Regarding health concerns related to the urinary system or kidneys, it’s essential to understand the difference between a nephrologist and a urologist. While both specialists deal with similar body parts, their expertise varies significantly. In this blog, we’ll explore the role of each, their specific focus areas, and when you should consult one over the other. Let’s understand the key differences between a nephrologist vs urologist so that you can choose the right one for your health needs.
What is a Nephrologist?
A nephrologist is a medical doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating kidney-related diseases. The primary focus of nephrology is on kidney function and issues that affect how the kidneys filter waste and manage bodily fluids. Nephrologists are concerned with disorders such as:
- Chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- Kidney failure or end-stage renal disease (ESRD)
- Glomerular diseases (e.g., glomerulonephritis)
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Hypertension (especially if it’s linked to kidney problems)
- Kidney stones (usually once the condition progresses)
Education and Training of a Nephrologist:
To become a nephrologist, a physician first completes a residency in internal medicine followed by a fellowship in nephrology, typically taking around 6-8 years after medical school. During their training, nephrologists focus on the medical (non-surgical) treatment of kidney conditions.
What is a Urologist?
A urologist is a medical doctor who specializes in treating diseases and disorders of the urinary tract in both men and women, as well as the male reproductive system. Urologists handle issues like:
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Bladder and kidney stones
- Prostate disorders (enlarged prostate, prostate cancer)
- Male infertility
- Erectile dysfunction
- Incontinence
- Cancers of the urinary tract (bladder, kidney)
Education and Training of a Urologist:
Urologists typically complete a residency in urology after medical school, lasting about 5-6 years. Their training focuses on both medical and surgical treatments of the urinary system and male reproductive organs. The below difference will give you more knowledge about the same.
| Criteria | Nephrologist | Urologist |
| Focus Area | Kidney function and diseases | Urinary system and male reproductive organs |
| Common Conditions Treated | Chronic kidney disease (CKD), kidney failure, electrolyte imbalances | Urinary tract infections (UTIs), bladder and prostate disorders, kidney stones |
| Medical Approach | Non-surgical (focuses on medical treatments) | Both medical and surgical treatments |
| Procedures Performed | Manages dialysis, kidney transplant care, and medication management | Performs surgeries like kidney stone removal, prostate surgery, vasectomy |
| Diagnostic Tools | Blood tests, urine tests, kidney biopsies, imaging studies | Cystoscopy, urodynamic testing, imaging studies |
| Specialized Training | Internal medicine followed by a nephrology fellowship | Urology residency focusing on both medical and surgical aspects |
| Conditions Managed | Kidney failure, electrolyte imbalances, hypertension related to kidneys | UTIs, prostate issues, kidney and bladder stones, male infertility |
| When to See | If you have CKD, need dialysis, kidney transplant, or severe hypertension | If you have urinary tract infections, bladder or kidney stones, or reproductive issues |
| Treatment Methods | Medication, lifestyle changes, dialysis | Medication, surgery, and minimally complicated procedures |
When to See a Nephrologist vs Urologist?
Deciding whether to see a nephrologist vs urologist depends on your symptoms and medical condition.
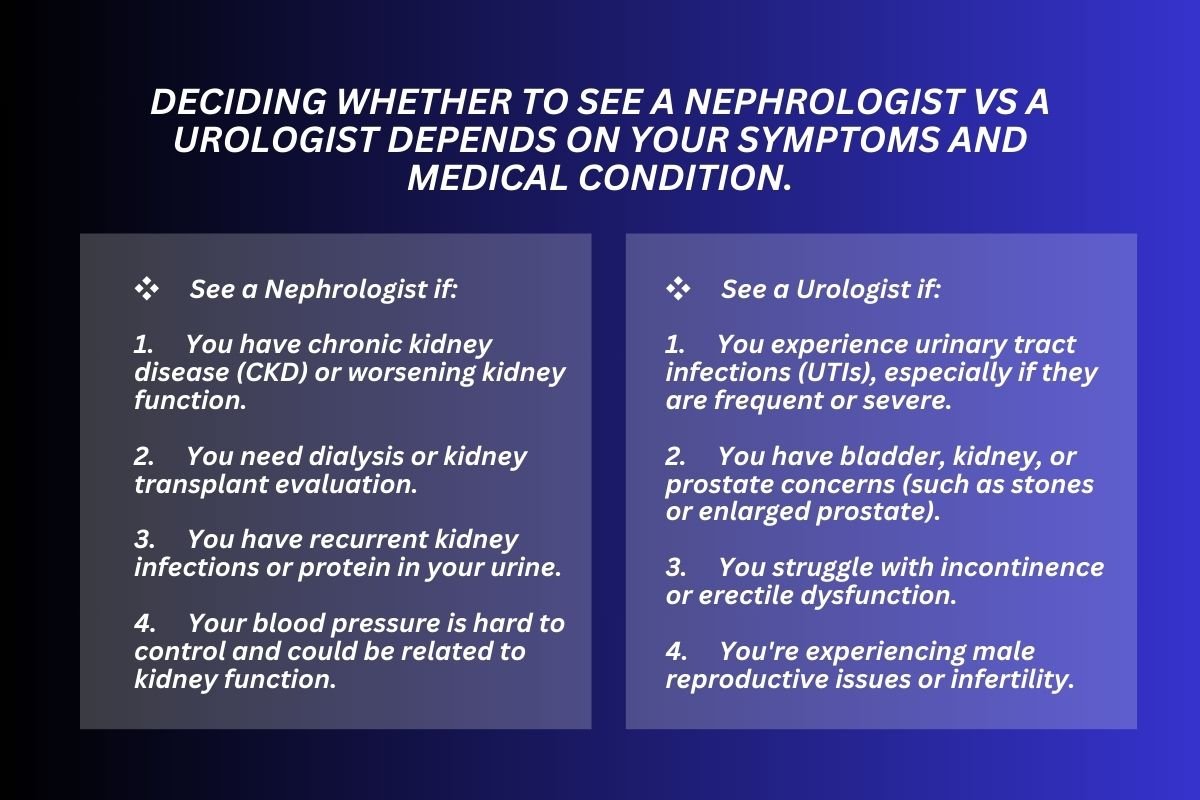
1. See a Nephrologist if:
- You have chronic kidney disease (CKD) or worsening kidney function.
