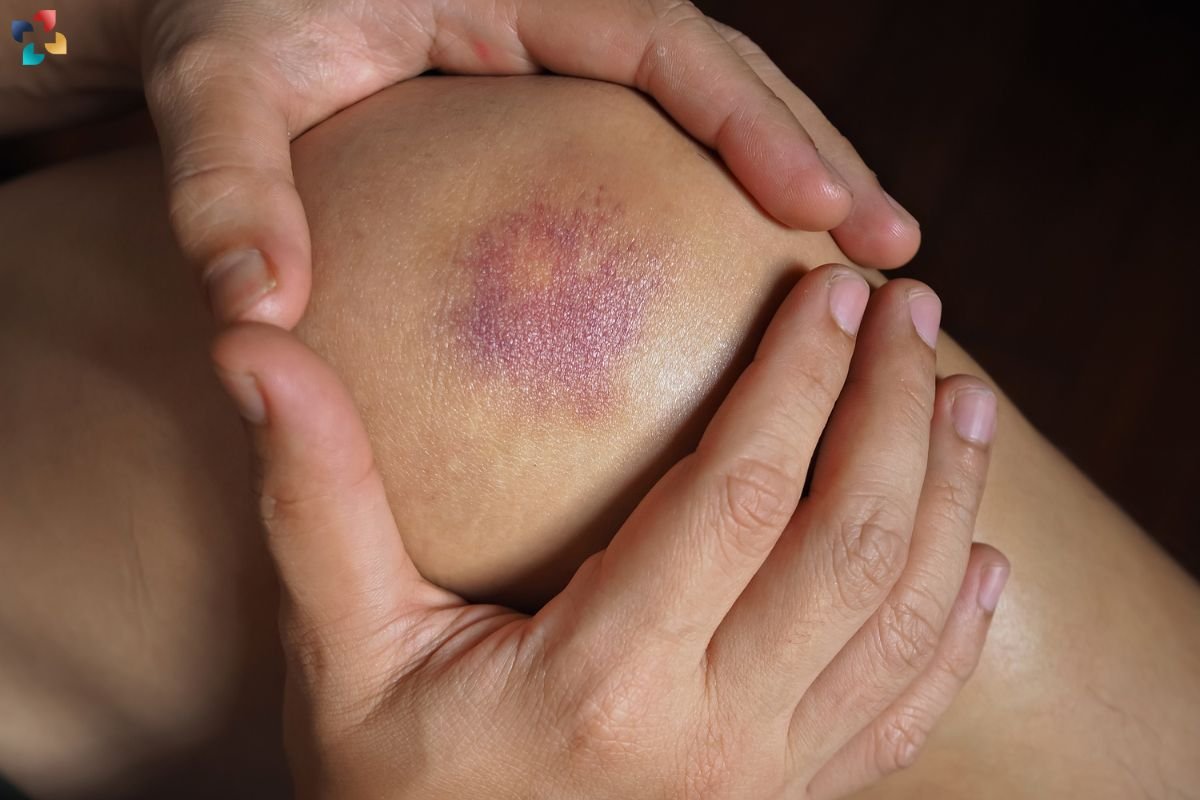
A knee contusion, commonly known as a bruise, is an injury to the knee that can range from mild to severe. Whether it results from a sports injury, a fall, or a direct impact, a knee contusion can cause significant pain and discomfort. Understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and recovery process is crucial for managing this condition effectively. This comprehensive guide will delve into everything you need to know about knee contusions.
What is a Knee Contusion?
It is a type of bruise that occurs when blood vessels under the skin are damaged due to a direct blow or impact to the knee. This trauma causes blood to leak into the surrounding tissues, leading to swelling, discoloration, and pain. While it might seem minor compared to more severe knee injuries, it can still have a considerable impact on mobility and daily activities.
