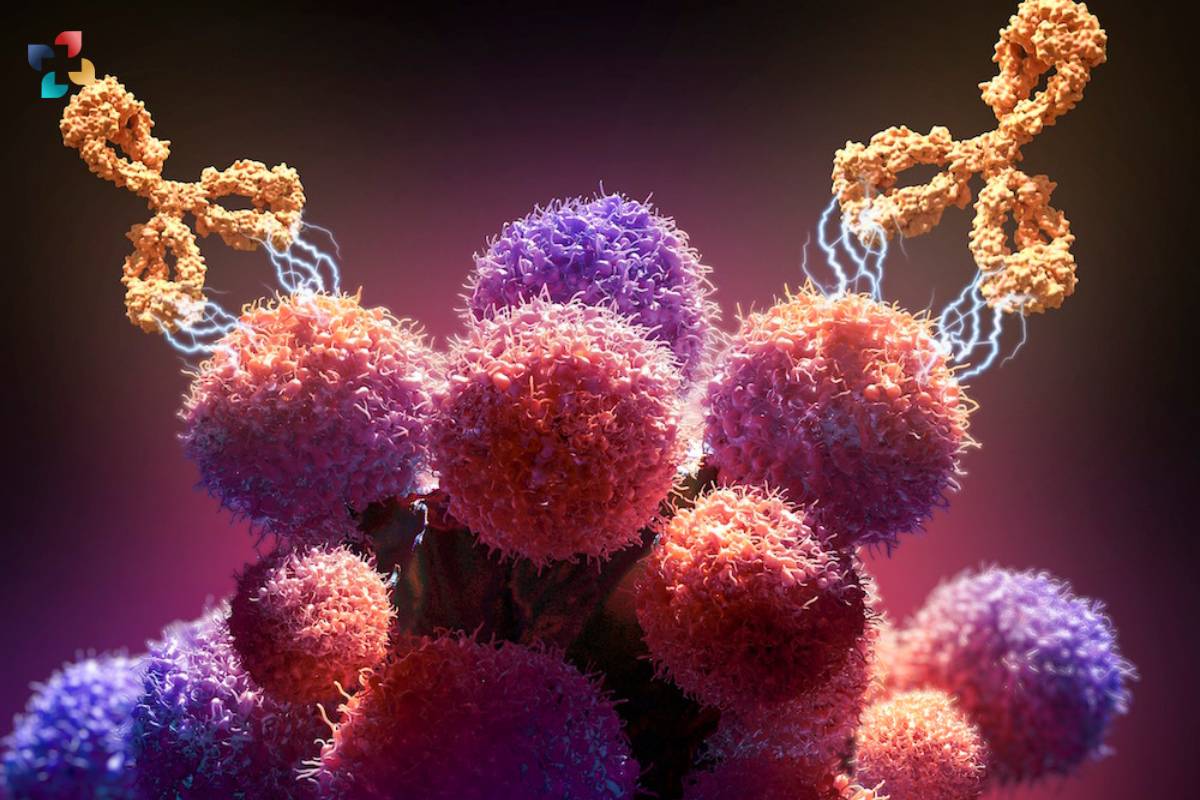
Source- Dana Farber Cancer Institute
In the realm of modern medicine, antibody therapy has emerged as a revolutionary approach to treating various diseases. Harnessing the power of the body’s immune system, antibody therapy offers targeted and precise treatment options for a wide range of conditions. From cancer to autoimmune disorders, the potential applications of antibody therapy are vast and promising. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of antibody therapy, exploring its mechanisms, applications, and future prospects.
Understanding Antibody Therapy:
Antibody therapy, also known as immunotherapy, involves the use of antibodies – specialized proteins produced by the immune system – to target and neutralize specific molecules or cells associated with disease. These antibodies can be naturally occurring or engineered in the laboratory to enhance their therapeutic properties. By precisely targeting disease-causing agents, it offers a highly targeted approach to treatment, minimizing damage to healthy tissues and reducing side effects.
