Source-Genetic-Engineering-and-Biotechnology-News
With medulloblastoma cancer making up about 20% of pediatric brain tumors, it is one of the most common malignant brain tumors that affect children. Even though it doesn’t often affect adults, its aggressiveness and possibility of spreading require early detection and intervention. We delve into the complexities of medulloblastoma cancer in this extensive guide, including clinical manifestations, diagnostic techniques, treatment options, and the most recent developments in research and management tactics.
Understanding Medulloblastoma Cancer:
Medulloblastoma cancer originates in the cerebellum, the region of the brain responsible for coordinating movement and balance. It arises from the primitive neuroectodermal cells, which are precursor cells that give rise to various types of brain cells. This malignant tumor tends to infiltrate surrounding brain tissue and can spread through the cerebrospinal fluid to other parts of the central nervous system. The etiology of medulloblastoma cancer remains largely unknown, although certain genetic syndromes and exposure to radiation may increase the risk of its development.
Clinical Presentation and Symptoms:
The clinical presentation of medulloblastoma cancer varies depending on factors such as tumor size, location, and proximity to critical brain structures. Common symptoms may include persistent headaches, nausea and vomiting, gait disturbances, changes in vision or coordination, and behavioral changes in children. Additionally, younger children may exhibit irritability, lethargy, and developmental delays. The onset of symptoms is often insidious, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment initiation, which can impact patient outcomes and prognosis.
Diagnosis and Imaging Studies:
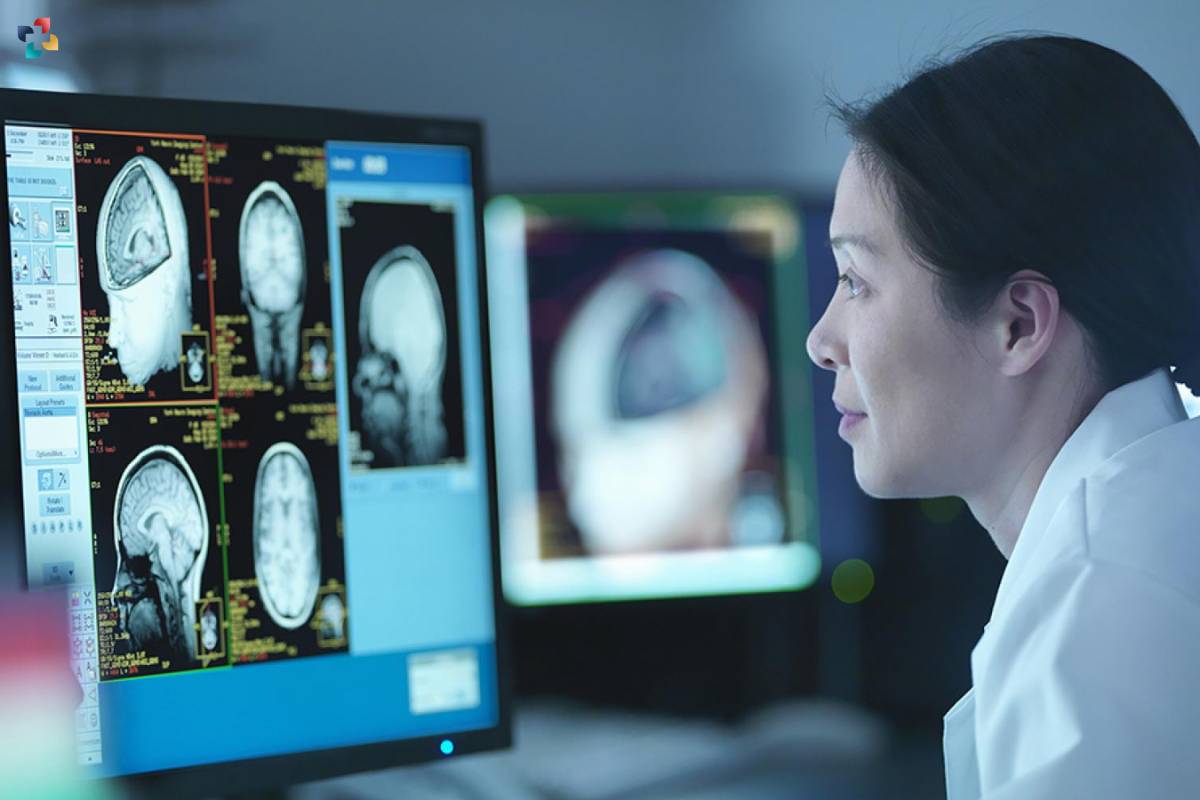
The diagnosis of medulloblastoma cancer typically involves a combination of imaging studies and histopathological examination. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the imaging modality of choice for visualizing brain tumors, providing detailed anatomical information, and delineating tumor characteristics such as size, location, and involvement of surrounding structures. Computed tomography (CT) scans may also be used to assess bony involvement and evaluate for signs of hydrocephalus. Additionally, a lumbar puncture may be performed to analyze cerebrospinal fluid for the presence of tumor cells, which can indicate metastasis or leptomeningeal spread.
