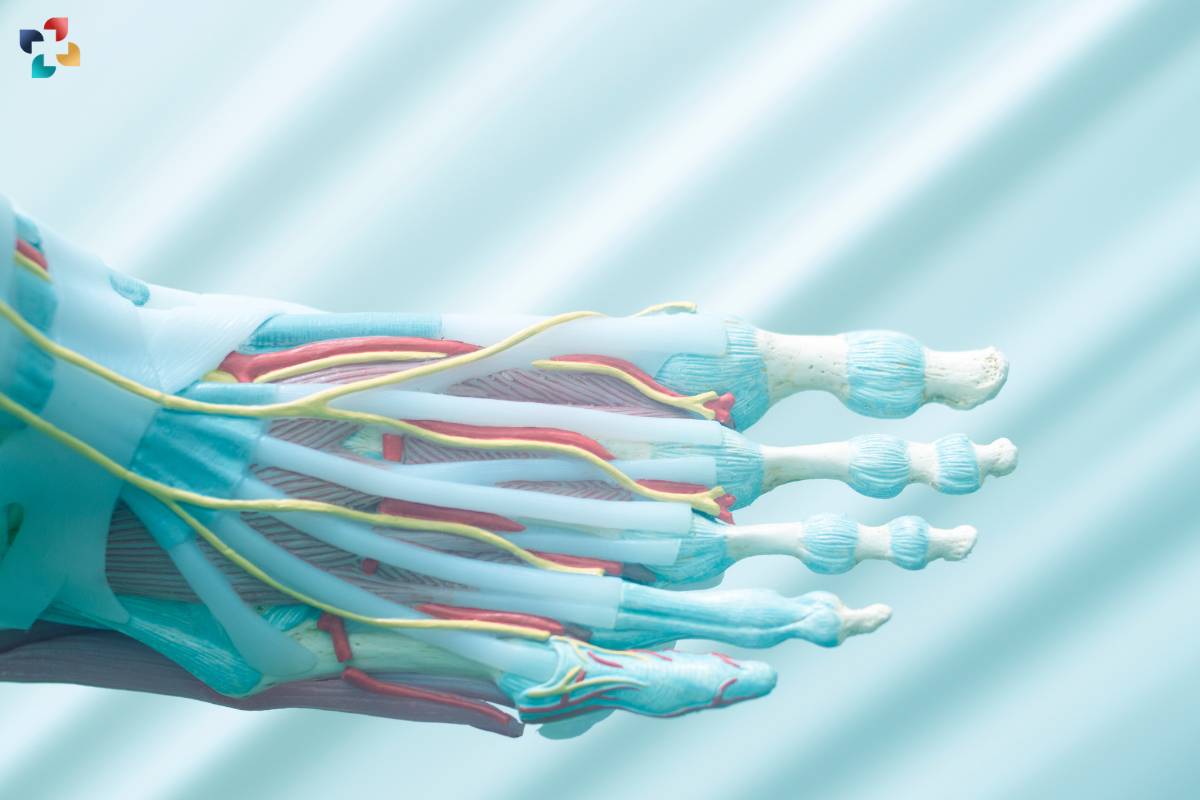
The human body is a complex system of muscles, tendons, and ligaments that work together to facilitate movement and provide stability. One such crucial muscle is the Flexor Digitorum Longus, which plays a vital role in the movement of the foot and toes. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the anatomy, function, common injuries, and exercises related to the Flexor Digitorum Longus muscle.