Causes of Knee Contusion
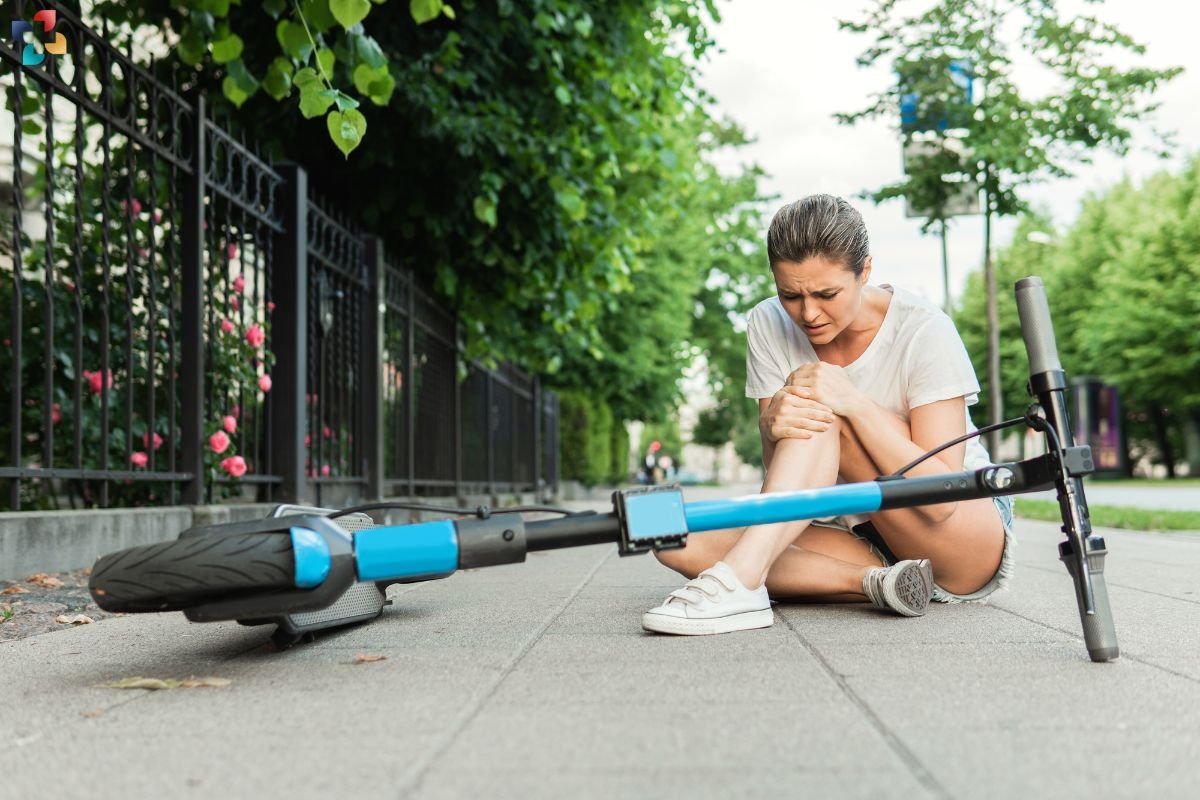

These are typically caused by a variety of factors:
- Sports Injuries: Contact sports like football, hockey, and basketball often involve physical collisions that can result in a knee contusion. A direct hit or tackle can lead to bruising.
- Accidents: Falls or accidents that involve a direct impact on the knee can cause a contusion. For instance, slipping on a wet surface or bumping into a hard object can result in this type of injury.
- Vehicle Accidents: Car accidents or collisions where the knee strikes the dashboard or steering wheel can lead to a knee contusion.
- Repeated Stress: Continuous pressure or repetitive movements, such as kneeling for long periods, can cause a contusion over time.
Symptoms of Knee Contusion
The symptoms of this can vary depending on the severity of the injury. Common symptoms include:
- Pain: Pain is typically localized to the area of impact and can range from mild to severe.
- Swelling: Swelling around the knee is common and can increase over time, depending on the extent of the bruising.
- Discoloration: The skin may change color, turning from red to purple or blue as the bruise develops.
- Tenderness: The affected area may be tender to the touch.
- Restricted Movement: In severe cases, the knee may become stiff, limiting the range of motion.
Diagnosis of Knee Contusion
To diagnose a knee contusion, a healthcare provider will typically perform a physical examination and ask about the mechanism of injury. They may also recommend imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRI, to rule out more serious injuries like fractures or ligament tears.
