(source-.mayoclinic.org_.jpg)
Tumors, infections, and life-threatening diseases such as Cancer are diagnosed with the help of soft tissue biopsy. Soft tissue means skin, fat, muscle, and tendons, and biopsy refers to removing this soft tissue or some cells from the patient’s body, which is observed under the microscope. Doctors use this procedure to diagnose and check if the person is suffering from any of the above-mentioned diseases or conditions.
In this article, you will understand the different types of biopsies, the procedures followed by doctors, their needs, and the risks a patient might need to go through during the soft tissue biopsy.
Types of Soft Tissue Biopsy
There are several types of soft tissue biopsy procedures, and each one is suited for different situations. The choice of biopsy type depends on several factors, such as the location of the tissue, the size of the abnormality, and the overall health of the patient.
1. Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA)
- Procedure: In this procedure, a thin needle is inserted into the abnormal tissue to extract cells or fluid. It is often used to evaluate lumps or masses in areas like the neck, breast, or lymph nodes.
- Advantages: FNA is quick, less painful, and involves minimal recovery time.
- Limitations: It may not always provide enough tissue for a definitive diagnosis, requiring further testing.
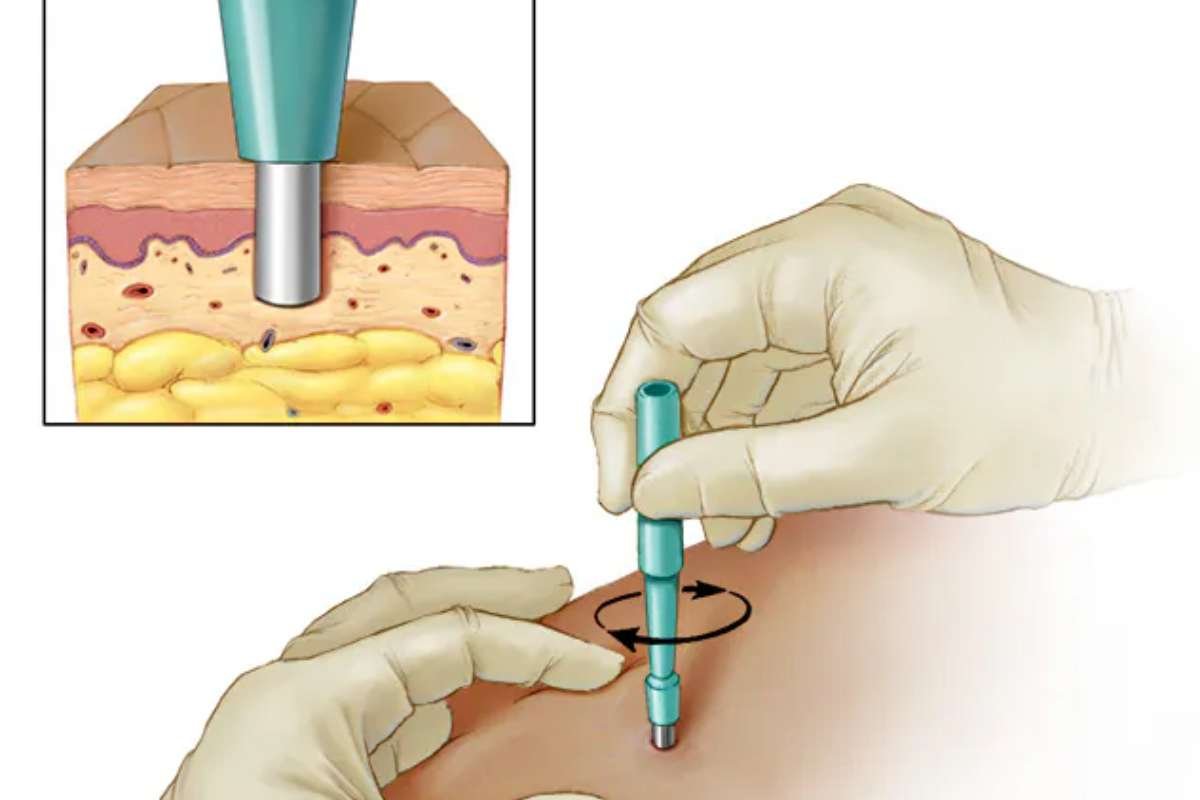
2. Core Needle Biopsy (CNB)
- Procedure: A larger, hollow needle is used to remove a small cylinder of tissue, providing a more substantial sample than FNA. This is often performed under local anesthesia and can be guided by imaging techniques like ultrasound or MRI.
- Advantages: CNB offers a more comprehensive tissue sample, increasing diagnostic accuracy.
- Limitations: CNB is slightly more invasive than FNA and has a short recovery time.
3. Incisional Biopsy
- Procedure: During an incisional biopsy, a surgeon makes a small incision to remove a portion of the abnormal tissue. This type of biopsy is used when the suspicious area is too large or located in a difficult-to-reach area.
- Advantages: Provides a larger tissue sample for analysis.
- Limitations: Requires a minor surgical procedure, leading to a longer recovery time compared to needle biopsies.
