1. Largest Model Trained On Echocardiography Images Assesses Heart Structure and Function
Data Collection:
- Aggregated over 1,000,000 cardiac ultrasound videos with expert interpretations.
- Dataset encompasses diverse cardiac conditions for robust training.
EchoCLIP Development:
- Engineered by Cedars-Sinai’s expert team.
- Empowered to deliver clinician-level evaluations and device identification.
- Enables patient tracking across multiple videos, capturing evolving heart conditions.
Key Features:
- Provides preliminary cardiac assessments quickly.
- Monitors longitudinal changes in heart health.
- Identifies existing cardiac conditions accurately.
- Recognizes implanted devices such as pacemakers and repaired valves.
- Offers automated text interpretations for enhanced clinical insights.
Performance:
- Demonstrates remarkable accuracy in cardiac function assessment.
- Effectively differentiates individual patients across disparate studies.
- Detects critical clinical changes, including post-surgical variations.
Significance:
- Represents the largest model trained on echocardiography images to date.
- Highlights the transformative potential of extensive datasets in refining medical AI models.
- Redefines echocardiogram analysis through the integration of generative AI, promising enhanced diagnostic capabilities.
Conclusion:
EchoCLIP represents a paradigm shift in echocardiogram interpretation, driven by cutting-edge AI technology and extensive dataset utilization. Its development marks a milestone in cardiac care, promising unmatched accuracy, efficiency, and depth in assessing heart health. As EchoCLIP undergoes further validation and integration into clinical practice, it holds the potential to revolutionize cardiac diagnostics, improve patient outcomes, and empower healthcare providers with advanced tools for comprehensive cardiovascular care.
2. GPT-4, Google Gemini Fall Short in Breast Imaging Classification
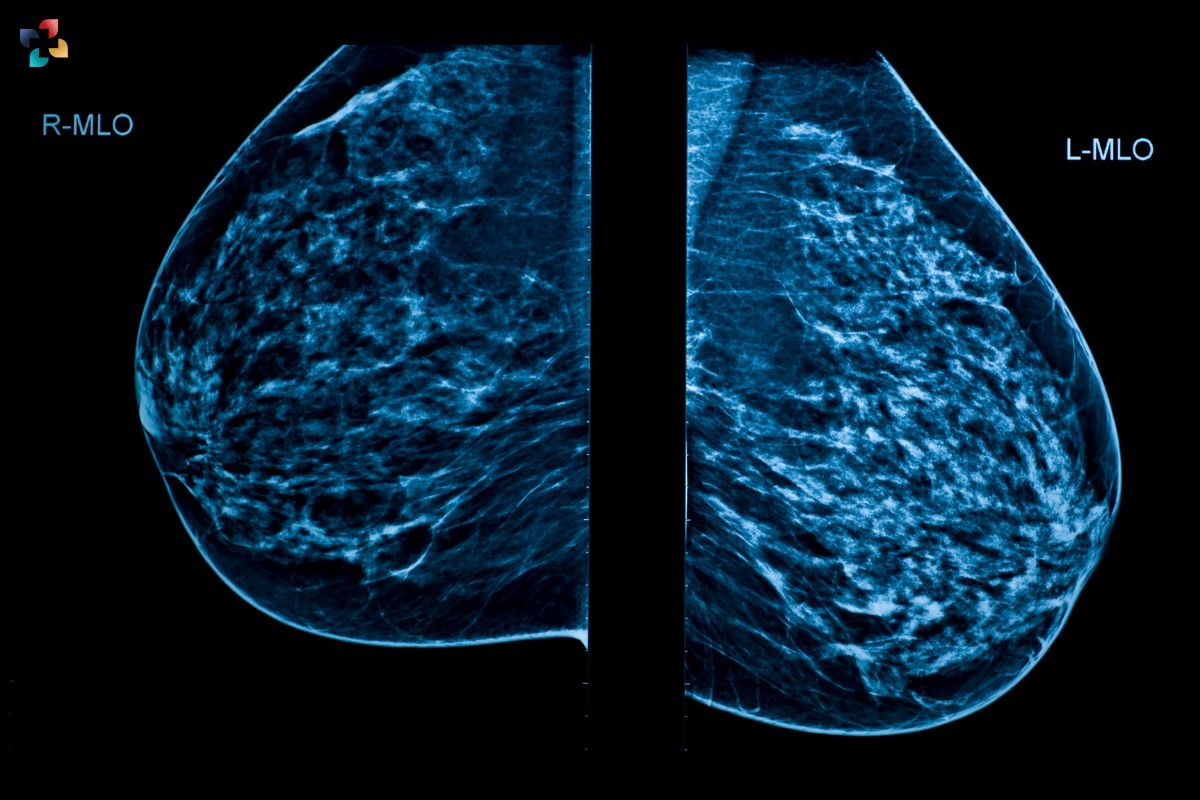
Study Objective:
- Assess the agreement between human radiologists and LLMs in categorizing Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) classifications.
