Source- nature.com
Transverse myelitis (TM) is a rare neurological disorder characterized by inflammation of the spinal cord. This condition can lead to a range of symptoms, including pain, weakness, sensory disturbances, and bowel or bladder dysfunction. While transverse myelitis is relatively uncommon, understanding its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options is crucial for those affected and their caregivers.
Transverse myelitis (TM) is a complex and often debilitating condition that can have a profound impact on individuals’ lives. While it is considered rare, affecting an estimated 1 to 5 individuals per million annually, its effects can be significant and long-lasting. The inflammation of the spinal cord characteristic of TM can disrupt the transmission of nerve signals between the brain and the rest of the body, leading to a variety of symptoms that can vary widely in severity and duration.
One of the challenges in managing transverse myelitis is the variability of its presentation. Symptoms can develop suddenly or progress gradually over time, and they may affect different areas of the body depending on the location and extent of the spinal cord inflammation. Some individuals may experience mild symptoms that resolve spontaneously, while others may face more severe and persistent symptoms that require ongoing medical intervention and support.
In addition to the physical symptoms associated with it, the condition can also have significant emotional and psychological effects on individuals and their families. Coping with chronic pain, mobility limitations, and changes in bowel or bladder function can be challenging, and the uncertainty of the condition’s course can contribute to anxiety and depression.
Despite its challenges, there is hope for individuals living with transverse myelitis. Advances in medical research and treatment options have improved outcomes for many patients, and ongoing efforts to raise awareness, promote early diagnosis, and develop new therapies continue to offer promise for the future. By fostering greater understanding and support for individuals affected by TM, we can work together to improve their quality of life and ensure that they receive the care and assistance they need to thrive.
Symptoms of Transverse Myelitis
Transverse myelitis typically presents with symptoms that develop rapidly over hours to days. Common manifestations include:
- Sensory abnormalities such as numbness, tingling, or burning sensations.
- Motor difficulties, such as weakness or paralysis of the limbs.
- Bowel and bladder dysfunction, leading to urinary or fecal incontinence.
- Pain, which may be localized to the back or neck region and may worsen with movement.
- Coordination problems, including difficulty walking or maintaining balance.
Causes of Transverse Myelitis
The exact cause of transverse myelitis is often unknown, but it is believed to result from an abnormal immune response that targets the spinal cord. This immune-mediated inflammation can be triggered by various factors, including:
1. Infections: Viral, bacterial, fungal, or parasitic infections can precede the onset of TM.
2. Autoimmune disorders: Conditions such as multiple sclerosis, neuromyelitis optica, and lupus can predispose individuals to develop transverse myelitis.
3. Vaccinations: While rare, certain vaccines have been associated with the development of TM.
4. Trauma: Spinal cord injuries or surgeries can sometimes lead to inflammation and subsequent TM.
5. Other factors: Vascular disorders, metabolic conditions, and exposure to toxins may also contribute to the development of transverse myelitis.
Diagnosing Transverse Myelitis
Diagnosing transverse myelitis involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional, including:
1. Medical history: A detailed history of symptoms, medical conditions, and recent infections or vaccinations is obtained.
2. Physical examination: A thorough neurological examination is performed to assess motor, sensory, and reflex functions.
