The landscape of healthcare is undergoing a profound transformation, fueled by the convergence of cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, and big data analytics. At the forefront of this revolution are medical devices, which are evolving rapidly to enhance diagnostic accuracy, streamline treatment processes, and personalize care for individual patients. In this article, we delve into the exciting realm of the future of medical devices, exploring how AI, robotics, and personalized medicine are reshaping the healthcare paradigm.
AI-Powered Diagnostics: Revolutionizing Healthcare:
Artificial intelligence has emerged as a game-changer in the future of medical devices, particularly in the realm of diagnostics. AI algorithms, trained on vast datasets of medical images, patient records, and clinical outcomes, possess the ability to analyze complex data with unparalleled speed and accuracy. This capability holds immense potential for improving the early detection and diagnosis of diseases, leading to more timely interventions and better patient outcomes.
AI-powered diagnostic devices, ranging from advanced imaging systems to handheld diagnostic tools, are poised to revolutionize medical practice. For instance, machine learning algorithms can sift through massive volumes of medical images—such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans—to identify subtle patterns indicative of disease pathology. In doing so, these AI systems assist radiologists and clinicians in making more accurate diagnoses, reducing errors, and expediting treatment decisions.
Moreover, AI-driven diagnostic devices have the potential to extend healthcare access to underserved regions, where expert medical expertise may be scarce. Telemedicine platforms equipped with AI diagnostics can enable remote consultations and triage, bringing expert medical opinions to patients in remote areas and facilitating timely interventions.
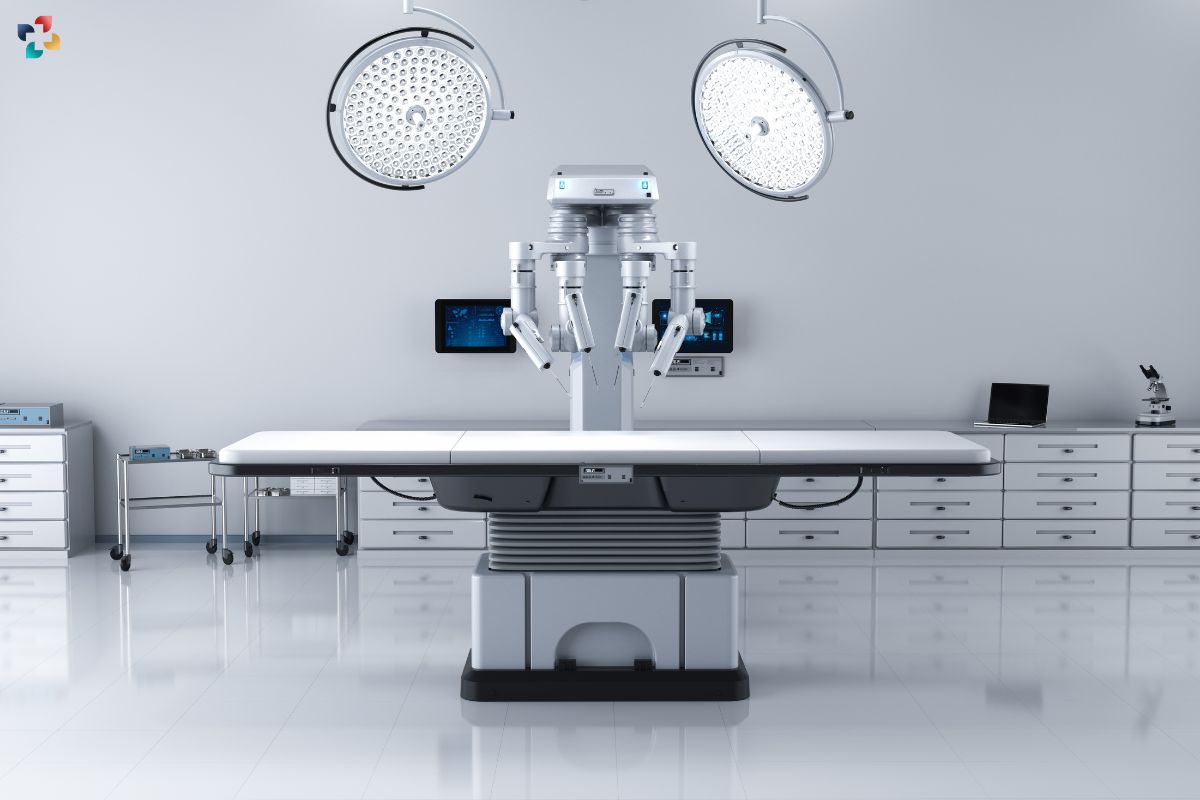
Surgical Robots: Pioneering Precision and Minimally Invasive Surgery:
In the realm of surgical interventions, robotics technology is revolutionizing the way procedures are performed. The future of medical devices is surgical robots, equipped with advanced AI algorithms and precision instruments, which offer unprecedented levels of precision, dexterity, and control to surgeons. These robotic systems enable minimally invasive procedures, characterized by smaller incisions, reduced trauma to surrounding tissues, and faster recovery times for patients.
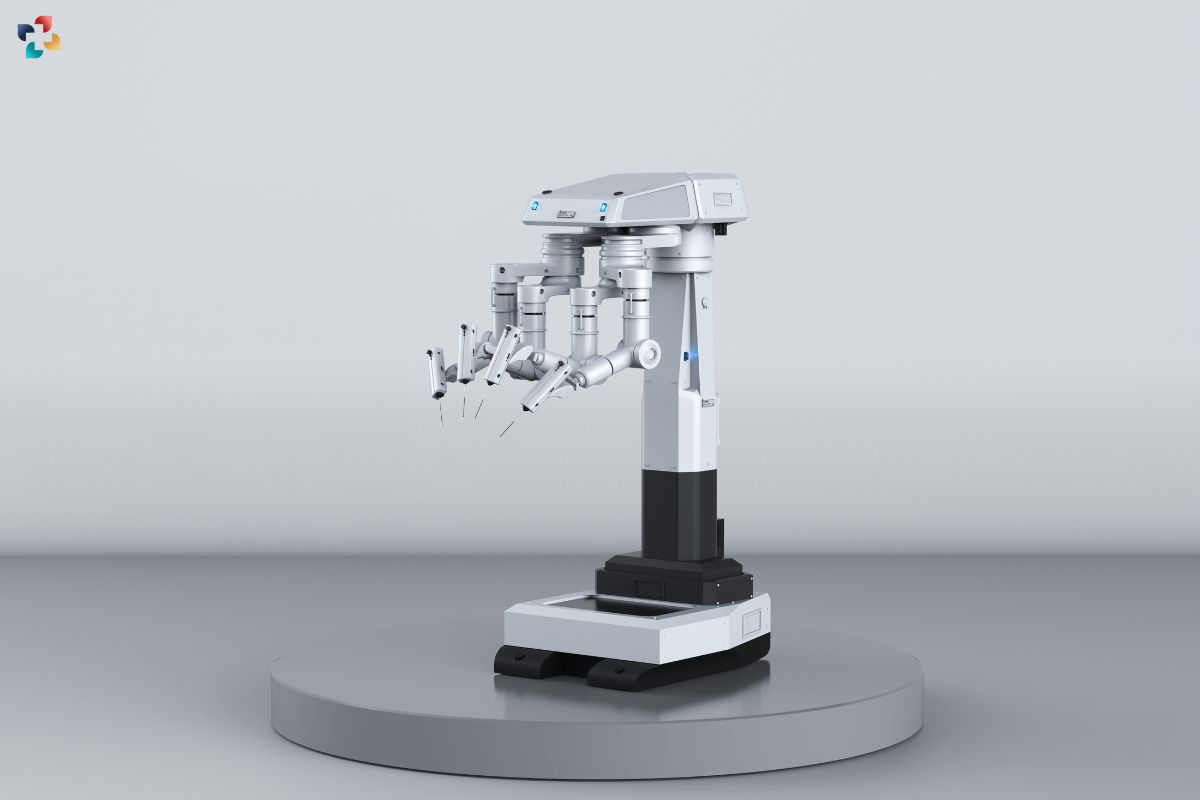

From robotic-assisted laparoscopic surgeries to intricate neurosurgical procedures, surgical robots are transforming the surgical landscape across various specialties. By augmenting the capabilities of human surgeons with robotic precision and real-time feedback, these systems enhance surgical outcomes while minimizing the risks associated with traditional open surgeries.
