In recent times, amidst the global health crisis, the significance of monitoring vital signs has become more pronounced than ever. Among the array of medical devices aiding in this endeavor, the pulse oximeter stands out as a critical tool for assessing oxygen saturation levels in the blood. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the functionality, benefits, and applications of the Pulse Oximeter in modern healthcare.
What is a Pulse Oximeter?
A Pulse Oximeter is a compact, non-invasive medical device used to measure the oxygen saturation level (SpO2) in the blood. It operates by emitting light wavelengths through the skin, which then detects the amount of oxygen-carrying hemoglobin present in the arterial blood. This vital information provides insights into the efficiency of oxygen delivery to various organs and tissues in the body.
Accuracy and Reliability
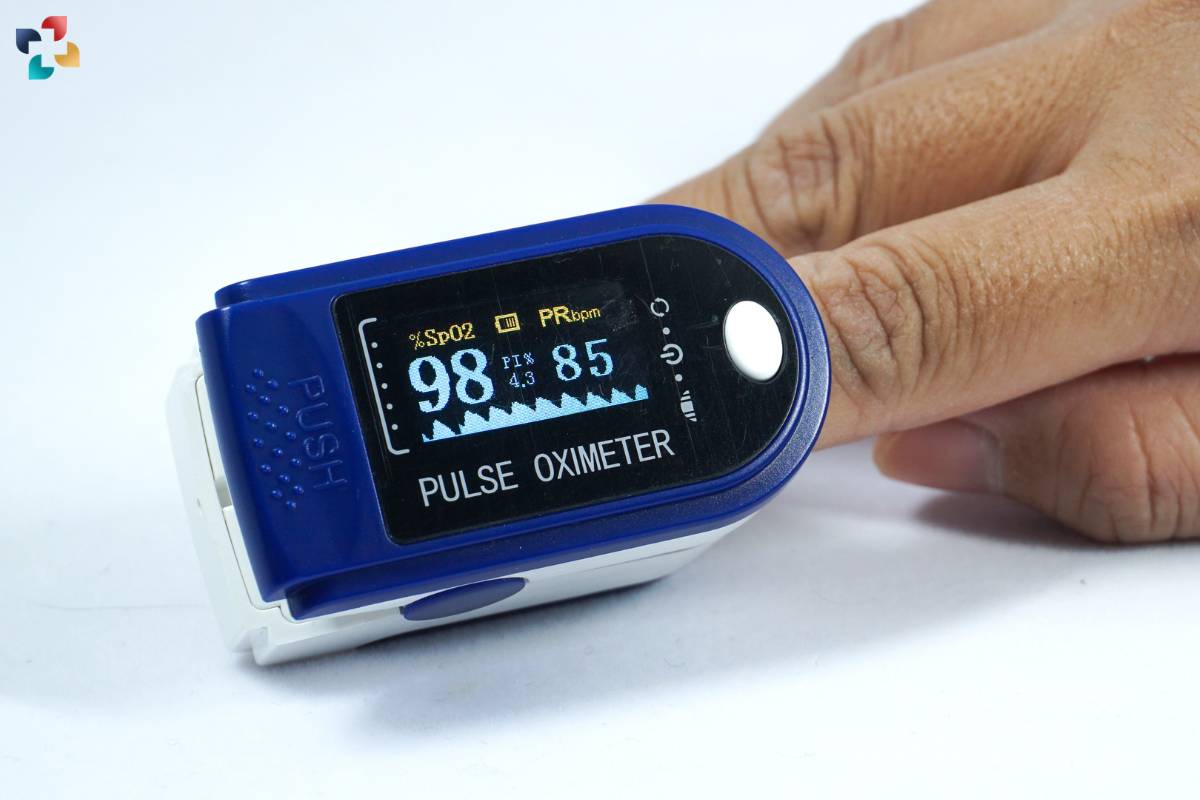
One of the key attributes of the Pulse Oximeter is its accuracy in providing real-time SpO2 readings. With advancements in technology, modern pulse oximeters offer high precision and reliability, making them indispensable tools for healthcare professionals in various clinical settings. From hospitals and clinics to home care settings, these devices serve as invaluable aids in monitoring patients’ respiratory status.