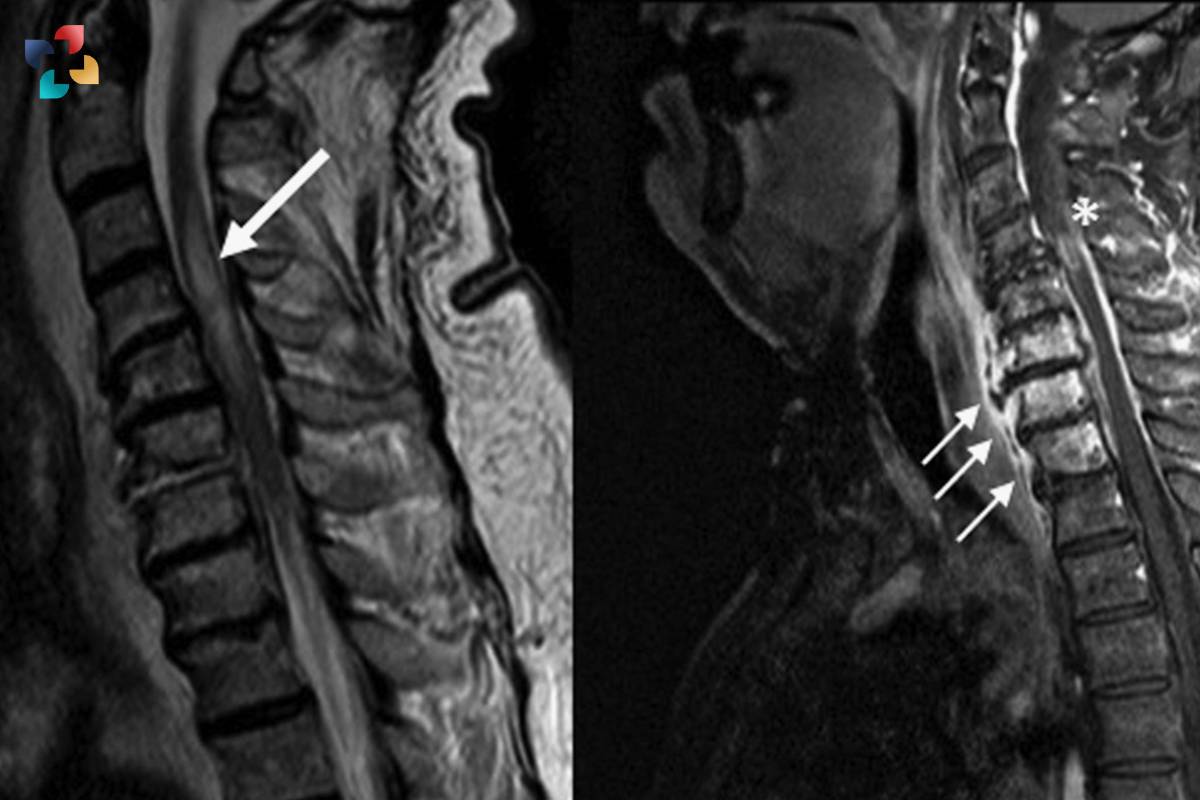
3. Imaging studies: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spine is the preferred imaging modality for visualizing inflammation or lesions in the spinal cord.
4. Laboratory tests: Blood tests may be conducted to rule out infectious or autoimmune causes of TM, such as viral titers, autoimmune panels, or cerebrospinal fluid analysis.
5. Electrophysiological studies: Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies (NCS) may be performed to evaluate nerve function and detect abnormalities in muscle activity.
Treating Transverse Myelitis
Treatment for transverse myelitis focuses on reducing inflammation, managing symptoms, and preventing complications. Depending on the severity and underlying cause of transverse myelitis, treatment options may include:
1. Corticosteroids: Intravenous administration of corticosteroids, such as methylprednisolone, is often used to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
2. Plasma exchange (plasmapheresis): This procedure involves removing and replacing plasma to remove harmful antibodies and other inflammatory factors from the bloodstream.
3. Immunosuppressive therapy: Medications that suppress the immune system, such as azathioprine, mycophenolate, or rituximab, may be prescribed for individuals with severe or refractory TM.
4. Pain management: Analgesic medications, physical therapy, and interventions such as nerve blocks or spinal cord stimulation may be utilized to manage pain associated with TM.
5. Rehabilitation: Occupational therapy, physical therapy, and assistive devices can help individuals regain strength, mobility, and independence following an episode of TM.
Conclusion
Transverse myelitis is a complex neurological condition that can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life. By understanding the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for transverse myelitis, healthcare professionals and patients alike can work together to effectively manage this condition and optimize outcomes. Continued research into the underlying mechanisms of TM and the development of novel therapeutic approaches are essential for improving the prognosis and quality of life for individuals affected by this challenging disorder.
FAQs
1. What causes transverse myelitis?
Transverse myelitis can be caused by various factors, including viral infections (such as herpes simplex, and Epstein-Barr virus), bacterial infections (such as Lyme disease), autoimmune disorders (such as multiple sclerosis), and other inflammatory conditions.
2. What are the common symptoms of transverse myelitis?
Common symptoms of transverse myelitis include pain, weakness, sensory disturbances (such as numbness, and tingling), bowel or bladder dysfunction, and in severe cases, paralysis. The specific symptoms experienced can vary depending on the location and severity of the spinal cord inflammation.
3. How is transverse myelitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis of transverse myelitis typically involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) of the spine, lumbar puncture (spinal tap) to analyze cerebrospinal fluid, and blood tests to rule out other possible causes.
4. What treatment options are available for transverse myelitis?
Treatment for transverse myelitis focuses on reducing inflammation, managing symptoms, and preventing complications. This may include corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, pain medications, physical therapy to improve mobility and function, and in some cases, immunosuppressive therapy or plasmapheresis.
5. Can transverse myelitis be cured?
While there is currently no cure for transverse myelitis, many individuals experience improvement in symptoms with appropriate treatment and support. Recovery can be variable and may depend on factors such as the underlying cause, severity of symptoms, and timely intervention. Rehabilitation and ongoing medical care can help individuals manage their condition and improve their quality of life.