Participants:
- Collaborative research conducted by teams from Switzerland, the United States, and the Netherlands.
- Analysis of 2,400 breast imaging reports in English, Italian, and Dutch.
Methodology:
- Evaluation of three LLMs: GPT-3.5, GPT-4, and Google Gemini (formerly Bard).
- LLMs assigned BI-RADS categories based on original radiologists’ reports.
Findings:
- Human-human agreement on BI-RADS categories approached perfection.
- Moderate agreement observed between humans and LLMs.
- Significant discordance in category assignments by LLMs, potentially impacting patient management decisions negatively.
Implications:
- Need for regulatory oversight of LLMs in healthcare applications.
- Raises caution regarding excessive reliance on LLMs for clinical decision-making.
- Emphasizes the importance of patient awareness regarding LLM limitations and potential consequences in healthcare.
Conclusion:
The study highlights the critical importance of carefully evaluating the role of Large Language Models (LLMs) in medical decision-making, particularly in the context of breast imaging report classification. While LLMs offer potential benefits in healthcare, their slight agreement with human experts and propensity for discordant category assignments showcase the necessity for regulatory oversight and informed use. As we navigate the integration of LLMs into clinical practice, it’s important to prioritize patient safety, maintain awareness of LLM limitations, and ensure that expert medical judgment remains paramount in healthcare decision-making processes.
3. Interventional Radiology’s Role in Obstetrics and Gynecology
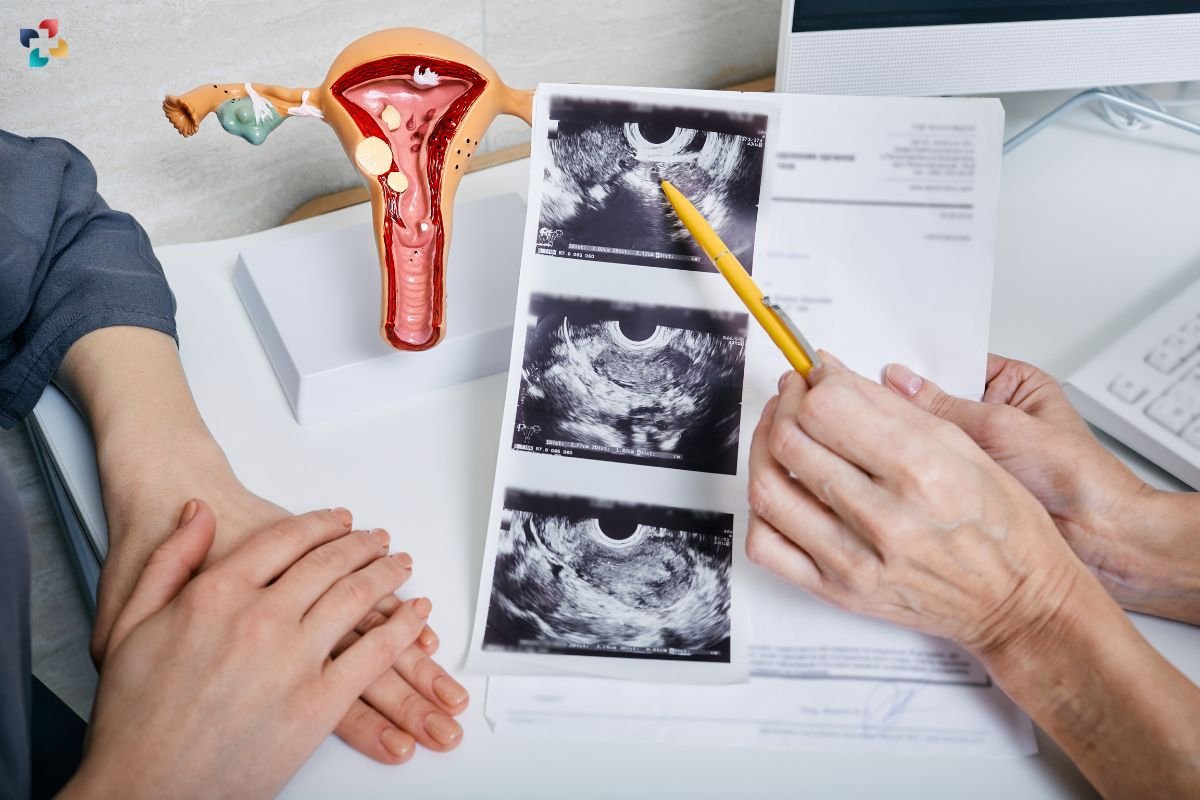
Pelvic Venous Disease (PeVD) Management:
- Interventional radiology (IR) offers personalized endovascular treatments for PeVD, including gonadal vein embolization and venous stent placement.
- Planned treatment approaches based on individual patient symptoms and underlying pathophysiology.
Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE):
- UAE serves as a minimally invasive alternative for managing symptomatic fibroids, preserving uterine function.
- Notable reduction in fibroid size and associated symptoms observed.
- Emerging as a potential treatment modality for adenomyosis.
IR in Obstetrics:
- IR presents effective solutions for managing high-risk bleeding conditions in obstetric patients.
- UAE emerges as a viable alternative to hysterectomy for conditions like postpartum hemorrhage and placenta accreta spectrum.
- Endovascular techniques, including occlusion balloons and embolization, demonstrate significant reductions in blood loss and adverse events.
