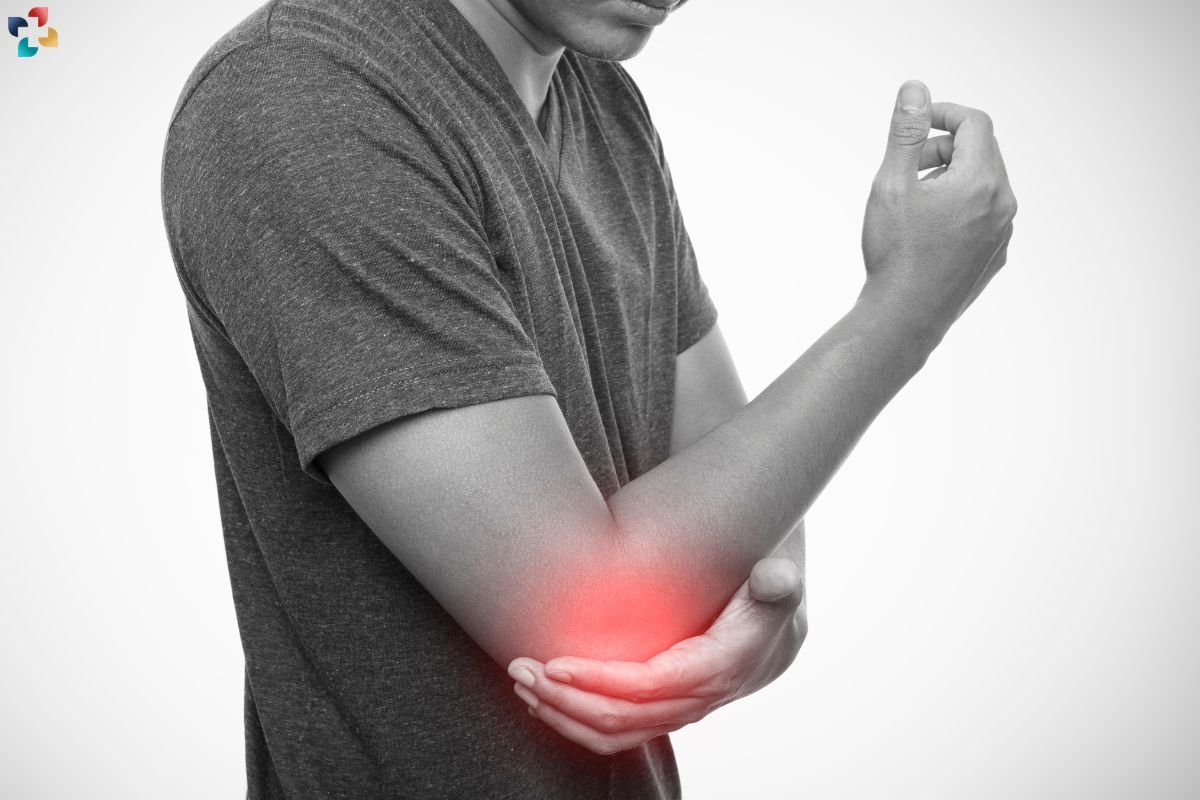
Triceps tendonitis is a condition characterized by inflammation and irritation of the triceps tendon, which connects the triceps muscle to the elbow bone (olecranon). This article delves into the multifaceted causes of triceps tendonitis and provides an in-depth exploration of effective treatment options to manage and alleviate symptoms.
Causes of Triceps Tendonitis:
Triceps tendonitis typically develops due to various factors that contribute to repetitive stress, overuse, or direct injury to the triceps tendon. Here’s a detailed look at the primary causes:
1. Overuse and Repetitive Strain
Activities involving repetitive arm movements, such as weightlifting (especially overhead triceps extensions), throwing sports (like baseball or javelin), or occupations requiring repeated lifting or pushing, can strain the triceps tendon. The repetitive nature of these activities leads to micro-trauma and inflammation in the tendon.
2. Sports Technique
Improper technique or form in sports that involve repetitive arm motions can significantly increase the risk of triceps tendonitis. Athletes who engage in throwing sports without proper training or those who lift weights incorrectly may experience excessive strain on the triceps tendon.
3. Age-related Degeneration
As people age, tendons naturally undergo degenerative changes. The triceps tendon becomes less flexible and more susceptible to injury and inflammation, making older individuals more prone to developing tendonitis.
4. Direct Trauma
A sudden impact or direct blow to the back of the upper arm, such as from a fall or contact sports injury, can cause acute trauma to the triceps tendon. This trauma leads to inflammation and pain, often requiring prompt medical attention.