Antibody therapy has revolutionized the field of medicine by providing targeted treatment options for a wide range of diseases, including cancer, autoimmune disorders, infectious diseases, and inflammatory conditions. One of the key advantages of antibody therapy is its ability to selectively target disease-causing agents while sparing healthy tissues. This precision targeting not only enhances the efficacy of treatment but also minimizes the risk of adverse reactions, such as those commonly associated with traditional chemotherapy or immunosuppressive drugs.
Moreover, it can be tailored to individual patients’ needs, allowing for personalized treatment strategies based on factors such as disease subtype, genetic makeup, and treatment response. This personalized approach has the potential to optimize treatment outcomes and improve patient quality of life.
As research in antibody therapy continues to advance, new and innovative approaches are being explored to further enhance its therapeutic potential. From the development of novel antibody formats to the discovery of innovative targets, the future of antibody therapy holds great promise for revolutionizing the way we treat and manage diseases.
Mechanisms of Action:
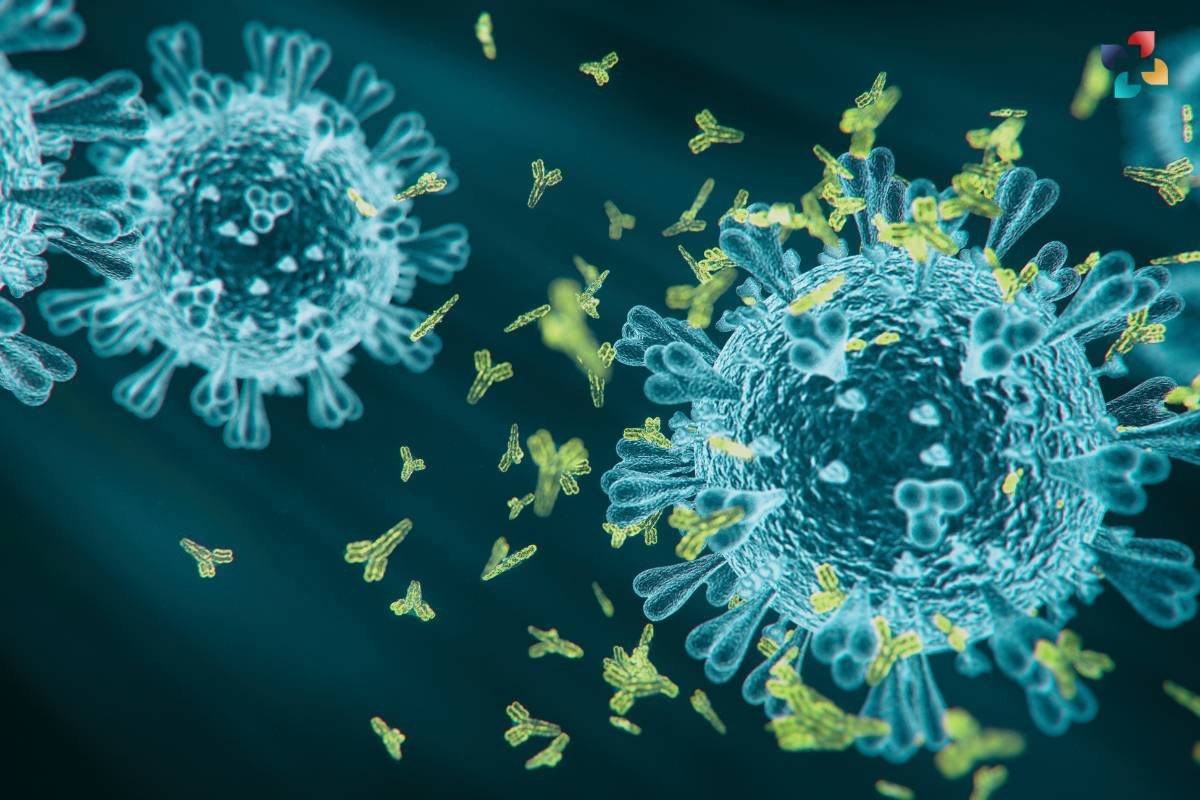
The mechanisms of action of antibody therapy vary depending on the specific disease being treated. In cancer therapy, for example, monoclonal antibodies – antibodies engineered to recognize and bind to specific proteins on cancer cells – can be used to directly target and kill tumor cells or to block signaling pathways that promote tumor growth and survival. This targeted approach helps to spare healthy cells from damage and minimize the side effects associated with traditional cancer treatments such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Applications of Antibody Therapy:
Antibody therapy has revolutionized the treatment landscape for a wide range of diseases, including cancer, autoimmune disorders, infectious diseases, and inflammatory conditions. In cancer therapy, monoclonal antibodies have been approved for the treatment of various cancers, including breast cancer, leukemia, lymphoma, and colorectal cancer. These antibodies can be used as standalone treatments or in combination with other cancer therapies to improve treatment outcomes.
In autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis, it offers targeted relief by blocking the activity of immune cells that mistakenly attack healthy tissues. Similarly, in infectious diseases such as COVID-19, monoclonal antibodies have shown promise in neutralizing the virus and reducing disease severity.
The versatility of antibody therapy extends beyond traditional disease categories, with ongoing research exploring its potential applications in areas such as regenerative medicine, transplantation, and neurodegenerative disorders. In regenerative medicine, antibodies targeting specific cell surface markers are being investigated for their ability to selectively eliminate diseased or dysfunctional cells while sparing healthy tissues. This approach holds promise for treating conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders by promoting tissue regeneration and repair.
Furthermore, it is being explored as a promising tool in organ transplantation to prevent graft rejection and improve transplant outcomes. By targeting immune cells responsible for transplant rejection, antibodies can help suppress the immune response and promote long-term graft acceptance without the need for high-dose immunosuppressive drugs, which carry significant risks of adverse effects.
In the field of neurodegenerative disorders, it holds potential for targeting pathological proteins such as amyloid-beta and tau, which are implicated in conditions like Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. By selectively binding to and clearing these toxic proteins from the brain, antibodies may slow disease progression and preserve cognitive function in affected individuals.
Future Prospects:
As research in antibody therapy continues to advance, new opportunities and challenges are emerging. Scientists are exploring innovative approaches to enhance the efficacy and safety of antibody therapy, including the development of bispecific antibodies that can target multiple disease targets simultaneously, as well as the use of antibody-drug conjugates to deliver cytotoxic drugs directly to cancer cells.

Additionally, the field of personalized medicine is driving the development of customized antibody therapies tailored to individual patient’s genetic makeup and disease profiles. By leveraging advances in genomics and bioinformatics, researchers hope to optimize treatment outcomes and minimize the risk of adverse reactions.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, antibody therapy represents a groundbreaking approach to treating a wide range of diseases, offering targeted and precise treatment options with minimal side effects. With ongoing research and technological advancements, the potential applications of antibody therapy are poised to expand further, ushering in a new era of personalized and precision medicine. As we continue to unravel the complexities of the immune system and harness its therapeutic potential, it holds immense promise for improving patient outcomes and transforming the future of healthcare.
FAQs
1. What is antibody therapy?
Antibody therapy, also known as immunotherapy, involves the use of antibodies – specialized proteins produced by the immune system – to target and neutralize specific molecules or cells associated with disease.
2. How does antibody therapy work?
Antibodies can bind to specific molecules or cells involved in disease processes, such as cancer cells or inflammatory proteins. By targeting these disease-causing agents, antibodies can block their activity, mark them for destruction by the immune system, or deliver therapeutic payloads directly to affected cells.
