Source – Physicians Group, LLC
A paradigm shift in the field of modern medicine has occurred, signaling the arrival of Regenerative Medicine. This innovative profession opens up new avenues for treating illnesses, injuries, and degenerative problems by utilizing the body’s natural ability to heal. This in-depth investigation delves into the core of Regenerative Medicine, revealing its tenets, examining a range of applications, and considering the possibility that it could revolutionize healthcare in the future.
Understanding Regenerative Medicine: Unleashing the Body’s Healing Potential
1. Defining Regenerative Medicine
Regenerative Medicine represents a branch of medical science focused on harnessing the body’s natural regenerative capabilities to repair, replace, or restore damaged tissues or organs. Unlike traditional approaches that primarily alleviate symptoms, Regenerative Medicine aims to address the root cause by stimulating the body’s inherent ability to heal itself.
2. Key Principles: At the core of Regenerative Medicine are three key principles:
I. Cellular Therapy
Involves the use of cells to promote healing and regeneration. Stem cells, in particular, play a pivotal role in different regenerative approaches.
II. Tissue Engineering
Encompasses the creation of functional tissues or organs in the laboratory for transplantation or to stimulate the body’s own repair mechanisms.
III. Medical Devices and Artificial Organs
Includes the development of devices to support natural healing processes or replace damaged organs temporarily or permanently.

3. Cellular Components:
Stem cells, the unsung heroes of Regenerative Medicine, possess the remarkable ability to transform into various cell types, making them crucial in repairing and regenerating damaged tissues. These cells can be sourced from various places, including bone marrow, adipose tissue, and even embryonic sources, raising ethical considerations and sparking ongoing research.
Applications of Regenerative Medicine: Healing Across Diverse Fronts:
1. Orthopedic Regeneration
Orthopedic conditions, such as osteoarthritis and musculoskeletal injuries, have been a focal point for Regenerative Medicine. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have shown promise in promoting the regeneration of cartilage and bone tissues. Innovations like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy and growth factor injections also aid in tissue repair and pain management.
2. Cardiovascular Regeneration
Heart diseases, a leading cause of global morbidity and mortality, have spurred research into cardiovascular regeneration. Stem cell therapies aim to repair damaged heart tissues post-heart attacks, enhance blood vessel formation, and improve overall heart function. These interventions hold the potential to mitigate the impact of cardiovascular disorders.
3. Neurological Regeneration
The intricate nature of the nervous system presents unique challenges, but Regenerative Medicine offers hope in neurological disorders. Stem cell therapies aim to repair damaged neural tissues, providing potential treatments for conditions like spinal cord injuries, stroke, and neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s.
4. Dermatological Applications
Regenerative approaches have found their way into dermatology, offering solutions for wound healing, scar reduction, and even hair restoration. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and stem cell therapies contribute to tissue repair, collagen formation, and skin rejuvenation, opening avenues for cosmetic and therapeutic applications.
5. Diabetes Management
In the realm of metabolic disorders, particularly diabetes, Regenerative Medicine explores the potential of pancreatic islet transplantation and stem cell therapies to regenerate insulin-producing cells. These approaches aim to address the root cause of diabetes, offering a more sustainable and comprehensive treatment strategy.
6. Vision Restoration

