In the ever-evolving landscape of global health, infectious diseases like HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria continue to pose significant challenges, claiming millions of lives annually. Emerging infectious diseases, like the recent COVID-19 pandemic, further highlight the need for robust and accessible diagnostic tools to combat these threats. This article explores the crucial role of In Vitro Diagnostics (IVDs) in tackling infectious diseases and identifies opportunities to strengthen their contribution to global health and pandemic preparedness.
What are In Vitro Diagnostics (IVDs)?
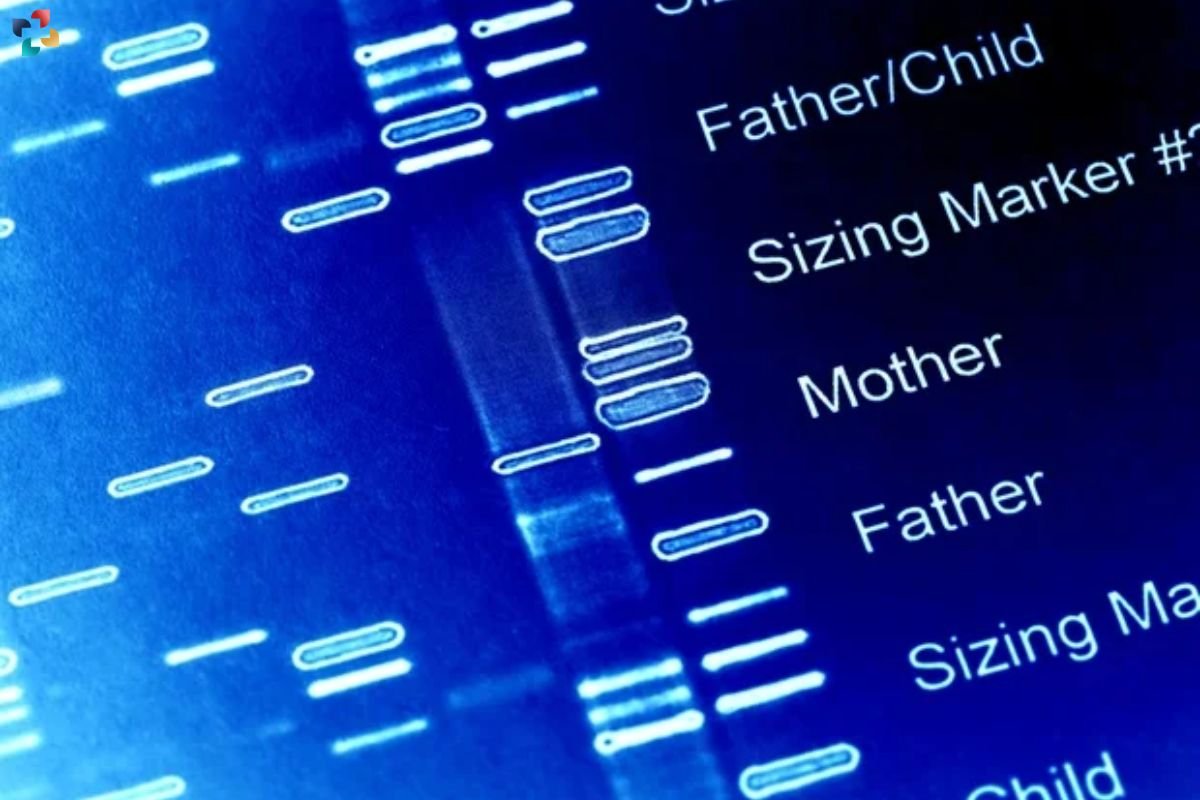
In Vitro Diagnostics are medical tests conducted outside the living body (in vitro means “in glass” in Latin). These tests play a vital role in diagnosing and monitoring infectious diseases by detecting the presence of pathogens (like viruses or bacteria) or antibodies developed by the body in response to infection.
Common examples of IVDs include:
1. Rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs)
These are user-friendly, point-of-care tests that provide quick results, often within minutes, making them ideal for resource-limited settings.
2. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
This technique detects and measures antibodies or antigens in a sample, helping diagnose and monitor various infections.
3. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
This highly sensitive technique amplifies specific DNA sequences, allowing for the detection of minute amounts of pathogens.
How In Vitro Diagnostics Contribute to Global Health:
1. Early diagnosis and treatment
Accurate and timely diagnosis is crucial for initiating appropriate treatment and preventing further transmission of infectious diseases. IVDs enable healthcare professionals to make informed decisions quickly, leading to improved patient outcomes and reduced disease burden.
2. Enhanced disease surveillance
Effective disease surveillance relies on accurate and timely data. IVDs play a vital role in collecting and analyzing data on disease prevalence and spread, allowing public health authorities to implement targeted interventions and control outbreaks.
3. Improved resource allocation
By facilitating early diagnosis and targeted treatment, IVDs can help healthcare systems optimize resource allocation, directing resources toward those who need them most.
Challenges in Utilizing In Vitro Diagnostics in Global Health:
In resource-limited settings, the challenges surrounding the accessibility and affordability of advanced in In Vitro Diagnostics (IVDs) continue to pose significant barriers to effective healthcare delivery. High costs and complex infrastructure requirements often limit the availability of these technologies, particularly in remote areas with limited healthcare facilities. As a result, patients in these regions face delays in diagnosis and treatment, leading to poorer health outcomes and increased mortality rates.
Standardization and quality control represent additional hurdles in the effective deployment of In Vitro Diagnostics in resource-limited settings. Variations in testing protocols, reagents, and equipment can result in inconsistent and unreliable results, undermining efforts to control diseases and manage patient care. Without stringent quality assurance measures and standardized testing procedures, healthcare providers may struggle to make accurate diagnoses and implement appropriate treatment plans.
Furthermore, the shortage of skilled workforce and technical expertise further exacerbates the challenges associated with utilizing advanced IVDs in resource-limited settings. Healthcare professionals in these regions often lack the necessary training and skills to operate and interpret the results of complex diagnostic tests, hindering the effective implementation and utilization of these technologies.
Despite these challenges, there are opportunities to strengthen the role of IVDs in global health and improve healthcare delivery in resource-limited settings:
1. Development of low-cost, point-of-care In Vitro Diagnostics
Investing in research and development initiatives aimed at creating user-friendly, affordable, and accurate diagnostic tools tailored for resource-limited settings is critical. These innovations should be designed to require minimal infrastructure and technical expertise, enabling decentralized testing and rapid diagnosis at the point of care.
2. Strengthening supply chains and infrastructure
Building resilient and efficient supply chains for IVDs and associated equipment is essential to ensure consistent availability and accessibility of diagnostic tests in resource-limited settings. This requires investments in infrastructure development, transportation networks, and storage facilities to support the timely delivery of essential diagnostic products to remote regions.
3. Investments in workforce development
Providing comprehensive training programs and capacity-building initiatives for healthcare professionals in low- and middle-income countries is crucial to enhancing their skills and competencies in utilizing advanced IVDs. This includes training on test administration, result interpretation, quality assurance, and troubleshooting, empowering healthcare providers to effectively leverage diagnostic technologies in patient care.
4. Promoting international collaboration
Fostering collaborative partnerships between governments, research institutions, non-profit organizations, and private companies can accelerate the development, deployment, and affordability of In Vitro Diagnostics globally. By pooling resources, expertise, and innovative solutions, stakeholders can address the complex challenges associated with improving access to diagnostic testing in resource-limited settings and advance efforts to achieve universal health coverage and disease control goals.
In conclusion, addressing the challenges surrounding accessibility and affordability of advanced IVDs in resource-limited settings requires a multifaceted approach that combines technological innovation, infrastructure development, capacity building, and collaborative partnerships. By investing in these strategies, stakeholders can strengthen the role of IVDs in global health and contribute to the delivery of equitable and quality healthcare services for all.
The Road Ahead
In Vitro Diagnostics play a critical role in the fight against infectious diseases and pandemic preparedness. By addressing the existing challenges and embracing the identified opportunities, the global health community can harness the full potential of IVDs to create a healthier future for all. This requires continued investments in research, development, and implementation, coupled with international collaboration and a commitment to ensuring equitable access to these life-saving technologies.
Also Read: Understanding Gastrointestinal Diseases: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options