Ottawa Ankle Rules (OAR) is a set of guidelines used by healthcare professionals to determine whether an ankle injury requires further diagnostic imaging, such as X-rays. Developed in the late 20th century, these rules serve as a valuable tool in the assessment of ankle injuries, helping to streamline patient care and reduce unnecessary radiation exposure. In this article, we will delve into the details of the Ottawa Ankle Rules, their significance in clinical practice, and how they contribute to efficient and accurate diagnosis and management of ankle injuries.
Understanding Ottawa Ankle Rules
Ottawa Ankle Rules are a set of clinical decision guidelines used to identify patients who require X-rays following an ankle injury. These rules were first established by Dr. Ian Stiell and colleagues in Ottawa, Canada, in 1992, and have since been validated and adopted worldwide. The primary aim of OAR is to assist healthcare providers in determining which patients are at low risk of having significant ankle fractures, thus obviating the need for unnecessary imaging studies.
Ottawa Ankle Rules (OAR) have become an integral part of emergency medicine and orthopedics, guiding healthcare professionals in the assessment of ankle injuries with efficiency and accuracy. Dr. Ian Stiell and his colleagues developed these rules to address the challenge of unnecessary diagnostic imaging, particularly X-rays, which not only expose patients to radiation but also contribute to healthcare costs and resource utilization. By establishing clear criteria for identifying patients at low risk of ankle fractures, OAR has revolutionized the approach to ankle injury management.
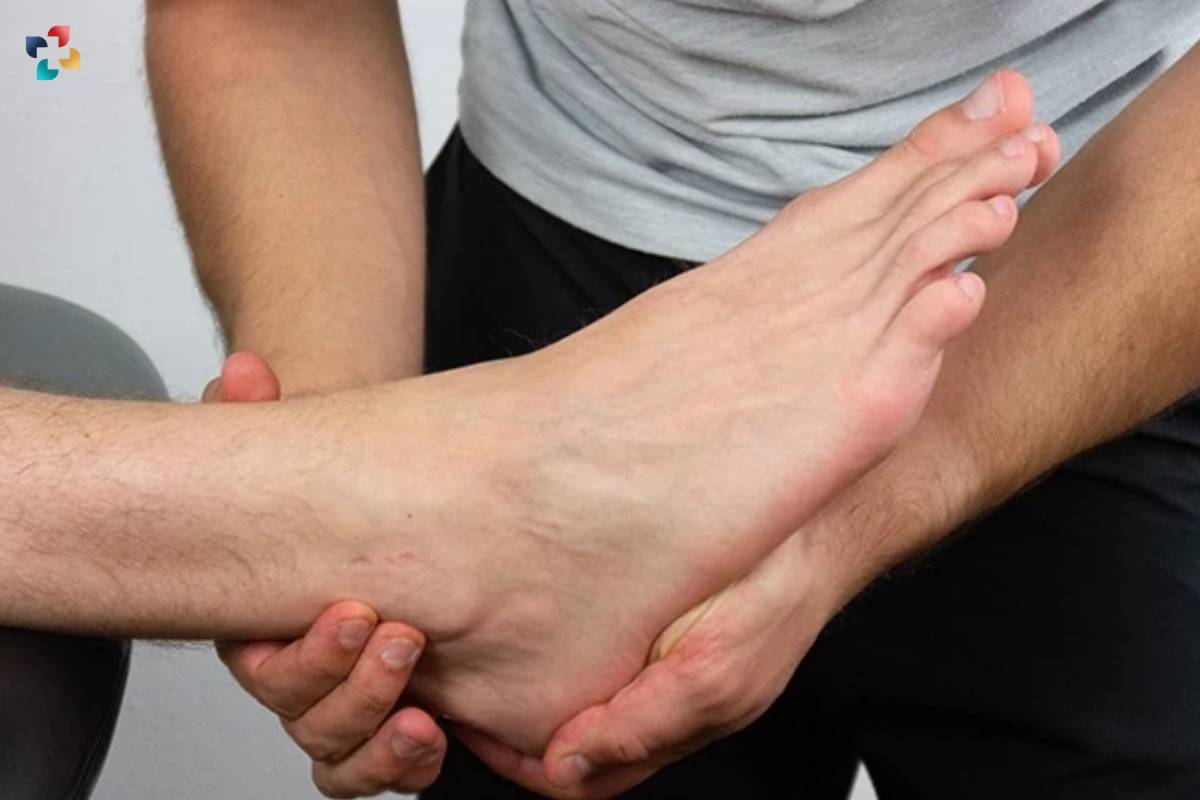
One of the key strengths of Ottawa Ankle Rules lies in their simplicity and ease of application. The criteria are straightforward and rely on clinical findings that can be readily assessed during a patient encounter. This simplicity enhances the accessibility and widespread adoption of OAR across various healthcare settings, from emergency departments to primary care clinics. Moreover, the rules have been extensively validated through research and clinical practice, further reinforcing their reliability and effectiveness.