Accuracy and reliability are paramount in the field of medical diagnostics, and the Pulse Oximeter excels in both aspects. The device’s ability to deliver precise and dependable SpO2 readings in real time is essential for effective patient care and treatment planning. With continuous advancements in technology, modern pulse oximeters have achieved remarkable levels of accuracy, instilling confidence in healthcare professionals across diverse clinical environments.
Whether in bustling hospital wards, specialized clinics, or the comfort of patients’ homes, these devices play a pivotal role in monitoring respiratory status and facilitating timely interventions. As healthcare continues to evolve, the Pulse Oximeter remains a steadfast ally, providing clinicians with the critical data needed to ensure optimal patient outcomes and improve overall healthcare delivery.
Applications in Healthcare
The utility of the Pulse Oximeter extends across a wide spectrum of healthcare scenarios. In critical care units, it plays a vital role in assessing patients’ respiratory function during surgeries, intensive care, and emergency situations. Additionally, it aids in the early detection of conditions such as hypoxemia, sleep apnea, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and asthma exacerbations.
In addition to its pivotal role in critical care units, the Pulse Oximeter finds widespread application in various healthcare settings. In surgical theaters, it provides crucial real-time feedback on patients’ oxygen saturation levels, enabling anesthesiologists and surgeons to optimize oxygen delivery and ensure patient safety during procedures.
Furthermore, in neonatal intensive care units, Pulse Oximeters are indispensable tools for monitoring the respiratory status of premature infants and detecting signs of respiratory distress syndrome or apnea. Beyond acute care settings, these devices also play a significant role in managing chronic respiratory conditions such as COPD, where regular monitoring of SpO2 levels is essential for disease management and exacerbation prevention.
1. Home Monitoring and Telemedicine
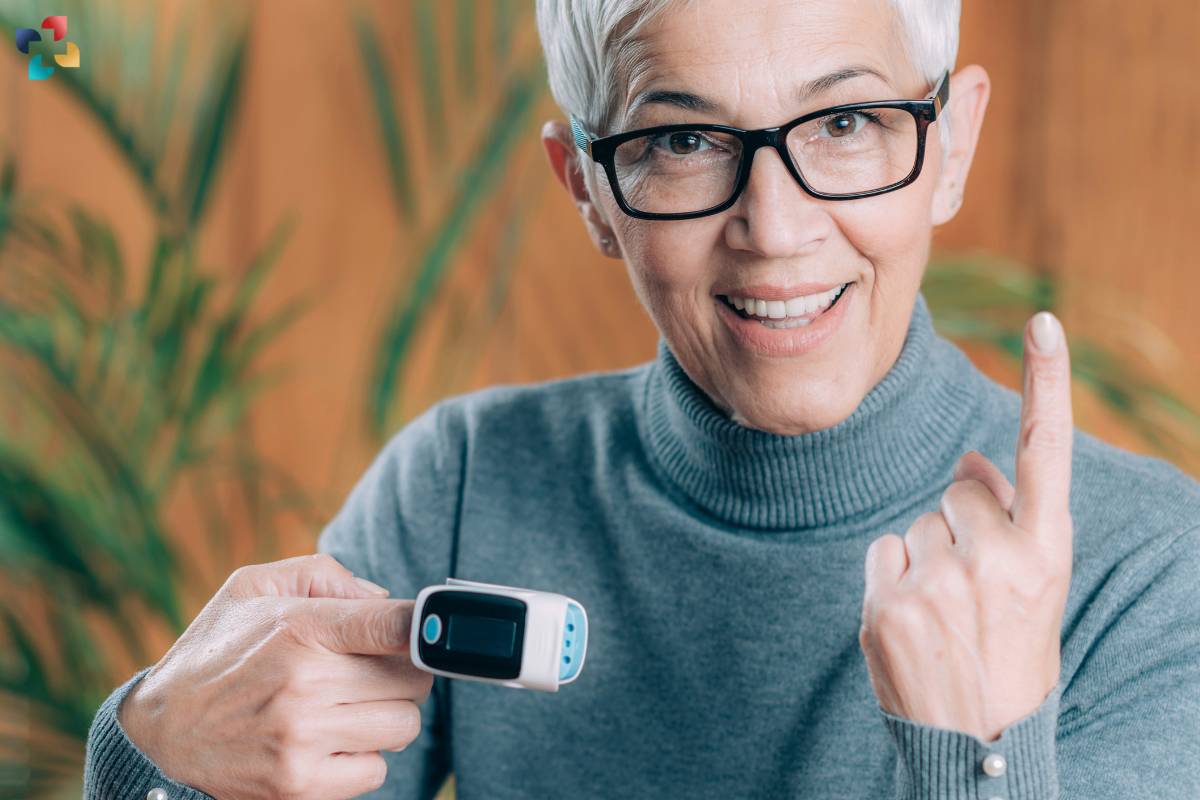