Anatomy of the Flexor Digitorum Longus
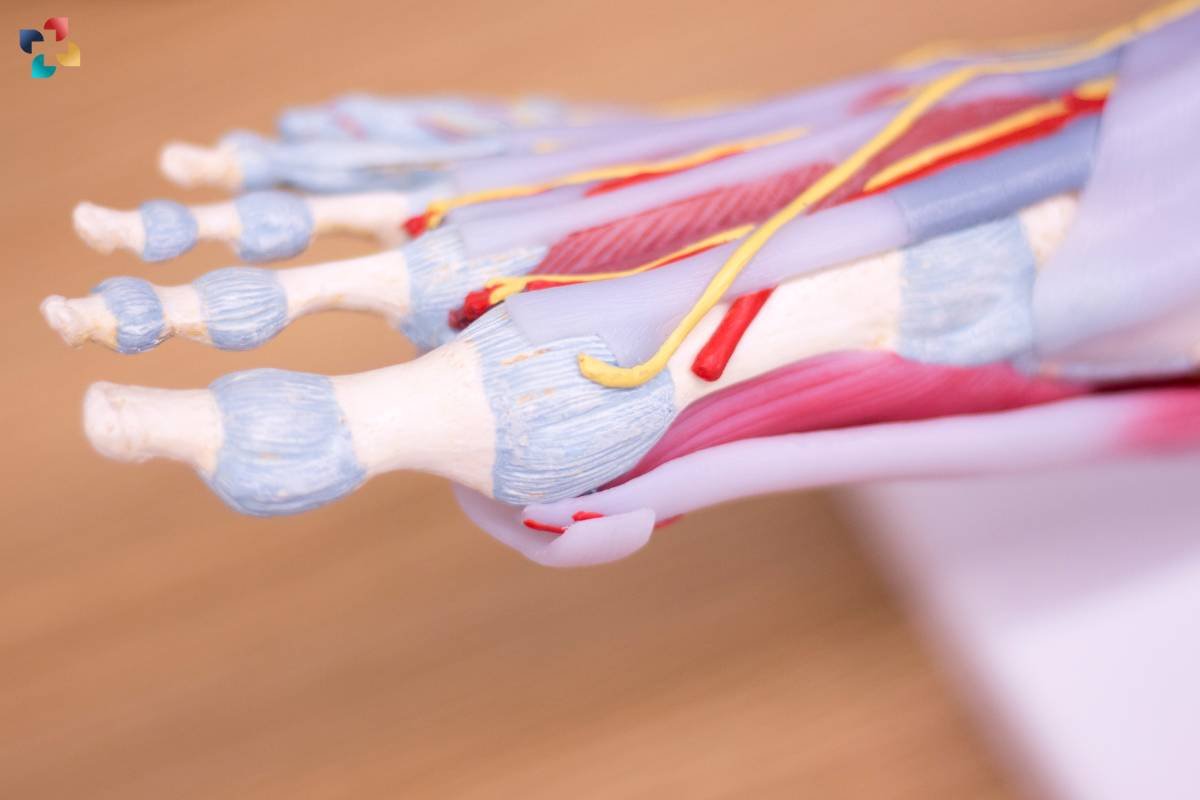
The Flexor Digitorum Longus is a long, slender muscle located in the deep posterior compartment of the leg. It originates from the posterior surface of the tibia, just below the knee joint, and extends down the leg before crossing the ankle joint and inserting into the plantar surface of the foot. This muscle passes under the foot through the tarsal tunnel, along with the posterior tibial artery and tibial nerve.
The Flexor Digitorum Longus muscle is part of the complex network of muscles and tendons that contribute to the movement and stability of the foot and ankle. Its unique anatomical location allows it to play a crucial role in various movements, including flexion of the toes and stabilization of the foot during walking, running, and other weight-bearing activities.
As the Flexor Digitorum Longus descends down the leg, it passes behind the medial malleolus, a bony prominence on the inner aspect of the ankle joint. From there, it travels along the sole of the foot, where it divides into four tendons, each of which attaches to the distal phalanges of the second through fifth toes.
The Flexor Digitorum Longus is situated deep within the leg, beneath other muscles and structures, such as the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles. Despite its deep location, the Flexor Digitorum Longus is vital for proper foot function and contributes to the overall stability and mobility of the lower extremities.
In addition to its role in toe flexion, the Flexor Digitorum Longus also assists in maintaining the arch of the foot and controlling pronation and supination, helping to support the body’s weight and absorb shock during movement. Its anatomical position and function highlight the importance of this muscle in maintaining proper foot mechanics and preventing injury during activities of daily living and sports.
