Maintaining sterility is of utmost importance in operative medicine to prevent the spread of infections and reduce the risk of complications. The consequences of not maintaining sterility can be dire, including surgical site infections, sepsis, and even death. In this article, we will discuss 10 pro tips to maintaining sterility in operative medicine.
Here are 10 Pro Tips to Maintaining Sterility in Operative Medicine;
1.Adhere to Standard Precautions
To maintain Sterility in Operative Medicine, it is imperative that standard precautions, which are fundamental measures designed to prevent infections, be observed at all times. Hand hygiene should be performed both before and after providing care to patients, and contaminated materials should be disposed of appropriately.
Other standard precautions include the use of masks, eye protection, and gloves when appropriate. The prevention of infectious agents’ ability to spread and the risk of cross-contamination are both helped along by strict adherence to standard precautions.
2.Proper Hand Hygiene

When it comes to maintaining sterility in operative medicine, having clean hands is one of the most important steps you can take. Before and after providing care to a patient, the hands should be washed thoroughly with soap and water for a minimum of twenty seconds. Sanitizers for the hands that contain alcohol can also be used, but using them is not an adequate replacement for washing one’s hands. Even if gloves were worn, it is important to wash one’s hands as soon as possible after coming into contact with any body fluids.
3.Use Sterile Equipment and Supplies
To avoid the spread of infectious agents during surgical procedures, every piece of apparatus and supply must use to be sterile. This includes things like drapes, gloves, gowns, and surgical instruments. Also included are sponges. The Sterility in Operative Medicine, equipment should be kept in an area that is clean and dry, and it should not be opened until just before it is used. Any supplies or equipment that are not sterile or that have been tainted in any way ought to be disposed of appropriately.
4.Create and Maintain Sterile Fields
The term “sterile field” refers to an area that has been sterilized and made ready to prevent the spread of infectious pathogens. During surgical procedures, Sterility in Operative Medicine, the operating room should be set up with these fields and they should be kept that way. The use of sterile drapes, gowns, and gloves is necessary to create a sterile field. On the sterile field, non-sterile items should be kept at a safe distance from the field, while sterile items should be placed directly on the field.
5.Follow Aseptic Techniques
During surgical procedures, Sterility in Operative Medicine aseptic techniques are actions that are carried out to ensure that the operating area remains sterile. These methods include the use of sterile gloves and gowns, the employment of sterile instruments, the avoidance of contact with non-sterile surfaces, and the implementation of sterile methods when handling and preparing sterile supplies. To lower the patient’s likelihood of contracting an infection during surgical procedures, aseptic procedures need to be followed at all times.
6.Proper Use of Antimicrobial Prophylaxis
Antimicrobial prophylaxis refers to the practice of administering antibiotics prior to surgical procedures in order to reduce the risk of infection. Before the beginning of surgery, antibiotics should be given, and then they should be stopped within the first twenty-four hours after surgery.
The kind of operation that will be performed and the patient’s health background should both be considered when choosing the antibiotic that will be administered. Antibiotic resistance can develop from the improper use of antibiotics, which is why they should only be taken when absolutely necessary.