The field of ophthalmology has embraced Regenerative Medicine to explore treatments for degenerative eye conditions. Stem cell therapies and tissue engineering promise to restore vision by repairing damaged retinal tissues or replacing dysfunctional cells, offering hope for conditions like age-related macular degeneration.
Innovations in Regenerative Therapies: A Glimpse into the Future
1. Stem Cell Therapies
Stem cells, with their remarkable ability to differentiate into various cell types, form the backbone of many Regenerative Medicine approaches. Embryonic stem cells, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), and adult stem cells are being harnessed for their regenerative potential, holding promise in treating a wide array of conditions.
2. Gene Editing Technologies
Advancements in gene editing technologies, including CRISPR-Cas9, have permeated the field of Regenerative Medicine. These tools enable precise modification of genes, allowing scientists to correct genetic defects or enhance cellular functions. The synergy between gene editing and Regenerative Medicine opens new avenues for personalized and targeted therapies.
3. 3D Bioprinting
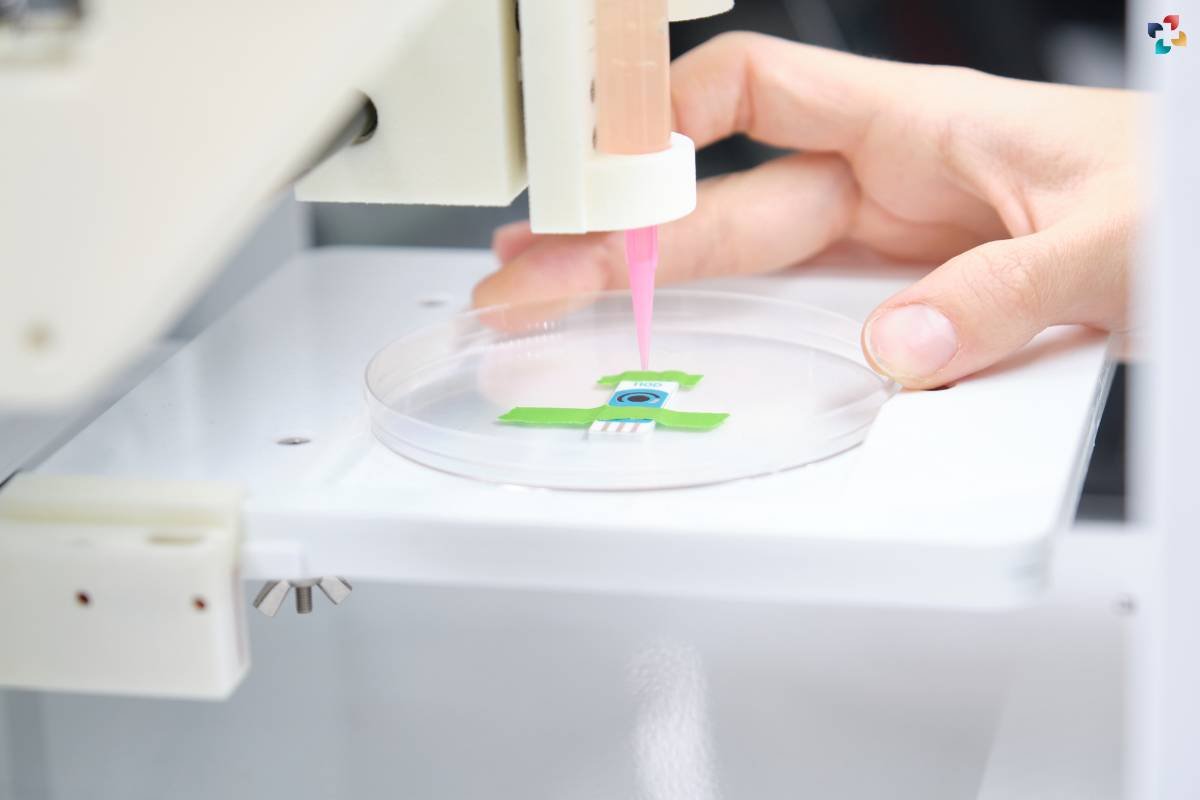

The marriage of Regenerative Medicine and 3D bioprinting is a testament to human ingenuity. This technology enables the fabrication of three-dimensional tissues and organs by layering bioinks containing cells. The potential for custom-designed organs for transplantation and complex tissue engineering scenarios is on the horizon.
4. Exosome Therapy
Exosomes, tiny extracellular vesicles released by cells, have garnered attention in Regenerative Medicine. These vesicles play a crucial role in intercellular communication and can carry bioactive molecules. Exosome therapy explores the use of these vesicles to stimulate regeneration, modulate immune responses, and enhance healing processes.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations: Navigating the Landscape:
1. Ethical Considerations
The groundbreaking nature of Regenerative Medicine raises ethical questions, particularly concerning the use of embryonic stem cells. The debate surrounding the ethical implications of sourcing and using stem cells has prompted ongoing discussions within the scientific and ethical communities.
2. Safety Concerns
Ensuring the safety and efficacy of Regenerative Medicine interventions is paramount. The potential for unintended consequences, such as tumor formation in stem cell therapies, necessitates rigorous preclinical and clinical testing to mitigate risks and enhance the safety profile of these innovative treatments.
3. Regulatory Frameworks
As Regenerative Medicine progresses, the development of robust regulatory frameworks becomes essential. Striking a balance between fostering innovation and ensuring patient safety requires the collaboration of regulatory bodies, researchers, and industry stakeholders. Establishing clear guidelines can facilitate responsible advancements in the field.
Future Outlook and Conclusion: Nurturing the Seeds of Progress
1. Paving the Way for Personalized Medicine
Regenerative Medicine is poised to usher in an era of personalized medicine, tailoring treatments to individual genetic profiles and specific medical conditions. The integration of genomics, gene editing, and Regenerative Medicine holds the promise of more effective, targeted, and patient-centric therapeutic interventions.
2. Collaborative Research and Global Impact
International collaboration is crucial in advancing Regenerative Medicine. Shared knowledge, resources, and collaborative efforts across borders can accelerate research, enhance the quality of clinical trials, and expand the global impact of Regenerative Medicine, particularly in addressing prevalent health challenges.
3. Bridging Science and Society
The translation of scientific breakthroughs into tangible therapies requires effective communication and collaboration between the scientific community and society at large. Educating the public about the potential benefits, risks, and ethical considerations of Regenerative Medicine fosters informed decision-making and ethical practices.
To sum up, regenerative medicine is at the vanguard of a revolution in medical science. This emerging discipline gives hope to many people suffering from crippling illnesses by enabling the body’s natural ability to repair and rejuvenate. Research, ethics, and technology innovation work together to pave the way for a time when healing is not only a treatment but a natural, choreographed process that occurs within the complex symphony of the human body as we explore the scientific boundaries of regenerative medicine.