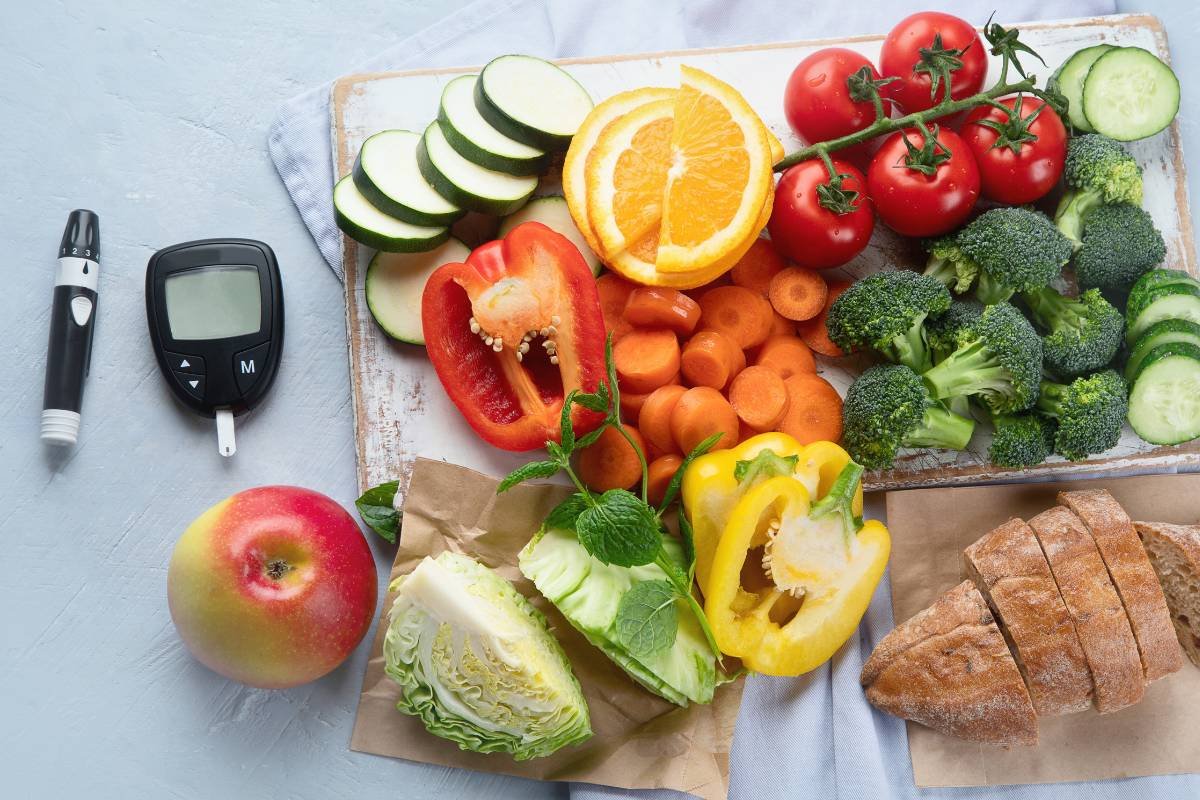
Understanding how various foods affect blood glucose levels is now more important for managing diabetes than simply avoiding sugar. The Low-carb Diet for Diabetes is one of the most talked-about dietary strategies nowadays. This eating pattern emphasizes eating more foods high in fiber, protein, and healthy fats while consuming fewer carbohydrates. Low-carb diets have become a potent tool for maintaining long-term metabolic health, enhancing insulin sensitivity, and stabilizing blood sugar thanks to mounting clinical evidence.
This guide describes the benefits of a low-carb diet for people with diabetes, what foods to eat and avoid, and how to follow it safely.
Understanding Diabetes and Carbohydrates
Diabetes, whether type 1 or type 2, involves impaired insulin function. Carbohydrates directly impact blood sugar because they are broken down into glucose during digestion. Foods high in refined carbs, such as white bread, sweets, sugary drinks, and processed snacks, cause rapid glucose spikes.
A low-carb approach limits these spikes by reducing the body’s reliance on glucose as a primary energy source. This is why many healthcare professionals now recommend carbohydrate moderation as part of diabetes management.
How a Low-Carb Diet Works
A low-carb diet typically restricts daily carbohydrate intake to anywhere between 20 and 130 grams, depending on individual needs. Instead of carbs, calories come from:
- Lean proteins
- Healthy fats
- Non-starchy vegetables
By lowering carb intake, the body requires less insulin to manage blood sugar levels. Over time, this can lead to improved insulin sensitivity, making glucose control easier.
For many individuals, adopting a Low-carb Diet for Diabetes results in more stable energy levels, fewer glucose fluctuations, and improved HbA1c readings.
Key Benefits of a Low-Carb Diet for Diabetes
1. Improved Blood Sugar Control
Lower carb intake directly reduces post-meal blood glucose spikes, making daily readings more predictable and manageable.
2. Reduced Medication Dependence
Some people with type 2 diabetes experience reduced reliance on insulin or oral medications under medical supervision.
3. Weight Management
Low-carb diets often lead to natural calorie reduction, helping with weight loss, a critical factor in improving insulin resistance.
4. Better Heart Health
When focused on healthy fats, a low-carb diet can improve triglyceride levels and increase HDL (good cholesterol).
Foods to Eat on a Low-Carb Diet

