The field of medicine is constantly evolving, striving to find innovative solutions to address the challenges posed by various diseases and injuries. One such breakthrough in the realm of medical research is the advent of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. These interdisciplinary fields offer the promise of revolutionizing traditional medical practices by repairing or replacing damaged tissues and organs in the human body. This blog aims to delve into the fascinating world of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, understanding their principles, applications, and the groundbreaking research being conducted in these areas.
What are tissue engineering and regenerative medicine?

Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine involve the application of engineering principles and biological sciences to develop functional tissues or organs that can restore, maintain, or improve the normal function of the body. This multidisciplinary field combines expertise from various disciplines such as biology, chemistry, materials science, and engineering to create living, functional tissues that can replace or repair damaged ones.
Tissue engineering refers to the fabrication of functional tissues using a combination of cells, biomaterials, and biochemical factors. This approach involves growing cells in a lab and then seeding them onto a scaffold made of biocompatible materials. The scaffold acts as a support structure, providing the necessary architecture for the cells to organize and develop into functional tissues.
Regenerative medicine, on the other hand, focuses on stimulating the body’s innate healing processes to repair or replace damaged tissues or organs. This can be achieved through the administration of stem cells, growth factors, or other bioactive molecules that promote tissue regeneration.
How do tissue engineering and regenerative medicine work?
Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine work by harnessing the body’s inherent healing mechanisms or by creating artificial cellular structures to restore or replace damaged tissues. The process generally involves three key components: cells, scaffolds, and biochemical cues.

By combining these three components in a controlled environment within the body or in the laboratory, tissue engineering and regenerative medicine aim to create functional tissues or organs that can seamlessly integrate with the surrounding biological milieu.
How do tissue engineering and regenerative medicine fit in with current medical practices?
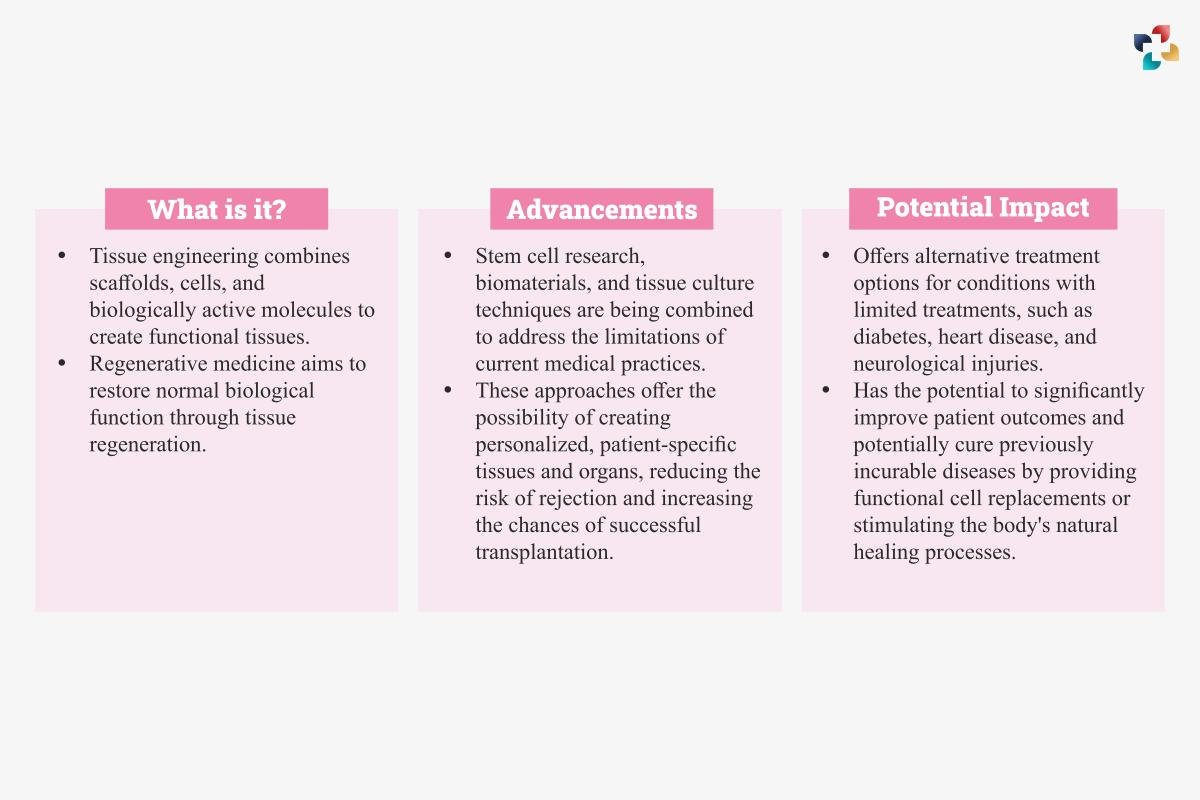
What is it?
- Tissue engineering combines scaffolds, cells, and biologically active molecules to create functional tissues.
- Regenerative medicine aims to restore normal biological function through tissue regeneration.
Advancements
- Stem cell research, biomaterials, and tissue culture techniques are being combined to address the limitations of current medical practices.
- These approaches offer the possibility of creating personalized, patient-specific tissues and organs, reducing the risk of rejection and increasing the chances of successful transplantation.
Potential Impact
- Offers alternative treatment options for conditions with limited treatments, such as diabetes, heart disease, and neurological injuries.
