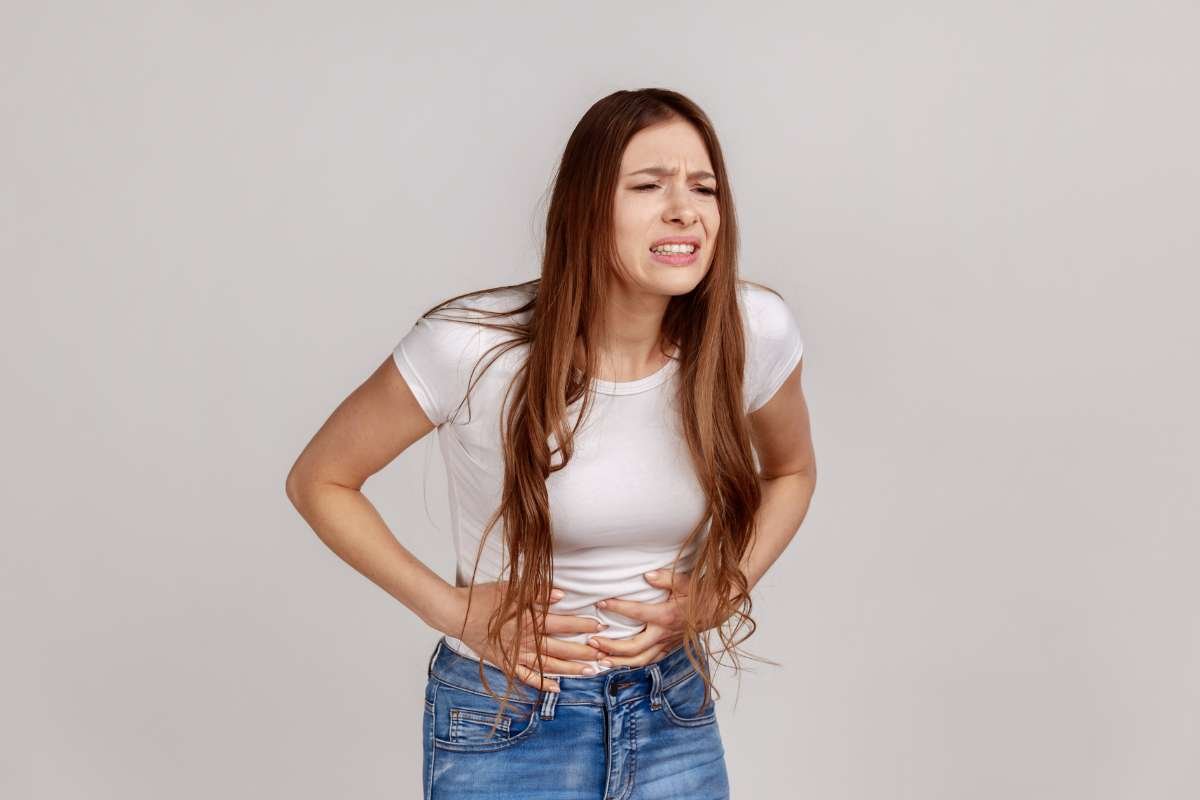
The knee joint is the hardest working joint in the human body. With this joint, you can do movements like running, walking, folding your knees, etc. It needs to be taken care of. Knee aches when climbing the stairs or sitting in one place for a long time lead to knee pain. Prolonged knee pain results in Osteoarthritis. The cartilage inside the knee acts as a lubricant between two bones. It helps the body to move the bones freely. The oily element in between these two bones starts to get dry as we age. It leads to the two bones crushing upon each other due to lack of oiliness.
In simple words, it is like oiling a noisy door or window. As soon as you put grease into the hinges, the sound disappears and the functioning smoothens. Similarly, humans need to have a physical workout routine to prevent the symptoms of osteoarthritis.
Understanding the Ideal Time for Knee Replacement
Knee replacement surgery, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a medical procedure where the damaged or worn surfaces of the knee joint are replaced with artificial materials. From a doctor’s perspective, determining the ideal time for knee replacement involves a careful assessment of the patient’s overall health, level of pain, and the impact of knee dysfunction on daily activities. It’s crucial to exhaust non-surgical treatments before considering surgery, as a knee replacement is a major procedure with a significant recovery period.
Knee Replacement: 5 Precautions for Managing Osteoarthritis Symptoms
Osteoarthritis is a common form of arthritis that primarily affects the joints. When symptoms of osteoarthritis begin to surface, there are several precautions doctors recommend to manage the condition effectively:

1. Pain Management
Over-the-counter pain relievers, prescribed medications, and topical creams can help alleviate pain and inflammation associated with osteoarthritis.
2. Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the stress on weight-bearing joints like the knees. Excess weight can exacerbate osteoarthritis symptoms and progression. Excessive weight is the main cause of knee damage and leads to knee replacement.
3. Physical Therapy
An under-rated field where different types of exercises are stretches with some medical equipment to help a person get rid of knee pain. It is a specialized field of work where properly studied exercise sessions are taken by a physical therapist. Engaging in targeted exercises can strengthen the muscles around the knee joint, improving stability and function while reducing pain.
4. Assistive Devices
The use of braces, canes, or other assistive devices can help alleviate pressure on the knees and improve mobility.
5. Lifestyle Modifications
Adjustments in daily activities, such as avoiding high-impact exercises and opting for low-impact activities like swimming, can significantly reduce knee discomfort.
The Role of Age in Osteoarthritis
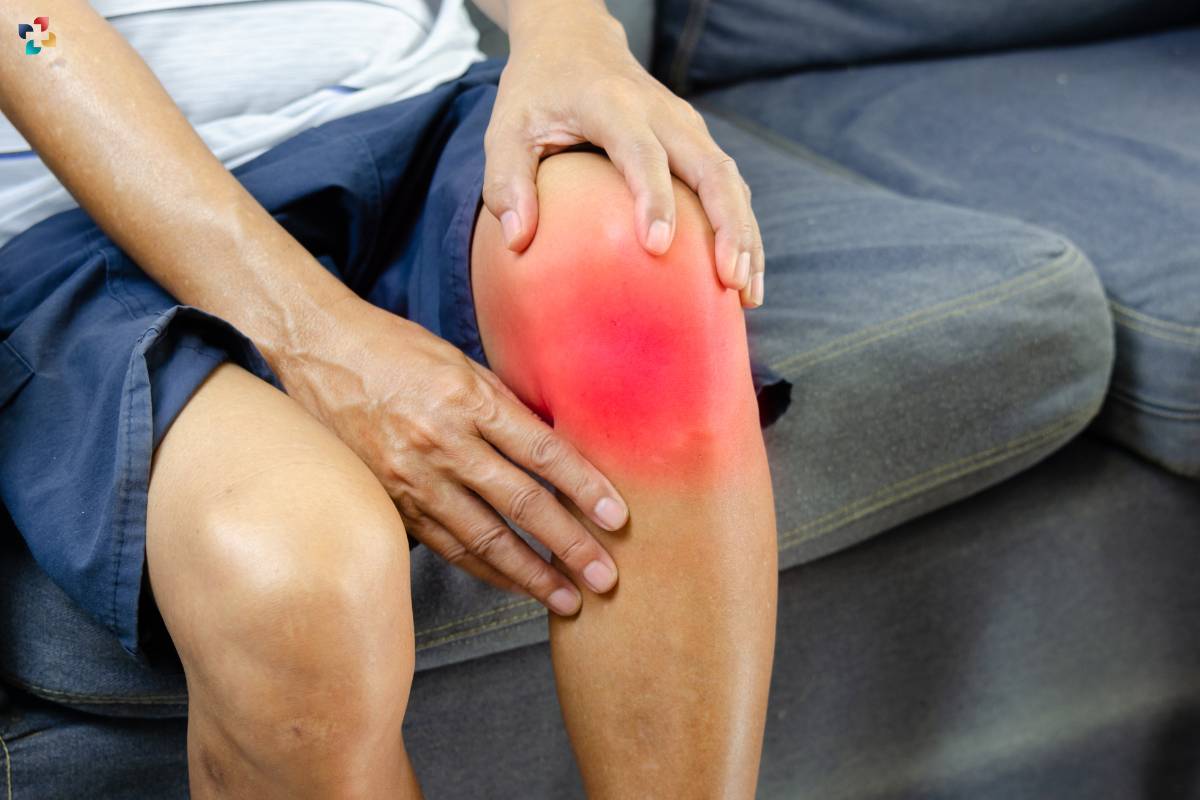
Age is a significant factor in the development of osteoarthritis, but it’s not the sole determinant. While it’s true that the risk of developing osteoarthritis increases with age due to the cumulative effects of joint use and natural degeneration, younger individuals can also experience this condition, particularly if they’ve experienced joint injuries or have a genetic predisposition. Therefore, age alone shouldn’t be the sole criterion for determining the need for knee replacement.
Recommended Frequency of Knee Check-ups
Regular check-ups play a vital role in the early detection and management of knee problems, including osteoarthritis. For individuals with a family history of osteoarthritis or those who engage in activities that put excessive strain on the knees, such as athletes, regular check-ups are even more important. Generally, it’s advisable to have a comprehensive knee assessment every one to two years, especially as you approach middle age and beyond.