4. Excisional Biopsy:
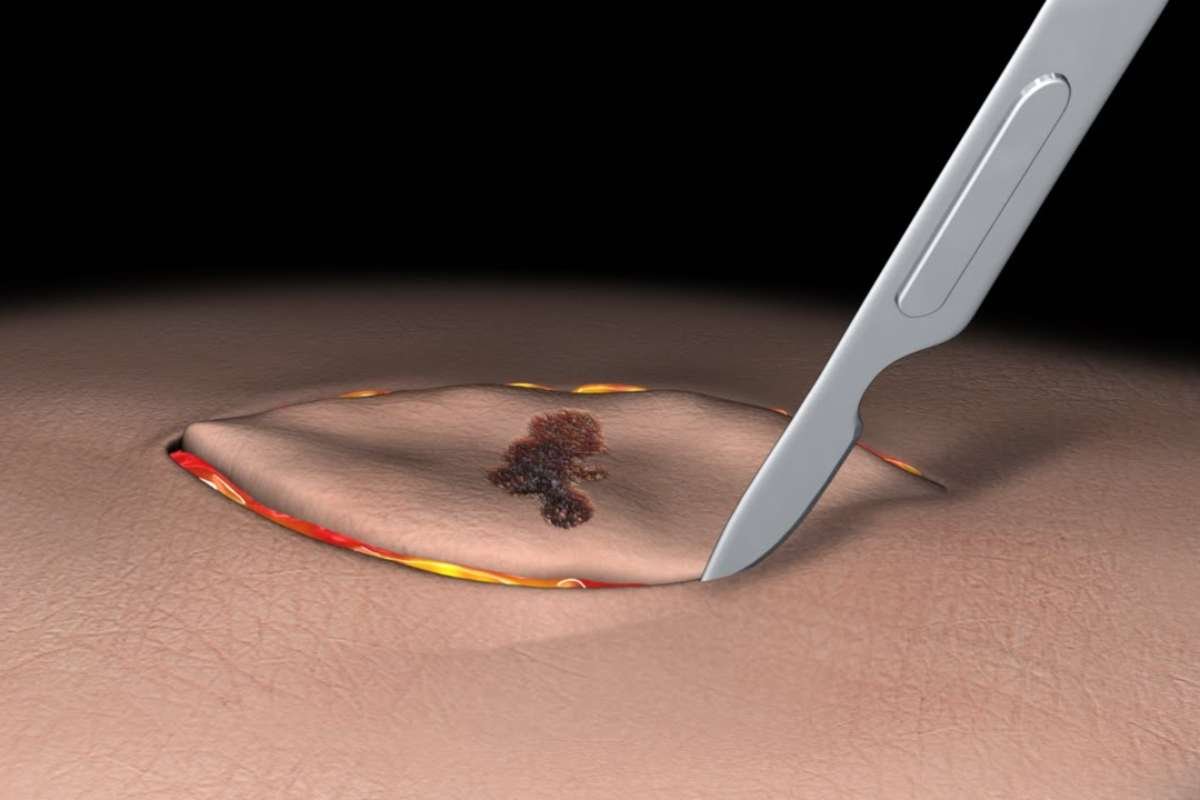
- Procedure: In an excisional biopsy, the entire abnormal area or mass is removed for examination. This is often done in cases where the lump or mass needs to be completely removed for both diagnosis and treatment.
- Advantages: Provides the most comprehensive tissue sample and can be diagnostic and therapeutic.
- Limitations: It is the most invasive type of soft tissue biopsy and requires a longer recovery period.
When is a Soft Tissue Biopsy Needed?
If your doctor finds an abnormal growth or sudden swelling, or you are suffering from constant pain in your soft tissues, then a biopsy might be required. It is useful for diagnosing the following conditions:
- Cancer: To determine whether a lump or mass is malignant (cancerous) or benign (non-cancerous).
- Infections: To identify the presence of bacteria, fungi, or other pathogens.
- Inflammatory Diseases: To assess conditions like sarcoidosis or autoimmune disorders that affect soft tissues.
- Soft Tissue Sarcomas: To confirm the presence of a rare type of cancer that forms in soft tissues.
The final decision is taken by the doctor if a biopsy is required or not.
What to Expect During a Soft Tissue Biopsy?
This section will help you to understand what steps are taken during the procedure and might help you to stay calm during the biopsy.
1. Preparation
- Your healthcare provider will explain the procedure and ask about your medical history, allergies, and medications.
- You may be asked to stop taking blood-thinning medications a few days before the procedure to reduce the risk of bleeding.
2. The Procedure
- Depending on the type of soft tissue biopsy, you will either be seated or lying down during the procedure.
- For needle biopsies, the area will be cleaned and numbed with a local anesthetic. If you are undergoing an incisional or excisional biopsy, you may receive a general anesthetic or sedation.
- The doctor will use the appropriate tool to remove the tissue sample. Imaging techniques like ultrasound, CT, or MRI may be used to guide the needle or incision.
3. After the Procedure
- After the soft tissue biopsy, the sample will be sent to a pathology lab for analysis.
- You may experience some mild pain or discomfort at the biopsy site. Over-the-counter pain relievers and rest are usually sufficient to manage these symptoms.
- Your doctor will provide instructions on how to care for the biopsy site and when to expect your results.
4. Results
- The duration of this procedure is approximately a few days to a week. Your doctor will check your report and inform you if any further testing, treatment, or monitoring is required.
Risks and Complications of Soft Tissue Biopsy
Soft tissue biopsy is a safe process, but you need to know that there are some risks when you go with this procedure.
- Bleeding: Some bleeding at the biopsy site is normal, but excessive bleeding may require medical attention.
- Infection: There is a small risk of infection at the biopsy site, which can be minimized by following your doctor’s care instructions.
- Pain or Discomfort: Mild pain or swelling may occur at the biopsy site, usually resolving within a few days.
Your doctor will give you precautions and necessary tips that you should follow to reduce the risk of complications.
Take Away
Through this article, we can understand that Biopsy is a powerful diagnostic procedure to treat various medical conditions in modern medicine. Though there are many benefits as well as risks of Biopsy, doctors can recommend solutions to avoid these risks that may harm the patient. It is very useful as it guides doctors in making treatment decisions and management strategies.