5. Muscle Imbalance
Weakness or imbalance in the muscles surrounding the triceps, including the biceps, shoulder muscles, and even the muscles of the forearm, can disrupt the biomechanics of the elbow joint. This imbalance places undue stress on the triceps tendon during movement, predisposing it to tendonitis.
6. Repetitive Elbow Extension Against Resistance
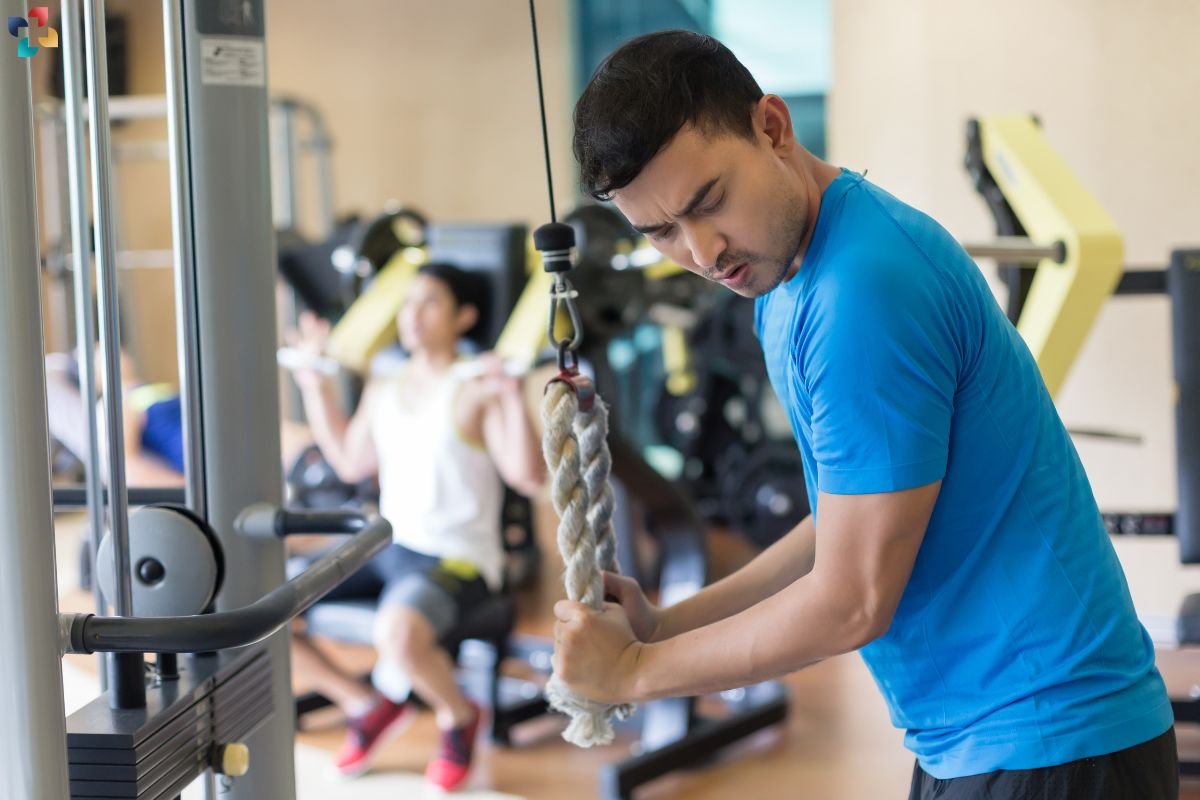

Activities that involve prolonged or forceful extension of the elbow joint against resistance, such as certain gym exercises (e.g., triceps dips or cable pushdowns) or occupational tasks (e.g., painting overhead), can strain the triceps tendon over time.
7. Poor Warm-up or Cool-down Practices
Failing to warm up adequately before physical activity or neglecting to perform proper stretching and cool-down exercises afterward can increase the risk of triceps tendonitis. Cold muscles are more prone to injury during strenuous activity.
8. Poor Posture
Maintaining poor posture, particularly with rounded shoulders or prolonged periods of sitting with inadequate arm support, can lead to chronic stress and strain on the triceps tendon. This can exacerbate inflammation and contribute to the development of tendonitis.
9. Underlying Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or metabolic disorders like diabetes, can predispose individuals to tendonitis throughout the body, including the triceps tendon. These conditions may exacerbate inflammation and delay healing.
10. Occupational Factors
Jobs or hobbies that involve repetitive arm movements or prolonged overhead activities (e.g., carpentry, plumbing, overhead assembly work) can place continuous stress on the triceps tendon, increasing the likelihood of developing tendonitis.