Furthermore, In the future of medical devices, surgical robots hold the promise of overcoming geographical barriers in healthcare delivery. Remote surgical procedures, facilitated by teleoperated robotic systems, enable expert surgeons to perform interventions on patients located miles away, bridging the gap between patients and specialized healthcare providers.
Personalized Medicine Devices: Tailoring Treatment to Individual Patients:
The era of personalized medicine is dawning, fueled by advances in genomics, molecular diagnostics, and wearable technologies. Personalized medicine devices, tailored to the unique genetic makeup and physiological characteristics of individual patients, are poised to revolutionize treatment paradigms across various disease conditions.
These devices encompass a wide spectrum of innovations, ranging from pharmacogenomic assays that predict drug responses based on genetic profiles to wearable biosensors that continuously monitor vital signs and biomarkers in real-time. By harnessing the power of big data analytics and AI, personalized medicine devices offer insights into disease risk, progression, and response to therapy, enabling clinicians to tailor interventions for optimal outcomes.
For example, implantable medical devices equipped with sensors and AI algorithms can monitor cardiac function in patients with heart failure, predicting exacerbations and adjusting treatment strategies in real-time. Similarly, wearable devices capable of analyzing sweat or blood biomarkers can provide early warning signs of metabolic disorders or infectious diseases, empowering individuals to take proactive measures to safeguard their health.
Navigating the Complexities:
While the potential benefits of AI in healthcare are undeniable, its widespread adoption also raises ethical considerations that warrant scrutiny. One of the primary concerns revolves around data privacy and security, as AI algorithms rely on vast amounts of sensitive patient data to train and optimize their performance. Ensuring robust data governance frameworks and stringent security measures is imperative to safeguard patient confidentiality and prevent unauthorized access or misuse of healthcare data.
Moreover, there are concerns regarding the potential for algorithmic bias and discrimination in AI-powered healthcare systems. If not carefully designed and validated, AI algorithms may inadvertently perpetuate disparities in healthcare delivery, particularly among marginalized or underserved populations. Addressing bias in AI algorithms requires transparent methodologies, diverse training datasets, and ongoing monitoring to detect and mitigate biases that may arise.
Furthermore, the ethical implications of autonomous AI systems, such as surgical robots, raise questions about accountability, liability, and the delegation of decision-making authority. While these systems offer tremendous potential to improve patient outcomes, ensuring appropriate oversight, informed consent, and human oversight is essential to mitigate the risks of unintended harm or malpractice.
AI-powered Diagnostics and Surgical Robots:
Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a revolutionary force in the future of medical devices, particularly in diagnostics and surgical interventions. AI-powered diagnostic systems harness the capabilities of machine learning algorithms to analyze complex medical data, ranging from imaging scans to patient records, with unprecedented accuracy and efficiency. These systems can detect subtle patterns and anomalies that may elude human perception, thereby enhancing the accuracy and speed of diagnosis.
For instance, in radiology, AI algorithms trained on vast datasets of medical images can assist radiologists in detecting early signs of diseases such as cancer, neurological disorders, and cardiovascular conditions. By automating the process of image interpretation and flagging abnormalities for further review, AI-powered diagnostic tools enable healthcare providers to make more timely and accurate diagnoses, leading to improved patient outcomes.