- Has the potential to significantly improve patient outcomes and potentially cure previously incurable diseases by providing functional cell replacements or stimulating the body’s natural healing processes.
TERM has made a significant mark in the medical industry. Some successful implementations are as follows:
Where it can be applied?
- Supplemental Bladders and Small Arteries: Engineered bladders and arteries have been implanted in patients. This demonstrates the need for TERM and how it is used during organ shortage.
- Skin Grafts and Cartilage: These are among the most commonly used engineered tissues. They are applied to victims who have burns on their bodies.
- Windpipe Replacement: Fully engineered windpipes have been implanted in some cases when patients are not able to breathe.
What are NIH-funded researchers developing in the areas of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine?
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) in the United States, one of the leading funding agencies for biomedical research, has invested heavily in supporting innovative research in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Numerous exciting advancements and breakthroughs have been made in this field with the support of NIH funding.
NIH-funded researchers are developing various cutting-edge technologies and methodologies to advance the field. Some of the key areas of research include:
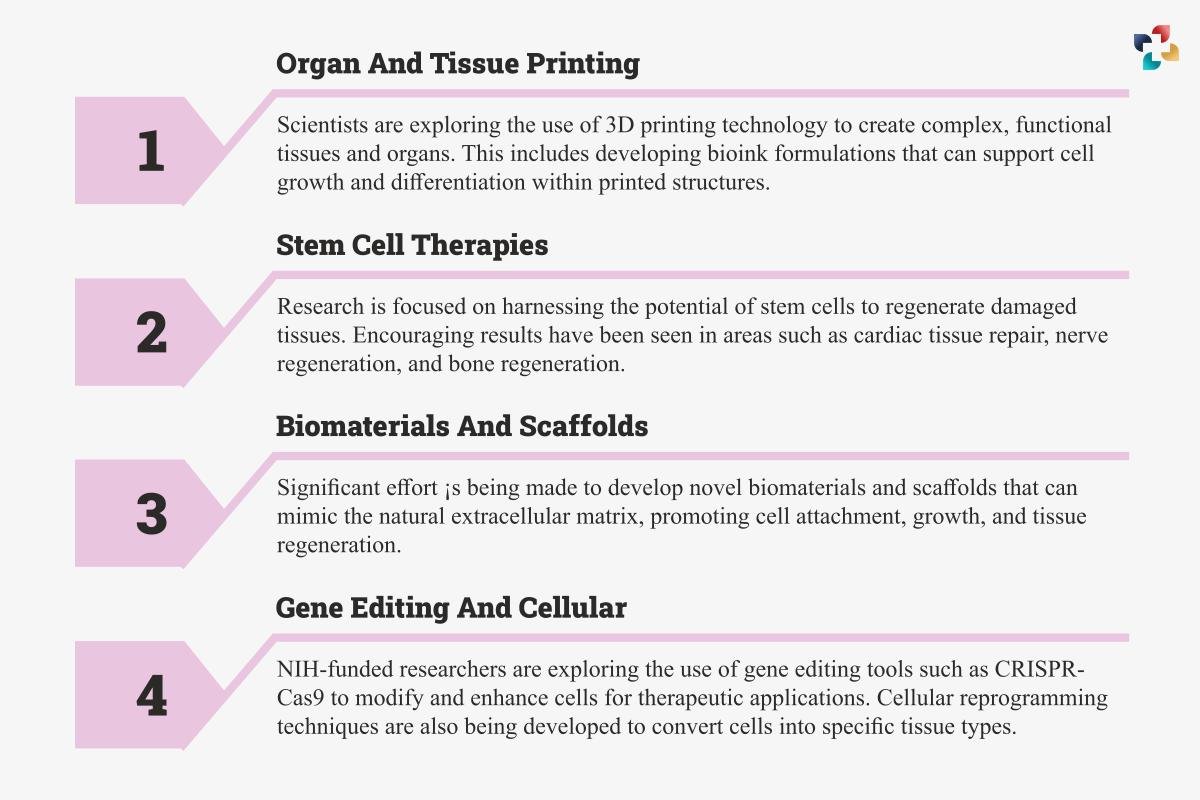
These are just a few examples of the incredible advancements being made in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine with the support of NIH funding. As the field continues to progress, the hope and excitement surrounding the potential for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine to revolutionize healthcare continue to grow.
Challenges
TERM has achieved several achievements, but faces several challenges too. Some of them are mentioned below:
- High Costs: The development and production of engineered tissues are costly. This limits its access.
- The complexity of Organ Systems: It is not easy for doctors or researchers to replicate structures and functions of large organs like the heart and brain. It’s quite a challenge for them.
The future of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine depends upon how doctors and researchers use this method. Advances in artificial intelligence, nanotechnology, and bioprinting could speed up the creation of functional tissues and organs.
Conclusion
Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine have the potential to redefine medical practices and improve patient outcomes. By combining principles from various disciplines, these fields aim to restore, repair, or replace damaged tissues and organs in the human body. As innovative techniques and technologies continue to emerge, the possibilities for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine seem limitless. With the support of government funding agencies like NIH, researchers are driving forward cutting-edge research and pioneering the future of healthcare. Exciting times lie ahead as these fields offer hope for a new era in medicine, where the human body’s natural regenerative potential can be harnessed to restore and enhance our lives.
Also Read: Is Telehealth the Present and Future of Healthcare?