Patient Education and Awareness:
- IR procedures for women’s health can be performed on an outpatient basis under conscious sedation.
- Limited patient awareness hampers global adoption of UAE and other IR treatments.
- Enhanced referral networks and collaborative efforts needed to improve access to IR services.
Conclusion:
Interventional Radiology (IR) advancements in women’s health offer personalized solutions for conditions like pelvic venous disease and fibroids. These minimally invasive procedures preserve uterine function while reducing symptoms and improving patient outcomes. Despite their effectiveness, increased patient education and collaboration among healthcare providers are needed to enhance awareness and access to IR services.
4. Dietary changes may treat pulmonary hypertension
Understanding Pulmonary Hypertension (PH):
- PH involves the progressive stiffening of lung blood vessels, leading to chronic lung disease, heart failure, and mortality.
- Conventional treatments address symptoms, yet the underlying mechanisms remained elusive until recent breakthroughs.
Discovery of Amino Acid Metabolism:
- Dr. Stephen Chan’s team uncovered that hypertensive pulmonary blood vessel cells exhibit an elevated demand for amino acids glutamine and serine.
- Metabolism of these amino acids triggers collagen overproduction, culminating in vessel stiffening and functional impairment.
Implications for Treatment:
- Targeting cellular uptake of glutamine and serine with specific drugs curtails excess collagen synthesis in PH rodent models.
- Dietary modifications, reducing intake of glutamine- and serine-rich foods, offer a promising adjunctive therapy to existing medications.
Innovative Diagnostic Tools:
- Dr. Chan’s group pioneered a novel PET scan-based diagnostic test for PH, utilizing a glutamine imaging tracer.
- This innovative approach enables early disease detection and facilitates treatment monitoring by visualizing amino acid metabolism in lung blood vessel cells.
Conclusion:
Understanding the pivotal role of amino acid metabolism in pulmonary hypertension offers promising avenues for innovative therapeutic interventions and diagnostic advancements. Dr. Stephen Chan’s research not only sheds light on the underlying mechanisms driving this condition but also opens new possibilities for personalized treatment strategies and early disease detection. With continued exploration in this field, we are moving closer to transforming the management of pulmonary hypertension and improving patient outcomes.