- You need dialysis or kidney transplant evaluation.
- You have recurrent kidney infections or protein in your urine.
- Your blood pressure is hard to control and could be related to kidney function.
2. See a Urologist if:
- You experience urinary tract infections (UTIs), especially if they are frequent or severe.
- You have bladder, kidney, or prostate concerns (such as stones or enlarged prostate).
- You struggle with incontinence or erectile dysfunction.
- You’re experiencing male reproductive issues or infertility.
Intersect Between Nephrology and Urology
While the focus of a nephrologist vs urologist differs, there are cases where both specialists may work together. For example:
- Kidney Stones: A nephrologist may initially manage a patient with kidney stones by addressing the underlying cause (e.g., metabolic issues). If surgery is needed to remove the stones, a urologist will take over.
- Kidney Transplants: A nephrologist will manage post-transplant care, but a urologist might be involved in the surgical aspects of kidney transplantation.
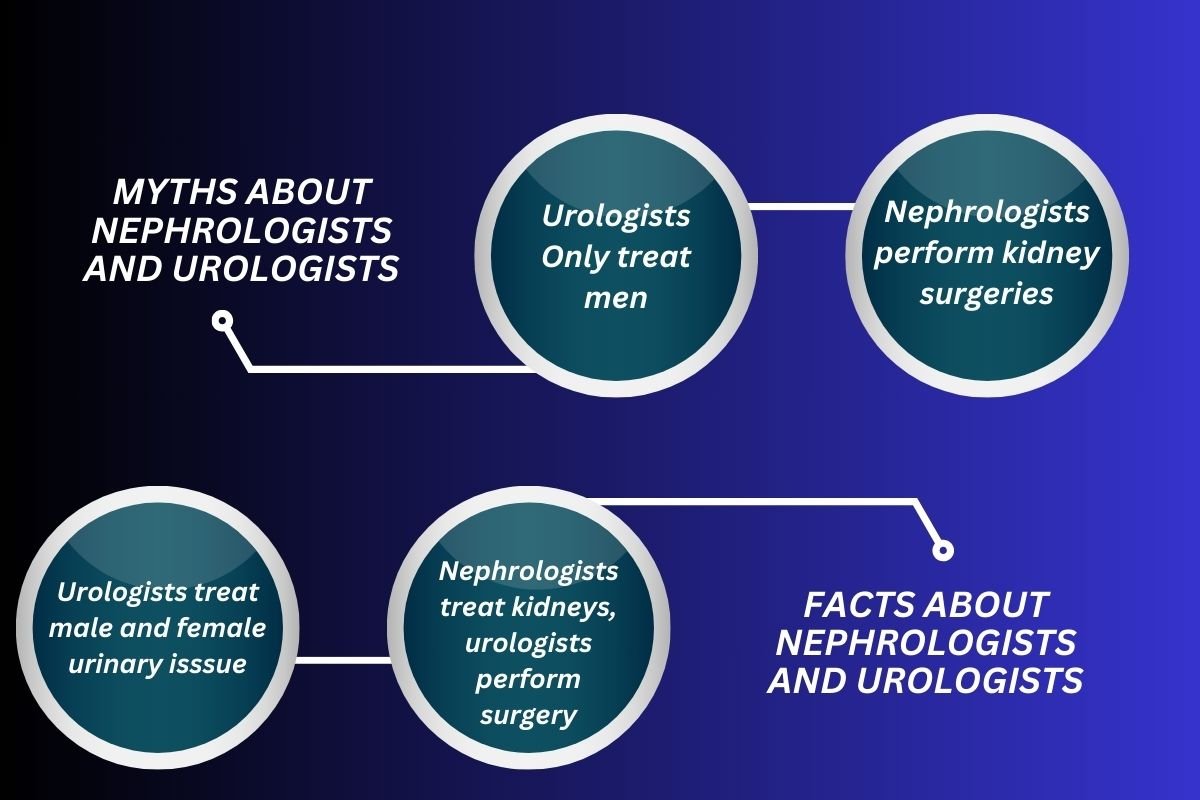
Common Myths About Nephrologists and Urologists
Conclusion
It is necessary to understand the difference between a nephrologist and vs urologist to receive the right care. Nephrologists focus on kidney function and treating kidney-related diseases through non-surgical methods, while urologists handle both medical and surgical issues involving the urinary system and male reproductive organs. The expertise of each specialist can significantly improve your health, especially for conditions involving the kidneys and urinary system.