In addition to their role in reducing unnecessary imaging, Ottawa Ankle Rules contribute to streamlined patient care and resource allocation. By accurately identifying patients who do not require X-rays, healthcare providers can focus their attention and resources on those who truly need further evaluation and intervention. This targeted approach optimizes workflow efficiency, reduces patient wait times, and enhances overall healthcare delivery.
Overall, the Ottawa Ankle Rules represent a remarkable example of evidence-based medicine translated into clinical practice. Their widespread adoption and proven effectiveness underscore their importance in modern healthcare, serving as a testament to the power of simple yet robust clinical decision guidelines. As healthcare continues to evolve, (OAR) remains a cornerstone in the evaluation and management of ankle injuries, benefiting both patients and healthcare providers alike.
Criteria for Applying Ottawa Ankle Rules
To apply the Ottawa Ankle Rules, healthcare providers assess specific criteria related to the mechanism of injury and clinical findings. The rules are typically applied to patients who present with acute ankle injuries within a certain timeframe from the time of injury, usually within 7 to 10 days. The criteria for applying OAR include:
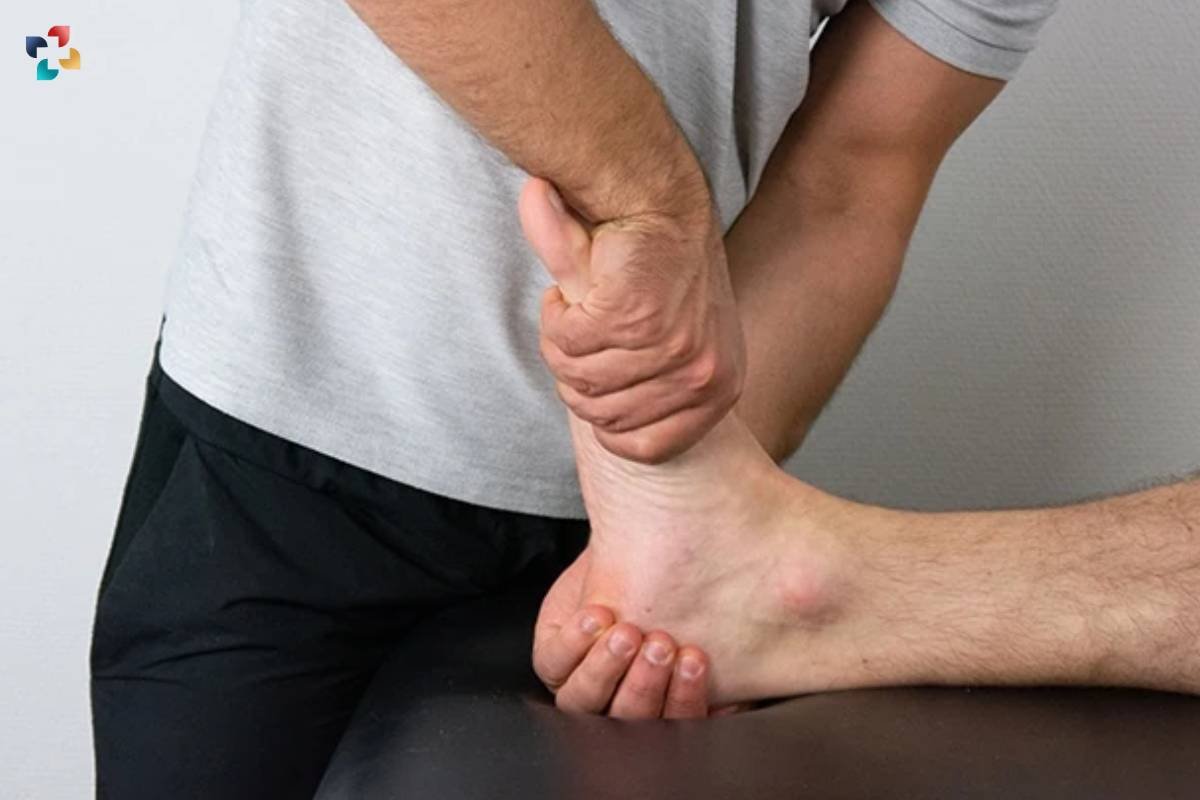
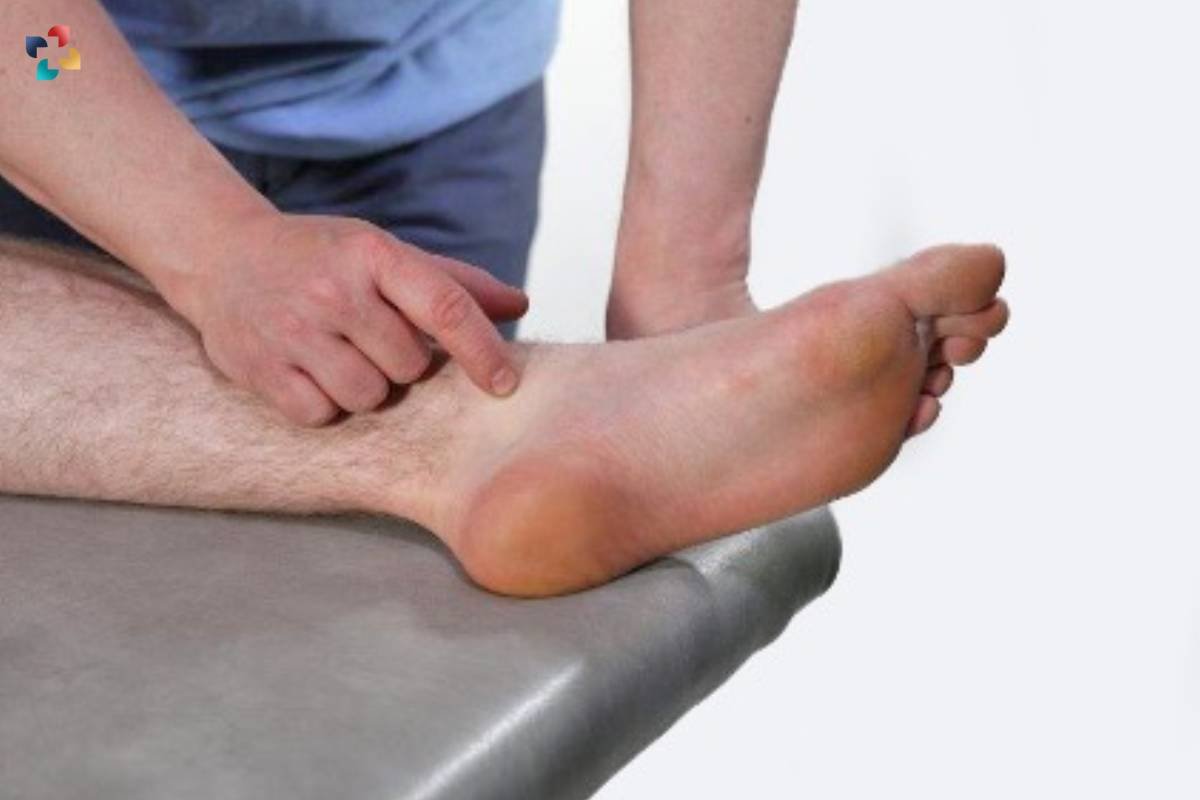
- Pain in the malleolar zone (medial or lateral) or inability to bear weight immediately after the injury.
- Tenderness to palpation over the posterior edge or tip of the lateral malleolus.
- Tenderness to palpation over the posterior edge or tip of the medial malleolus.
Application of Ottawa Ankle Rules
In clinical practice, healthcare providers use Ottawa Ankle Rules as a systematic approach to evaluating ankle injuries. When a patient presents with an ankle injury, the provider assesses the aforementioned criteria to determine if further diagnostic imaging, such as X-rays, is necessary. If the patient meets any of the criteria, X-rays are typically ordered to rule out the possibility of a fracture. Conversely, if the patient does not meet any of the criteria, X-rays are deemed unnecessary, and the patient is managed conservatively with appropriate symptomatic treatment and follow-up.