Treatment Modalities:
The management of medulloblastoma cancer is complex and multidisciplinary, involving a combination of surgical resection, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Surgical resection aims to achieve maximal tumor removal while preserving neurological function, although complete resection may not always be feasible due to the tumor’s location and infiltrative nature.
Adjuvant radiation therapy is typically administered to the entire central nervous system to eradicate residual tumor cells and prevent recurrence. Chemotherapy may also be used, either as a primary treatment modality or in conjunction with surgery and radiation therapy, to target remaining cancer cells and improve long-term survival rates.
Prognosis and Long-Term Outcomes:
The prognosis for patients with medulloblastoma cancer varies depending on factors such as age, tumor histology, extent of surgical resection, and response to treatment. While overall survival rates have improved with advances in multidisciplinary care and treatment modalities, certain subtypes of medulloblastoma cancer may exhibit more aggressive behavior and poorer outcomes. Long-term follow-up care is essential for monitoring disease progression, assessing treatment response, and managing potential late effects of therapy, such as cognitive impairment, endocrine dysfunction, and secondary malignancies.
Advancements in Research and Future Directions:
Many obstacles still need to be overcome to fully comprehend the biology and therapy of medulloblastoma cancer, especially when it comes to figuring out the molecular processes that underlie tumor growth and metastasis. To enhance outcomes and lessen treatment-related toxicity, ongoing research efforts are concentrated on finding new therapeutic targets, creating targeted medicines, and improving treatment approaches. Furthermore, cooperative projects like global consortia and clinical trial networks seek to maximize individualized treatment plans for medulloblastoma cancer patients and hasten the conversion of scientific discoveries into clinical practice.
In addition to identifying novel therapeutic targets and developing targeted therapies, researchers are also exploring innovative treatment modalities, such as immunotherapy and molecularly targeted agents, to enhance the efficacy of current treatment regimens. Immunotherapy, in particular, holds promise in harnessing the body’s immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells.
Moreover, advances in genomics and molecular profiling are paving the way for precision medicine approaches, enabling clinicians to tailor treatment strategies based on the unique genetic makeup of individual tumors. By addressing these challenges and embracing interdisciplinary collaborations, the future of medulloblastoma cancer research holds great potential for improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
FAQs:
1. What are the risk factors for developing medulloblastoma cancer?
Medulloblastoma cancer is most commonly diagnosed in children, with peak incidence occurring between 3 to 8 years of age. While the exact cause remains unknown, certain genetic syndromes, such as Gorlin syndrome and Li-Fraumeni syndrome, and exposure to ionizing radiation may increase the risk of developing this tumor.
2. How is medulloblastoma cancer diagnosed?
The diagnosis of medulloblastoma cancer involves a thorough clinical evaluation, neuroimaging studies (such as MRI and CT scans), and histopathological examination of tissue samples obtained through surgical resection or biopsy. Lumbar puncture may also be performed to analyze cerebrospinal fluid for the presence of tumor cells.
3. What are the treatment options for medulloblastoma cancer?
The primary treatment modalities for medulloblastoma cancer include surgical resection, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Surgical resection aims to remove as much of the tumor as possible, followed by adjuvant radiation therapy to eradicate residual cancer cells. Chemotherapy may be used in combination with surgery and radiation therapy to target remaining tumor cells and improve long-term survival rates.
4. What is the prognosis for patients with medulloblastoma cancer?
The prognosis for patients with medulloblastoma cancer varies depending on factors such as age, tumor histology, extent of surgical resection, and response to treatment. Overall survival rates have improved with advances in multidisciplinary care and treatment modalities, although certain subtypes of medulloblastoma cancer may exhibit more aggressive behavior and poorer outcomes.
5. Are there any ongoing research initiatives focused on medulloblastoma cancer?
Yes, there are several ongoing research initiatives focused on medulloblastoma cancer, including collaborative efforts to elucidate the molecular mechanisms driving tumor growth and metastasis, identify novel therapeutic targets, and develop targeted therapies. International consortia and clinical trial networks aim to accelerate the translation of scientific discoveries into clinical practice and optimize personalized treatment approaches for patients with medulloblastoma cancer.