Signs That Could Indicate Osteoarthritis
Detecting osteoarthritis in its early stages can prevent further joint damage and slow down its progression. Here are some signs to watch out for:
Joint Stiffness:
If you experience stiffness in your knees, especially in the morning or after prolonged periods of inactivity, it could be an early sign of osteoarthritis.
Pain and Swelling:
Persistent pain, swelling, or tenderness in the knee joint, especially after physical activity or extended periods of standing, might indicate the presence of osteoarthritis.
Crepitus:
This refers to a crunching or grinding sensation when moving the knee joint. Crepitus can be a result of the roughened cartilage surfaces rubbing against each other.
Limited Range of Motion:
Difficulty fully extending or bending your knee can be indicative of joint degeneration.
Weakness or Instability:
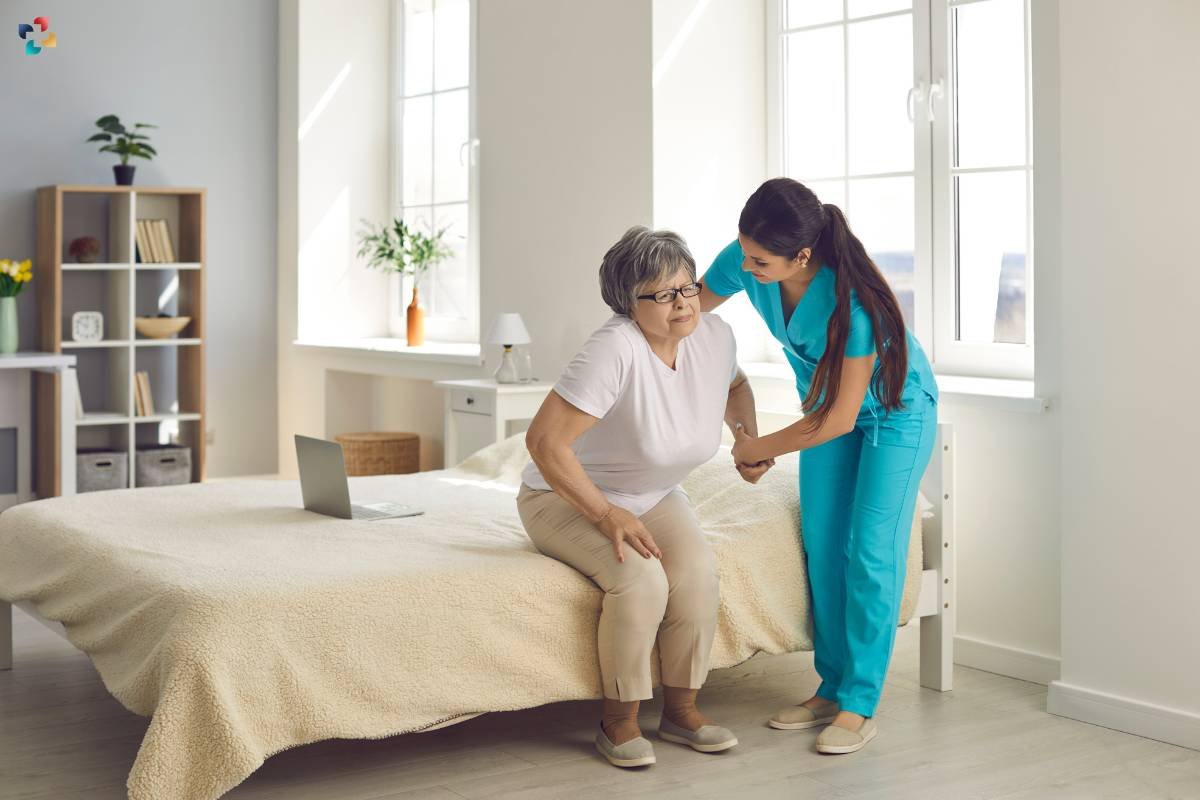

Osteoarthritis can lead to muscle weakness around the knee, causing instability and an increased risk of falls.
Progressive Nature:
Osteoarthritis tends to worsen gradually over time. If you notice that your knee pain and discomfort are worsening, it’s essential to seek medical advice.
Conclusion
In the complex realm of knee pain and osteoarthritis, the decision to undergo a knee replacement is not one to be taken lightly. From a doctor’s perspective, this choice hinges on a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s overall health, pain levels, and impact on daily life. While age is a factor in the development of osteoarthritis, it’s not the sole determinant and early detection and management are crucial. Regular knee check-ups can aid in identifying issues before they escalate, and understanding the signs of osteoarthritis empowers individuals to take proactive steps toward managing their knee health. Remember, the road to knee replacement should be navigated with care, consideration, and informed medical guidance.
Also Read: 8 Things We Learned About Fitness in 2023