In addition to diagnostics the future of medical devices, AI is also revolutionizing surgical interventions through the development of robotic-assisted surgical systems. Surgical robots, equipped with advanced AI algorithms and precision instruments, offer surgeons enhanced capabilities for performing minimally invasive procedures with unparalleled precision and control. These robots can execute complex maneuvers with sub-millimeter accuracy, enabling surgeons to operate with greater precision and dexterity than is possible with traditional surgical techniques.
Moreover, surgical robots provide real-time feedback and visualization capabilities, allowing surgeons to navigate anatomical structures with enhanced clarity and accuracy. This translates into shorter operating times, reduced blood loss, and faster recovery times for patients. From orthopedic surgeries to neurosurgical procedures, robotic-assisted surgery is transforming the landscape of surgical care, offering patients less invasive treatment options and improved outcomes.
Personalized Medicine Devices Tailored to Individual Patients:
Personalized medicine is revolutionizing healthcare by tailoring treatment strategies to the unique genetic makeup, physiological characteristics, and lifestyle factors of individual patients. Personalized medicine devices encompass a wide range of technologies, including genomic assays, molecular diagnostics, wearable sensors, and implantable devices, which enable clinicians to customize interventions based on a patient’s specific needs and preferences.
Genomic assays, for example, analyze an individual’s genetic profile to predict their risk of developing certain diseases, identify optimal treatment options, and optimize medication dosages. By integrating genomic data with clinical information, healthcare providers can deliver targeted therapies that are more effective and have fewer adverse effects, thus improving patient outcomes.
Wearable sensors and monitoring devices offer continuous real-time monitoring of vital signs, biomarkers, and physiological parameters, allowing for early detection of health issues and proactive interventions. These devices enable patients to actively participate in their healthcare management, empowering them to make informed decisions and adopt healthier lifestyles.
Implantable devices, such as pacemakers, insulin pumps, and neural stimulators, are increasingly being personalized to individual patients’ needs. Advanced sensors and AI algorithms embedded within these devices continuously monitor physiological signals and adjust treatment parameters in real-time, optimizing therapy delivery and enhancing patient comfort and safety.
Ethical Considerations of AI in Healthcare:
In the future of medical devices, integration of AI in healthcare holds tremendous promise for improving patient care and outcomes, it also raises complex ethical considerations that must be carefully addressed. One of the primary concerns is the privacy and security of patient data used to train and deploy AI algorithms. Healthcare organizations must ensure robust data governance frameworks and stringent security measures to safeguard patient confidentiality and prevent unauthorized access or misuse of sensitive health information.
Another ethical consideration is the potential for algorithmic bias and discrimination in AI-powered healthcare systems. If not properly addressed, AI algorithms may inadvertently perpetuate disparities in healthcare delivery, particularly among underserved or marginalized populations. To mitigate bias, it is essential to use diverse and representative training datasets, employ transparent methodologies, and implement ongoing monitoring and validation processes to detect and correct biases that may arise.
Furthermore, the introduction of autonomous AI systems, such as surgical robots, raises questions about accountability, liability, and the delegation of decision-making authority. While these systems offer tremendous potential to improve patient outcomes, ensuring appropriate oversight, informed consent, and human oversight is essential to mitigate the risks of unintended harm or malpractice.
Conclusion:
The future of medical devices is a convergence of AI, robotics, and personalized care, ushering in a new era of precision medicine and patient-centered healthcare delivery. From AI-powered diagnostics that revolutionize disease detection to surgical robots that enable precision surgery and personalized medicine devices tailored to individual patients, the possibilities are limitless. However, as we navigate this transformative journey, it is imperative to address the ethical considerations and ensure that these technologies are deployed responsibly, equitably, and in the best interests of patients and society as a whole. By harnessing the power of technology while upholding ethical principles, we can unlock the full potential of medical devices to advance human health and well-being in the decades to come.