9 Essential Things to Know How the Body Uses Protein to Repair Muscle Tissue
When Body Uses Protein to Repair Muscle Tissue to Boost Muscle Growth or definition, you’ve undoubtedly heard that lifting weights tears down a muscle, which results in the muscle being stronger or larger as it repairs the damage.
Treatment Options for Triceps Tendonitis:
Managing triceps tendonitis involves a comprehensive approach that combines rest, therapeutic interventions, and lifestyle modifications to promote healing and prevent recurrence. Here’s a detailed overview of effective treatment options:
1. Rest and Activity Modification
Ceasing or modifying activities that aggravate symptoms is essential for allowing the triceps tendon to heal. Avoiding overhead movements, heavy lifting, or repetitive arm actions can alleviate strain and inflammation.
2. Ice Therapy
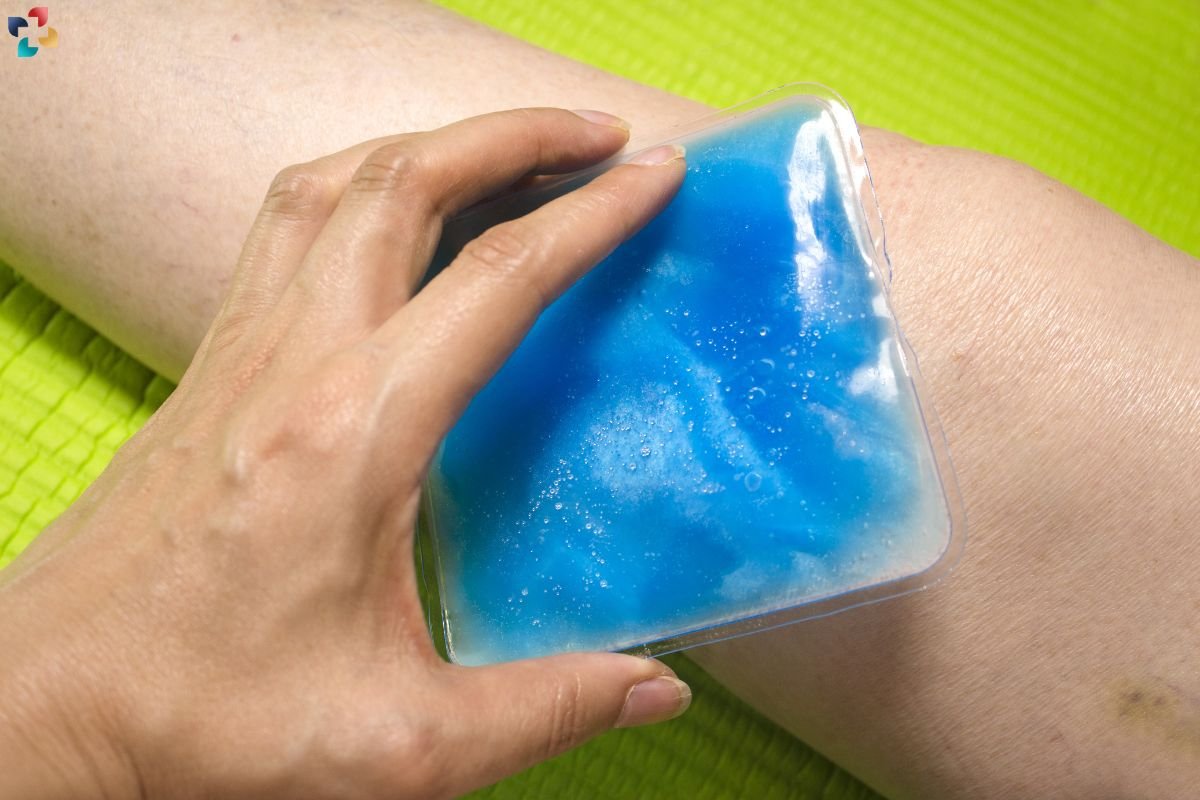

Applying ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes several times a day helps reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. Cold therapy can be especially beneficial after activities that exacerbate symptoms.
3. Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen or naproxen can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation in the triceps tendon. These should be used as directed and under medical supervision, especially for prolonged use.
4. Physical Therapy
A structured physical therapy program is crucial for rehabilitation. Physical therapists can prescribe stretching and strengthening exercises tailored to improve flexibility, correct muscle imbalances, and enhance the biomechanics of the elbow joint.
5. Ultrasound Therapy
Ultrasound treatment administered by healthcare professionals can promote tissue healing and reduce inflammation in the triceps tendon. This non-invasive therapy accelerates recovery and may be recommended in conjunction with other treatments.
