The term “gluten-free diet” has become more and more common in conversations about health and wellness in recent years. Knowing the foundations of a gluten-free diet is essential, regardless of whether you have personally adopted this dietary lifestyle or know someone who has. We’ll examine the complexities of gluten in this post, as well as the rationale behind being gluten-free, and offer helpful advice for anyone thinking about or already using this dietary strategy.
Understanding Gluten
Gluten is a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. It serves as a binding agent, giving elasticity to dough and contributing to the chewy texture of bread and other baked goods. While gluten is harmless for most people, individuals with celiac disease, wheat allergy, or gluten sensitivity must strictly avoid it.
Celiac Disease and Gluten Sensitivity
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder characterized by the body’s adverse reaction to gluten consumption. When individuals with celiac disease ingest gluten, their immune system mistakenly attacks the small intestine, leading to inflammation and damage. Gluten sensitivity, on the other hand, is a less severe condition where individuals experience gastrointestinal symptoms, fatigue, and other issues after consuming gluten, but without the autoimmune response seen in celiac disease.
Wheat Allergy

Wheat allergy is an allergic reaction to proteins found in wheat, including but not limited to gluten. Unlike celiac disease and gluten sensitivity, which involve the immune system, wheat allergy triggers an allergic response, ranging from mild symptoms like itching and hives to severe reactions such as anaphylaxis.
Reasons for Adopting a Gluten-Free Diet
People choose to follow a gluten-free diet for various reasons, including medical conditions, perceived health benefits, and lifestyle choices.
Celiac Disease Management
For individuals with celiac disease, a gluten-free diet is the only effective treatment. By eliminating gluten-containing foods, they can alleviate symptoms, promote healing of the small intestine, and prevent long-term complications.
Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity
Some individuals experience symptoms similar to those of celiac disease without having the autoimmune response. Adopting a gluten-free diet can help manage these symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Wheat Allergy Management
Those diagnosed with wheat allergy must avoid all forms of wheat, including gluten-containing products. A gluten-free diet is essential for preventing allergic reactions and ensuring optimal health.
Cross-Contamination Awareness
In addition to strict avoidance of wheat and gluten-containing products, individuals with wheat allergies must remain vigilant about cross-contamination. Shared cooking surfaces, utensils, and even airborne wheat particles during food preparation can pose a risk. It is advisable to thoroughly clean and sanitize kitchen equipment after each use and to use separate cooking tools and cutting boards to prevent inadvertent exposure to wheat allergens.
Hidden Sources of Wheat
Navigating a wheat-free lifestyle also involves being aware of potential hidden sources of wheat in various food products. Ingredients such as modified food starch, hydrolyzed vegetable protein, and certain food additives may contain wheat derivatives. Reading labels meticulously and staying informed about alternative names for wheat-derived ingredients is crucial in maintaining a wheat-free diet.
Nutritional Considerations
Eliminating wheat from the diet may result in a reduction of certain nutrients. Whole grains, a common source of fiber, vitamins, and minerals, are often found in wheat-containing products. Individuals with wheat allergies should work closely with healthcare professionals or dietitians to ensure they maintain a well-balanced diet, possibly incorporating alternative grains and nutrient-rich foods to compensate for any nutritional gaps that may arise due to the dietary restrictions imposed by a wheat allergy.
Educating Others
Living with a wheat allergy necessitates not only personal vigilance but also the education of friends, family, and coworkers about the severity of the condition. Creating awareness about the potential dangers of wheat exposure and the importance of maintaining a gluten-free lifestyle is crucial for building a supportive network. This proactive approach helps prevent accidental exposure, as those around the affected individual can better understand and accommodate their dietary needs.
In essence, managing a wheat allergy extends beyond the mere avoidance of wheat-containing foods. It involves a comprehensive approach that considers potential cross-contamination, hidden sources of wheat, nutritional balance, and community awareness. By staying informed and proactive, individuals with wheat allergies can lead a healthy and fulfilling life while minimizing the risk of allergic reactions.
Perceived Health Benefits
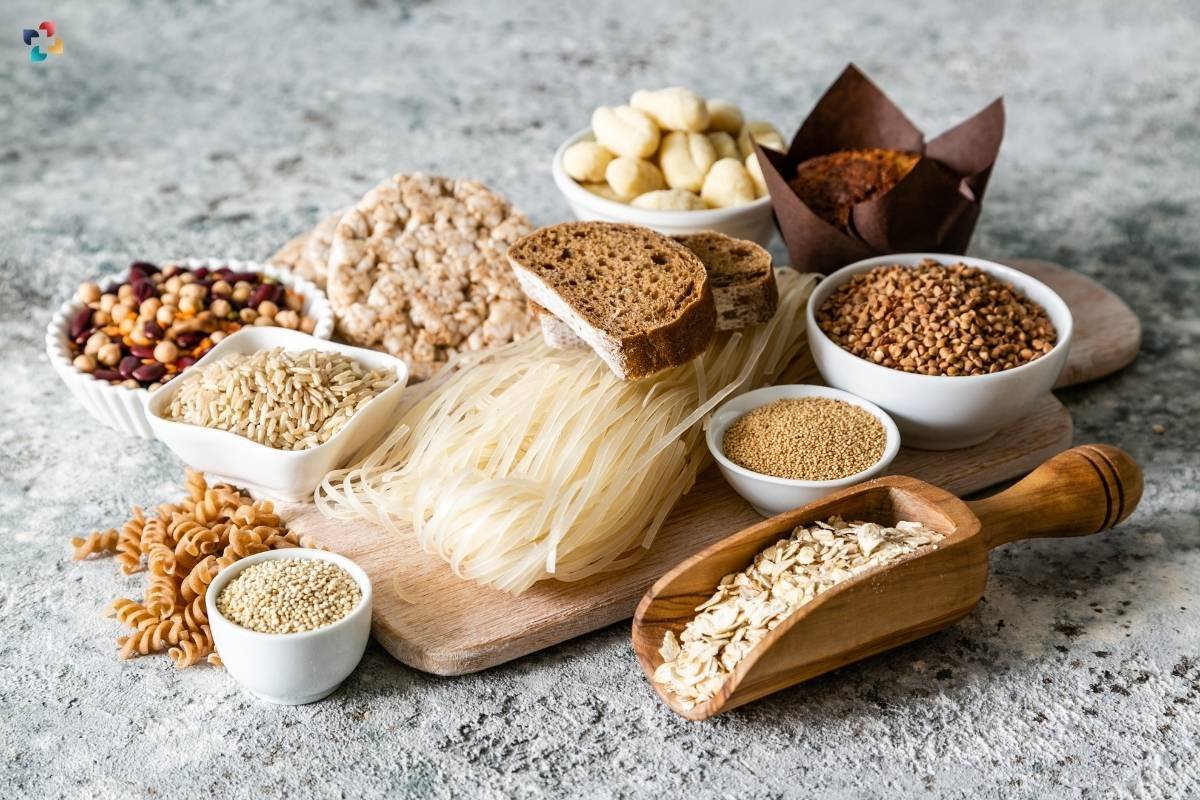