7.Proper Wound Care
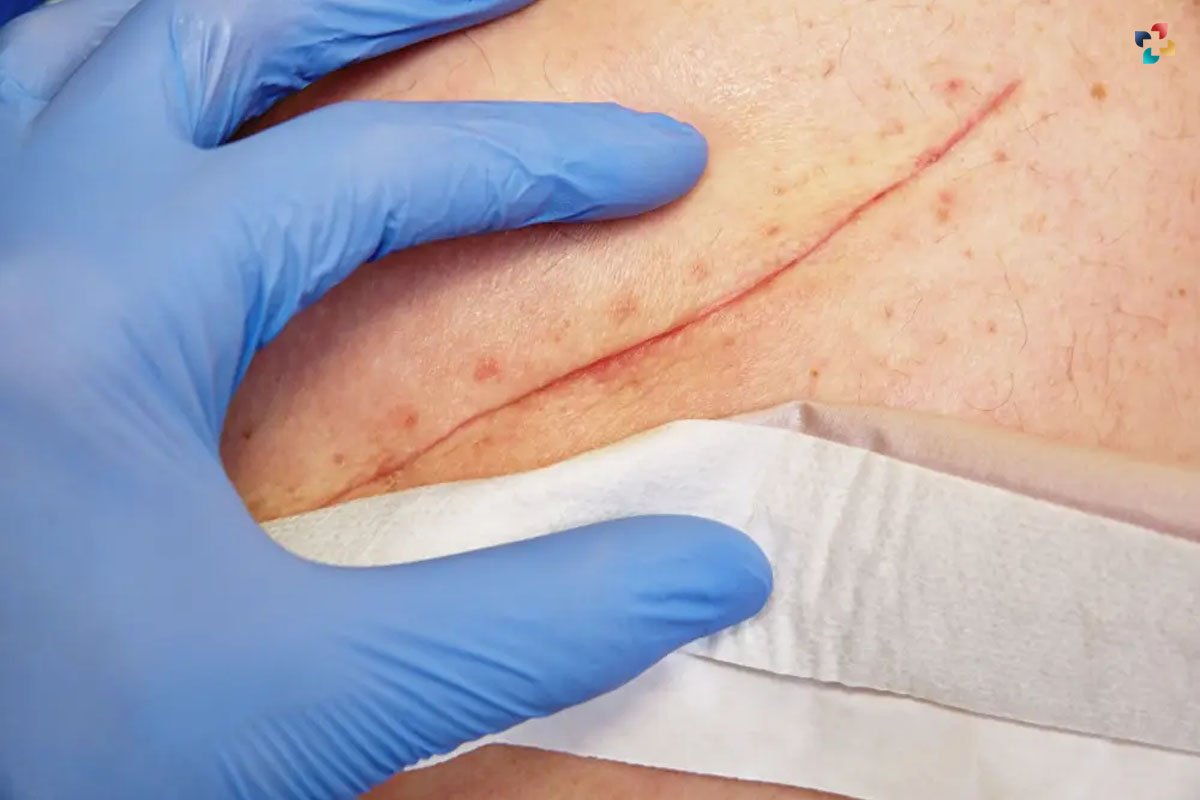
It is critical to treat wounds correctly to preserve Sterility in Operative Medicine and avoid infection. Immediately after surgical procedures, wounds should be washed and treated. The dressings should be changed regularly, and any symptoms of infection, including redness, swelling, or drainage, should be reported as soon as possible. A well-cared-for wound has a lower chance of becoming infected and heals faster as a result.
8.Use of Sterilization and Disinfection
When it comes to operational medicine, sterilization and disinfection are two practices that are essential for avoiding the transmission of infection. The elimination of all microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, and fungus, is an essential step in the sterilization process.
The removal of bacteria from hard surfaces and pieces of equipment is the primary goal of the disinfection procedure. Before being used, each piece of apparatus and supply that is going to be utilized in surgical treatment has to be either sterilized or disinfected.
9. Appropriate Waste Management
It is necessary to have effective waste management to keep a Sterility in Operative Medicine and stop the spread of infection. During surgical procedures, any waste should be carefully disposed of in the containers that have been specifically designated for that purpose.
Sharps should be disposed of in containers that are resistant to puncturing, and materials that have been contaminated should be disposed of in bags designated for biohazardous waste. To avoid contamination, waste bins should be tagged and placed in a location that is separate from the sterile area.
10. Proper Training and Education
When it comes to operative medicine, having the appropriate education and training is absolutely necessary for preserving sterility. Training on standard precautions, aseptic techniques, the appropriate use of antimicrobial prophylaxis, proper wound care, as well as sterilization and disinfection, should be provided to all members of the healthcare staff who participate in surgical procedures.

Education and training on a consistent basis can help ensure that medical staff are up to date on the most recent methods and best practices for maintaining sterility in their facilities.
BOTTOM LINE
In operative medicine, preserving sterility is essential for preventing the spread of infection and lessening the likelihood of complications from the procedure. Aseptic techniques, proper use of antimicrobial prophylaxis, proper wound care, proper use of sterilization and disinfection, proper waste management, and proper training and education are some of the tips that are discussed in this article that can help ensure that surgical procedures are performed in a safe and effective manner.
Other tips that are discussed in this article include adhering to standard precautions, proper hand hygiene, using sterile equipment and supplies, creating and maintaining sterile fields, and following aseptic techniques. If healthcare professionals adhere to these guidelines, they can help reduce the likelihood of patients contracting an infection and improve the outcomes for their patients.