3. What types of diseases can be treated with antibody therapy?
Antibody therapy has shown efficacy in treating a wide range of diseases, including cancer, autoimmune disorders, infectious diseases, and inflammatory conditions. It can also be used in transplantation to prevent graft rejection and promote long-term organ acceptance.
4. Are there any side effects associated with antibody therapy?
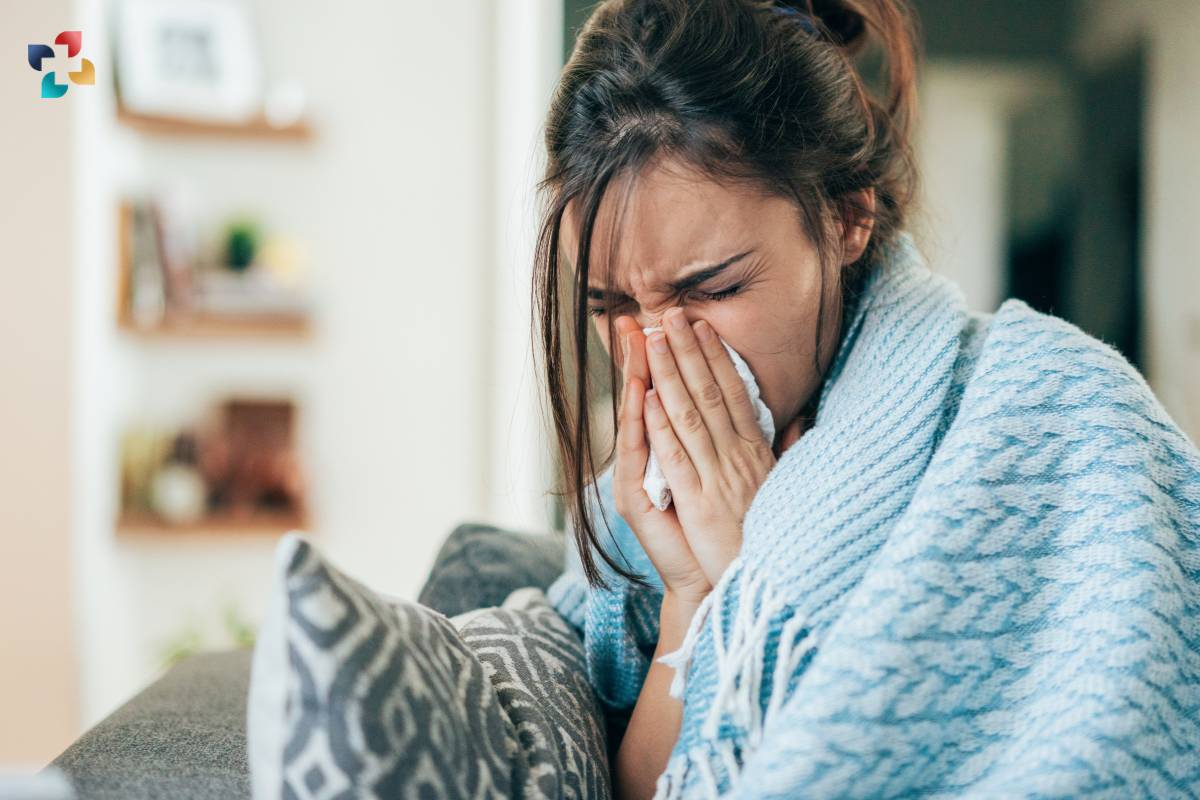

While antibody therapy is generally well-tolerated, some patients may experience side effects such as infusion reactions, flu-like symptoms, or immune-related adverse events. These side effects are usually mild to moderate and can be managed with supportive care or adjustments to treatment regimens.
5. How is antibody therapy administered?
Antibody therapy can be administered via intravenous infusion, subcutaneous injection, or intramuscular injection, depending on the specific antibody and disease being treated. Treatment regimens vary depending on the disease severity, patient’s response to therapy, and other individual factors.