Choosing the right foods is essential for success.
Protein Sources
- Eggs
- Fish (salmon, sardines, tuna)
- Chicken and turkey
- Tofu and paneer
Healthy Fats
- Olive oil
- Avocados
- Nuts and seeds
- Coconut oil (in moderation)
Low-Carb Vegetables
- Spinach
- Broccoli
- Cauliflower
- Zucchini
- Bell peppers
These foods help keep meals satisfying without causing glucose spikes, making the Low-carb Diet for Diabetes. Sustainable and nutrient-dense.
Foods to Limit or Avoid

To maintain stable blood sugar levels, it’s best to reduce or eliminate:
- White rice and refined grains
- Sugary beverages
- Pastries and desserts
- Packaged snacks
- Fruit juices
While whole fruits are nutritious, some high-sugar fruits should be consumed in moderation.
Read More:
- Transform Your Body and Mind with the Health Benefits of a Low-Carb Diet
- Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Transform Your Health with This Low-Carb Diet Meal Plan
Is a Low-Carb Diet Safe for Everyone?
For most people with type 2 diabetes, a low-carb diet is safe and effective when properly planned. However, individuals with type 1 diabetes or those on insulin must monitor blood sugar closely to avoid hypoglycemia.
Consulting a healthcare provider or registered dietitian is strongly recommended before starting a Low-carb Diet for Diabetes. This ensures nutritional adequacy and safe medication adjustments.
Common Myths About Low-Carb Diets
Myth 1: Low-carb means no carbs

Reality: Most plans allow non-starchy vegetables and small portions of complex carbs.
Myth 2: It’s too high in fat
Reality: A healthy low-carb diet emphasizes unsaturated fats, not processed or trans fats.
Myth 3: It’s unsustainable
Reality: With proper planning and variety, many people follow low-carb diets long term without feeling deprived.
Tips for Long-Term Success
- Track blood sugar regularly
- Focus on whole, unprocessed foods
- Stay hydrated
- Don’t skip fiber; vegetables are essential
- Adjust gradually rather than cutting carbs abruptly
Consistency is more important than perfection. Small, steady changes lead to lasting results.
Conclusion:
When it comes to managing diabetes, a well-planned low-carb strategy can be revolutionary. The Low-carb Diet for Diabetes provides both immediate and long-term health benefits by lowering glucose fluctuations, helping with weight control, and improving insulin sensitivity.
Customization and medical advice are essential, just like with any dietary modification. When implemented properly, this strategy enables people to manage their blood sugar levels one meal at a time.