Significance of Ottawa Ankle Rules
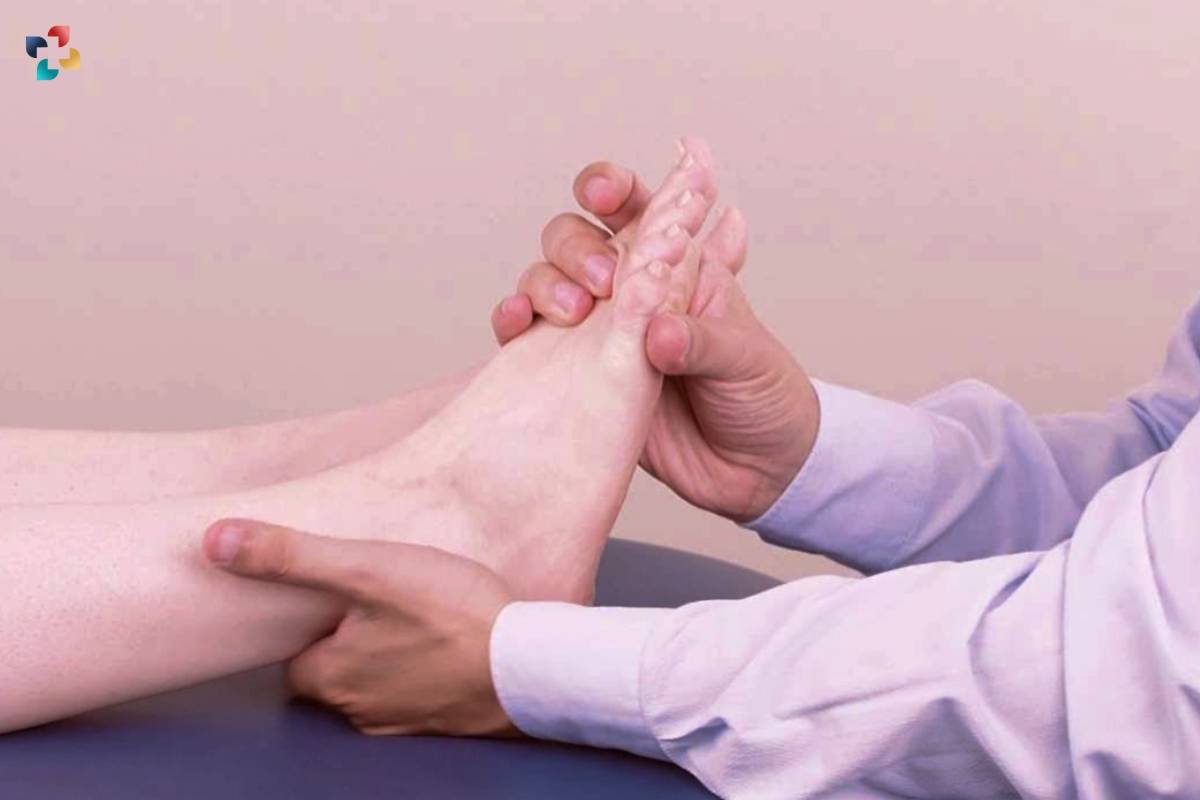
Ottawa Ankle Rules hold significant importance in clinical practice for several reasons. Firstly, they help healthcare providers identify patients at low risk of having ankle fractures, thereby reducing unnecessary radiation exposure and healthcare costs associated with imaging studies. Secondly, OAR facilitates timely decision-making, allowing providers to promptly initiate appropriate treatment and referral for patients with suspected fractures. Moreover, by standardizing the assessment of ankle injuries, (OAR) contributes to consistency and accuracy in clinical practice, ensuring optimal patient care and outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Ottawa Ankle Rules are valuable clinical decision guidelines used to assess ankle injuries and determine the need for X-ray imaging. By applying specific criteria related to the mechanism of injury and clinical findings, healthcare providers can effectively identify patients who require further evaluation for possible fractures. Ottawa Ankle Rules promote efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness in the diagnosis and management of ankle injuries, ultimately enhancing patient care and outcomes. As such, they remain an indispensable tool in the armamentarium of healthcare professionals involved in the evaluation and treatment of ankle injuries.
FAQs
1. What are Ottawa Ankle Rules?
Ottawa Ankle Rules are clinical decision guidelines used by healthcare professionals to determine whether a patient with an ankle injury requires X-rays for further evaluation. These rules help identify individuals at low risk of significant ankle fractures, thus reducing unnecessary imaging studies.
2. Who developed Ottawa Ankle Rules?
Ottawa Ankle Rules were developed by Dr. Ian Stiell and colleagues in Ottawa, Canada, in 1992. They were created to address the need for standardized criteria to guide the use of X-rays in ankle injury assessment.
3. What criteria are included in Ottawa Ankle Rules?
Ottawa Ankle Rules consist of specific criteria that healthcare providers assess during a physical examination of the ankle. These criteria include pain in the malleolar zone (medial or lateral aspect of the ankle), inability to bear weight immediately after the injury, and tenderness over the posterior edge or tip of the lateral malleolus or medial malleolus.
4. Why are Ottawa Ankle Rules important?
Ottawa Ankle Rules are important because they help reduce unnecessary radiation exposure from X-rays and decrease healthcare costs associated with imaging studies. By accurately identifying patients who are unlikely to have significant ankle fractures, these rules streamline patient care and resource allocation.
5. How accurate are Ottawa Ankle Rules?
Ottawa Ankle Rules have been extensively validated through research and clinical practice, demonstrating high sensitivity and specificity in identifying ankle fractures. Studies have shown that adherence to these rules can significantly reduce the number of unnecessary X-rays ordered for ankle injuries while maintaining patient safety and quality of care.