Treatment Options for Knee Contusion
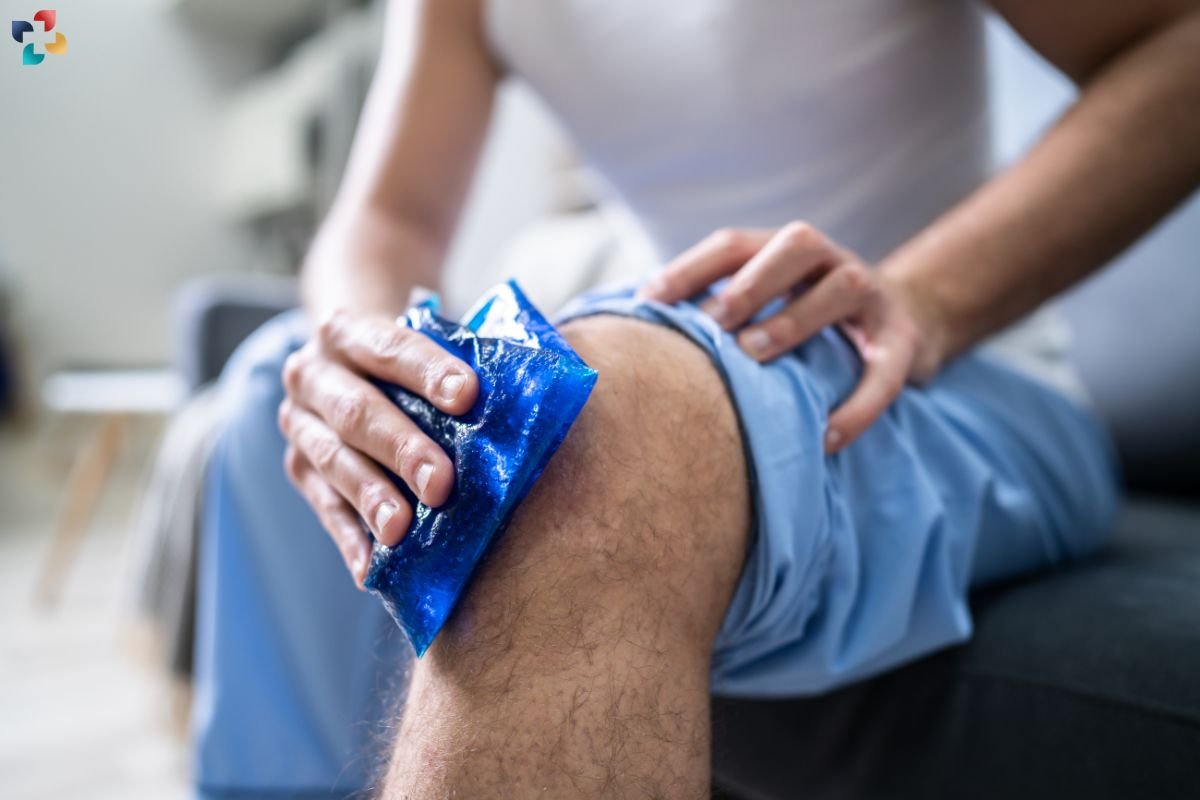
Treatment for a knee contusion primarily focuses on relieving pain, reducing swelling, and promoting healing. Here are some common treatment options:
1. Rest and Ice
Resting the affected knee and applying ice packs can help reduce pain and swelling. Ice should be applied for 15-20 minutes every 2-3 hours during the first 48 hours after the injury.
2. Compression
Using an elastic bandage or compression wrap can help control swelling. Ensure the wrap is snug but not too tight, as excessive compression can impair circulation.
3. Elevation
Elevating the knee above the level of the heart can help reduce swelling. This can be achieved by propping the leg up on pillows while resting.
4. Pain Relief
Over-the-counter pain medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and reduce inflammation. Always follow the dosage instructions and consult a healthcare provider if you have any concerns.
5. Physical Therapy
In cases of severe contusions or prolonged symptoms, physical therapy may be recommended. A physical therapist can guide exercises to improve strength and flexibility in the knee.
6. Avoiding Activity
Avoid activities that may aggravate the injury or cause further damage. Refrain from high-impact sports or strenuous movements until the knee has healed.

Does Your Pain Mean It’s Time for a Knee Replacement?
Knee replacement surgery, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a medical procedure where the damaged or worn surfaces of the knee joint are replaced with artificial materials.
Recovery and Prognosis
The recovery time for a knee contusion varies depending on the severity of the injury. Mild contusions may heal within a few weeks with proper care, while more severe cases may take longer. The following tips can help ensure a smooth recovery:
- Follow Medical Advice: Adhere to the treatment plan prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Gradual Return to Activity: Gradually resume activities and avoid rushing back into sports or physical activities.
- Monitor Symptoms: Keep an eye on your symptoms and seek medical attention if they worsen or if you experience new symptoms.
Prevention of Knee Contusions
While it may not be possible to prevent all this, you can reduce your risk by following these preventive measures:
- Wear Protective Gear: In sports or activities that involve physical contact, wear appropriate protective gear such as knee pads.
- Use Proper Technique: Ensure proper techniques and body mechanics during physical activities to minimize the risk of injury.
- Strengthen Muscles: Strengthening the muscles around the knee can help provide better support and reduce the risk of injury.
- Maintain Flexibility: Regular stretching and flexibility exercises can help keep the knee joint and surrounding muscles flexible and resilient.
When to See a Doctor?
While most knee contusions can be managed with self-care, it’s important to seek medical attention if:
- Severe Pain: The pain is intense or worsens over time.
- Significant Swelling: The swelling does not decrease or is accompanied by severe bruising.
- Inability to Move: You experience significant difficulty moving the knee or cannot bear weight.
- Symptoms Persist: Symptoms do not improve with standard treatment methods.
Conclusion
A knee contusion, though often less severe than other knee injuries, can still cause considerable discomfort and affect daily activities. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective management and recovery. By following the recommended treatment strategies and taking preventive measures, you can help ensure a smoother recovery and reduce the risk of future knee injuries. If symptoms persist or worsen, seeking medical attention is essential to rule out more serious conditions and receive appropriate care.