The advent of portable and user-friendly Pulse Oximeters has revolutionized home healthcare monitoring. Patients with chronic respiratory conditions or cardiovascular diseases can now monitor their SpO2 levels conveniently from the comfort of their homes. Furthermore, in the era of telemedicine, remote patient monitoring using Pulse Oximeters facilitates proactive healthcare management and timely intervention.
2. Sports and Fitness
Beyond clinical settings, Pulse Oximeters have found applications in sports and fitness arenas. Athletes and fitness enthusiasts utilize these devices to monitor their oxygen saturation levels during intense workouts or high-altitude training. By optimizing oxygen intake and recovery strategies, individuals can enhance their performance and mitigate the risk of exertional hypoxemia.
3. Travel and High Altitude
For travelers venturing into high-altitude regions, Pulse Oximeters serve as essential companions for assessing acclimatization and preventing altitude sickness. By monitoring SpO2 levels at various altitudes, travelers can gauge their physiological adaptation to reduced oxygen levels and take necessary precautions to ensure their well-being.
4. Pediatric Care
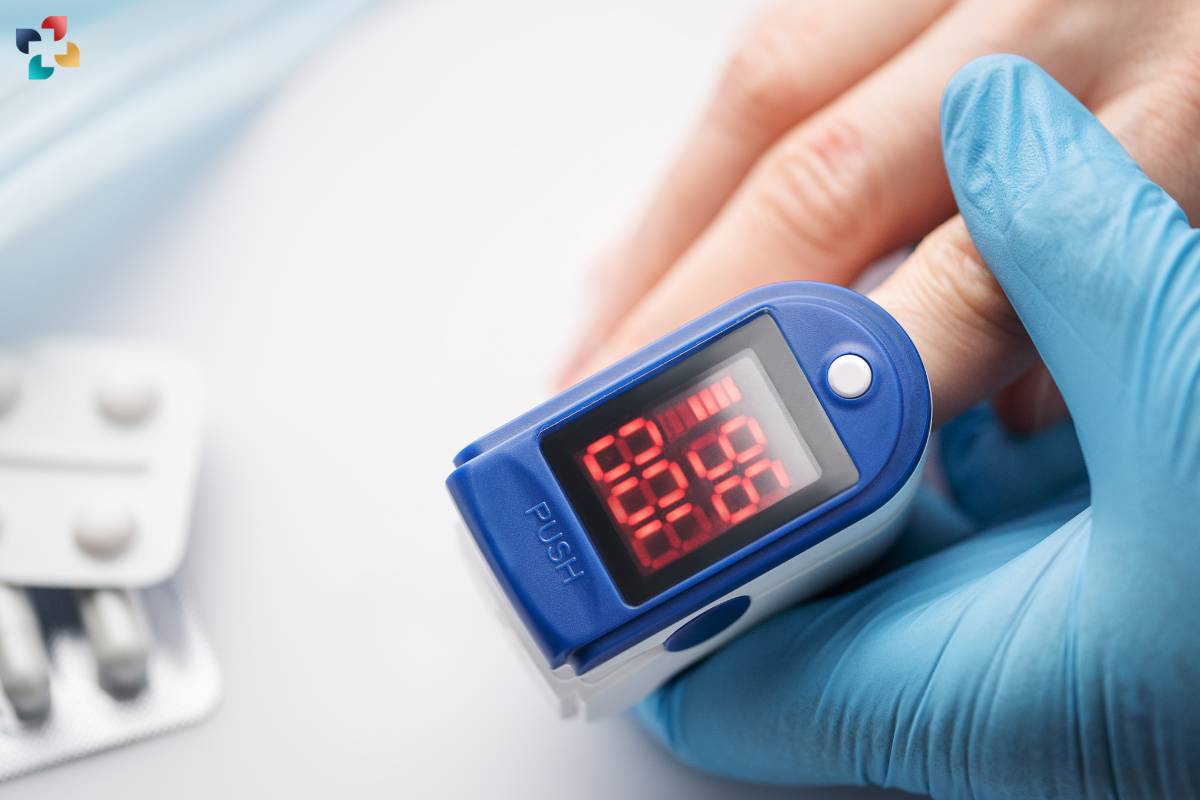
In pediatric care, Pulse Oximeters are invaluable tools for assessing respiratory function in infants and children. These devices provide quick and non-invasive measurements, making them ideal for monitoring young patients in clinical settings or at home. From assessing newborns’ oxygen saturation levels to monitoring children with respiratory illnesses, Pulse Oximeters play a crucial role in pediatric healthcare.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Pulse Oximeter emerges as a versatile and indispensable tool in modern healthcare. With its ability to provide accurate and real-time SpO2 readings, this compact device aids healthcare professionals in diagnosing and managing various respiratory and cardiovascular conditions. From critical care units and home healthcare settings to sports arenas and high-altitude environments, the Pulse Oximeter continues to revolutionize the way we monitor and manage our health. As we navigate the complexities of healthcare delivery, the Pulse Oximeter stands as a beacon of innovation and efficiency, empowering individuals and healthcare providers alike to make informed decisions and ensure optimal patient outcomes.