6. Bracing or Splinting
Immobilizing the elbow joint with a brace or splint can help reduce strain on the triceps tendon during activities that require arm extension. This allows the tendon to rest and heal effectively.
7. Steroid Injections
In cases of severe or persistent inflammation, corticosteroid injections directly into the affected tendon can provide significant relief from pain and inflammation. These injections should be administered by a healthcare professional and used judiciously due to potential side effects.
8. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP injections involve using the patient’s own blood plasma, enriched with platelets containing growth factors, to promote healing of the triceps tendon. This regenerative therapy may accelerate tissue repair and reduce symptoms.
9. Surgical Intervention
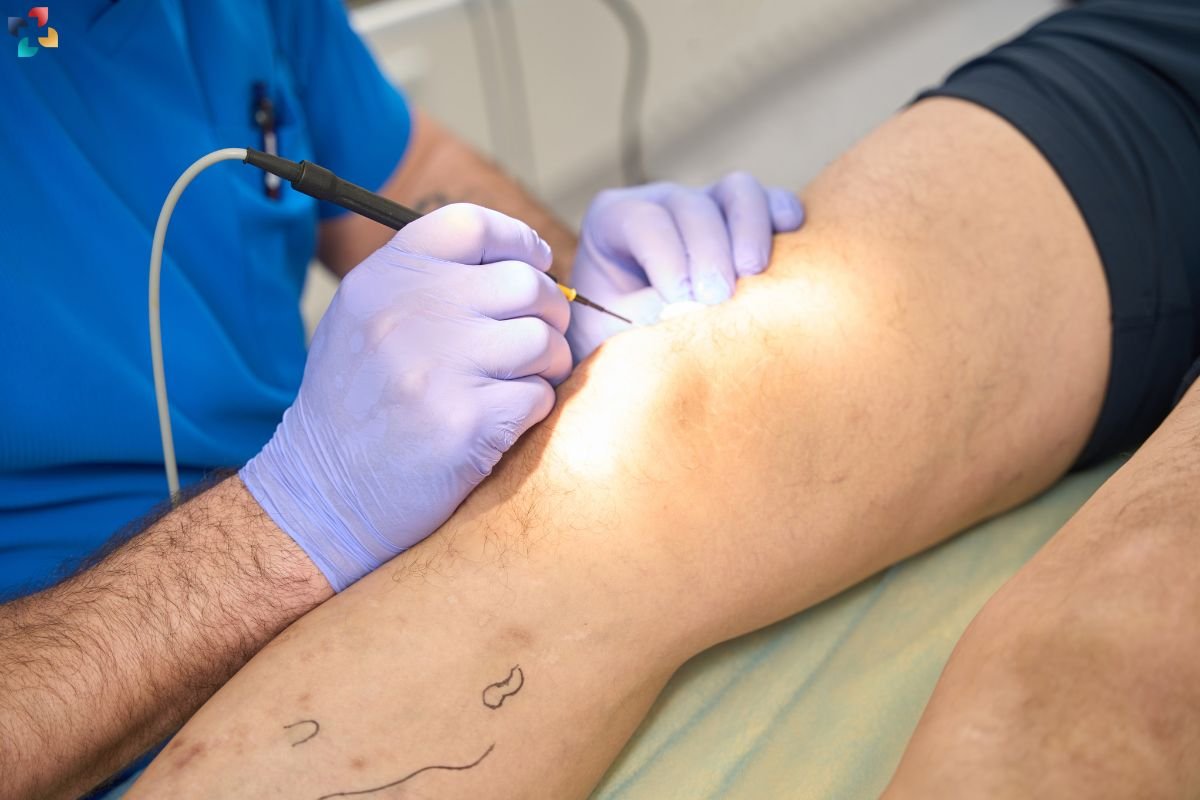
Surgical repair of the triceps tendon is rarely necessary but may be considered for severe cases of tendonitis that do not respond to conservative treatments. Surgical techniques aim to repair damaged tendon tissue and restore function to the elbow joint.
10. Preventive Measures
Once symptoms have resolved, implementing preventive measures is crucial to prevent recurrence of triceps tendonitis. This includes maintaining good posture, performing proper warm-up and cool-down exercises before and after physical activity, and gradually increasing exercise intensity and duration.
Conclusion
Triceps tendonitis is a challenging condition that requires prompt recognition and appropriate management to alleviate symptoms and facilitate recovery. By addressing the underlying causes, implementing targeted treatments, and adopting preventive measures, individuals can effectively manage triceps tendonitis and prevent future complications. Consultation with a healthcare professional is essential for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan tailored to individual needs and circumstances. With proper care and adherence to treatment recommendations, individuals can regain function and return to their normal activities without the limitations imposed by triceps tendonitis.