Beyond medical necessity, some people choose a gluten-free diet for perceived health benefits. Claims of increased energy, improved digestion, and weight loss are often associated with gluten elimination, although scientific evidence supporting these claims is limited.
Practical Tips for a Gluten-Free Lifestyle
Adopting a gluten-free diet requires careful consideration of food choices, label reading, and dining-out strategies. Here are some practical tips to help navigate a gluten-free lifestyle successfully.
Educate Yourself on Gluten-Free Foods
Familiarize yourself with naturally gluten-free foods, such as fruits, vegetables, meat, fish, dairy, and gluten-free grains like rice and quinoa. Being aware of these options can make meal planning easier and more diverse.
Read Labels Thoroughly
Gluten can hide in unexpected places, such as sauces, dressings, and processed foods. When grocery shopping, carefully read labels to identify gluten-containing ingredients like wheat, barley, and rye. Many products are now labeled explicitly as gluten-free, simplifying the selection process.
Explore Gluten-Free Alternatives
Fortunately, the rise in gluten-free awareness has led to a plethora of gluten-free alternatives. From gluten-free flours and pasta to bread and snacks, there are numerous options available. Experiment with different products to find those that suit your taste and dietary preferences.
Communicate Clearly when Dining Out

When dining out, communicate your dietary needs clearly to the restaurant staff. Ask about gluten-free options and inquire about food preparation methods to ensure cross-contamination is avoided. Many restaurants now offer gluten-free menus, making it easier for those with dietary restrictions to enjoy a diverse dining experience.
Create a Supportive Environment
If you’re adopting a gluten-free diet due to medical reasons, it’s essential to create a supportive environment. Educate friends and family about your dietary needs, and encourage open communication to avoid unintentional gluten exposure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the management of celiac disease, gluten sensitivity, and wheat allergy have made the gluten-free diet quite popular. People are investigating this nutritional strategy to enhance their health and well-being, whether out of necessity or choice. People may make more informed food decisions if they are aware of the basics of gluten, the benefits of switching to a gluten-free diet, and useful advice for adjusting to this way of life. It’s important to speak with healthcare providers for individualized guidance and support on your road to a gluten-free lifestyle, just like with any major dietary change.
Also Read: 7 Advantages of a Gluten-free Diet Plan