6 Health Monitoring Devices Every Home Should Have
In this article, we will explore six essential health monitoring devices that every home should consider having. From tracking your heart health to managing your sleep patterns, these devices can make a significant difference in your overall wellness.
FAQs
1. What is a Pulse Oximeter, and how does it work?
A Pulse Oximeter is a medical device used to measure the oxygen saturation level (SpO2) in the blood. It works by emitting light wavelengths through the skin, which then detects the amount of oxygen-carrying hemoglobin present in the arterial blood.
2. Are Pulse Oximeters accurate?
Yes, modern Pulse Oximeters are highly accurate in providing real-time SpO2 readings. They have undergone rigorous testing and advancements in technology have significantly improved their precision and reliability.
3. Who can benefit from using a Pulse Oximeter?
Pulse Oximeters are beneficial for individuals with respiratory conditions such as asthma, COPD, or sleep apnea, as well as those undergoing surgery, intensive care, or high-altitude activities. They are also useful for athletes and fitness enthusiasts to monitor oxygen levels during workouts.
4. How should I use a Pulse Oximeter?
To use a Pulse Oximeter, simply clip it onto your fingertip, earlobe, or other suitable body part. Wait for the device to display your SpO2 reading, which typically takes a few seconds. Ensure that the device is properly positioned and that there is good blood flow to the area being measured.
5. What should I do if my Pulse Oximeter shows low oxygen levels?
If your Pulse Oximeter indicates low oxygen levels (SpO2 below 90%), it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. Low oxygen levels can indicate underlying health issues or respiratory distress, and immediate intervention may be necessary. Contact your healthcare provider or seek emergency medical care if you experience symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, or confusion.