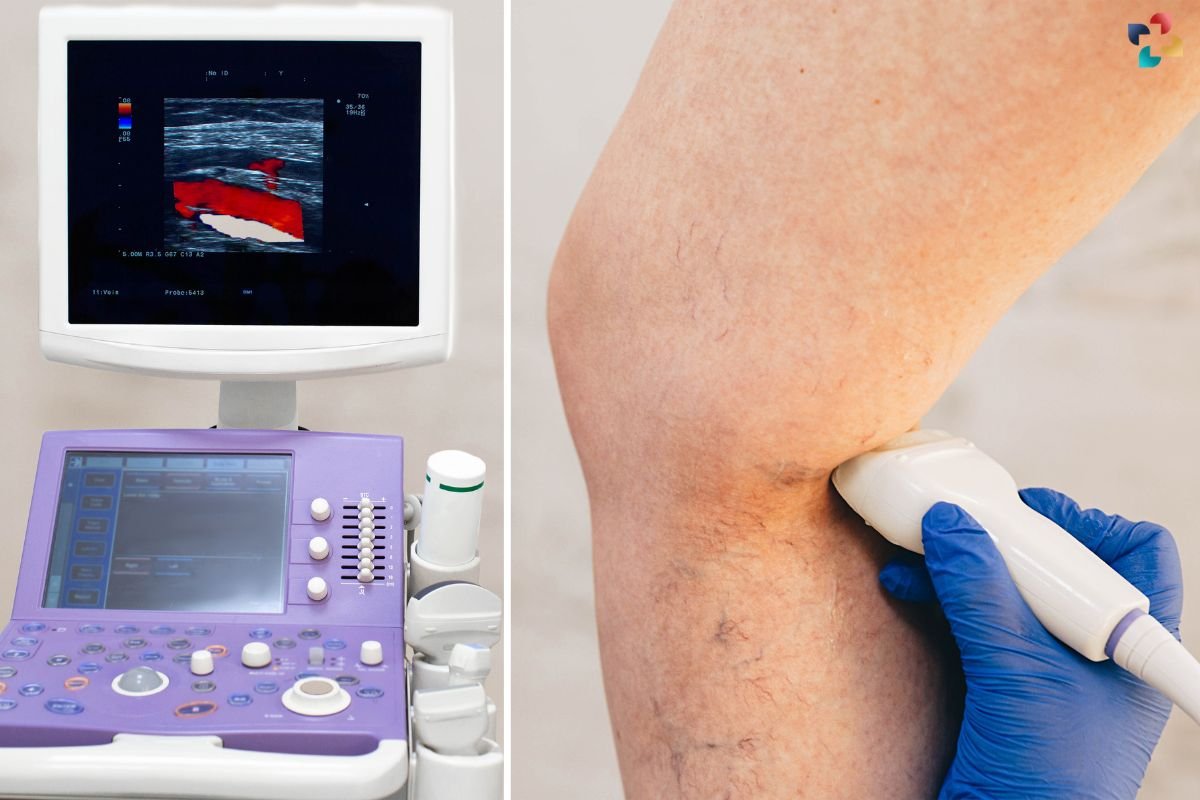
Healthcare providers should encourage patients to seek support and connect them with relevant resources. This holistic approach to DVT management, which addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of the condition, can enhance patient well-being and adherence to treatment plans.
Policy and Advocacy:
Policymakers and healthcare organizations must prioritize DVT awareness and prevention. This can be achieved through the implementation of public health initiatives, funding for research, and the development of comprehensive guidelines for DVT management. Advocacy efforts should also focus on ensuring that high-risk individuals have access to preventive measures, such as compression stockings and anticoagulant medications.
Additionally, workplace policies that encourage regular movement and the use of ergonomic equipment can help reduce the risk of DVT among employees. Employers should be educated about the importance of these measures and incentivized to implement them.
Conclusion:
Deep Leg Vein Thrombosis is a condition that demands our attention due to its potential for severe and life-threatening complications. By understanding the causes and symptoms of DVT, we can take proactive steps to reduce its incidence. Through education, technological innovation, patient empowerment, and supportive policies, we can improve the detection, prevention, and management of DVT.
The collective effort of individuals, healthcare providers, researchers, and policymakers is essential to combat this silent menace effectively. As we continue to advance our knowledge and tools, we can hope for a future where the risks associated with deep leg vein thrombosis are significantly diminished, ensuring a healthier and safer life for all.
Raising awareness and fostering a comprehensive approach to deep leg vein thrombosis can save lives. Whether it is through personal vigilance, community education, or systemic changes in healthcare practices, every step counts in the fight against DVT. By working together, we can unveil the dangers of this silent menace and pave the way for better health outcomes worldwide.

Understanding the Tibia and Fibula: The Dynamic Duo of the Lower Leg
This extensive guide aims to delve deeper into the anatomy, functions, common injuries, treatment options, and preventive measures. It highlights the significance of the tibia and fibula in maintaining overall musculoskeletal health.