Function of the Flexor Digitorum Longus
The primary function of the Flexor Digitorum Longus is to flex the second, third, fourth, and fifth toes, as well as to support the arch of the foot during walking and running. Additionally, it assists in plantar flexion of the foot at the ankle joint and inversion of the foot.
The Flexor Digitorum Longus muscle plays a crucial role in the intricate movements of the foot and ankle, contributing to both stability and mobility during various activities. One of its primary functions is toe flexion, which involves bending the second through fifth toes downward towards the sole of the foot. This movement is essential for activities such as walking, running, and maintaining balance, as it helps propel the body forward and aids in pushing off the ground with each step.
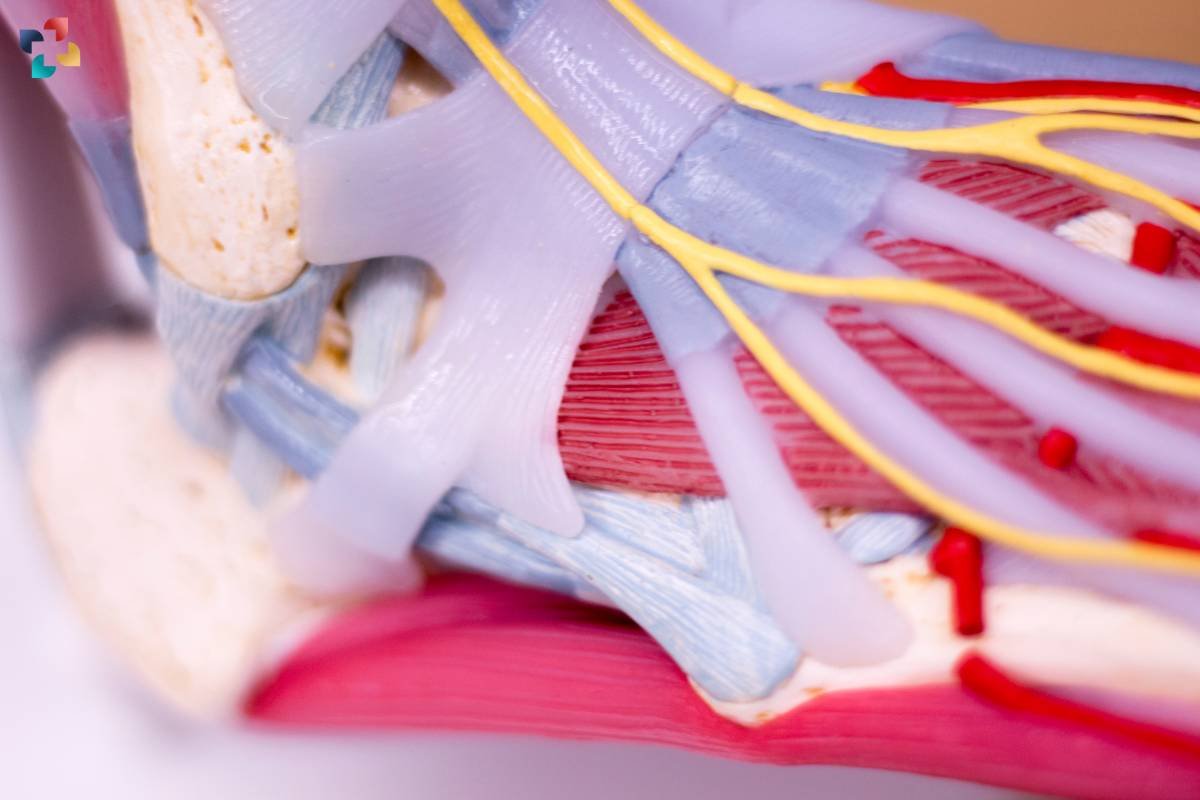
In addition to toe flexion, the Flexor Digitorum Longus also supports the arch of the foot, helping to maintain its structural integrity during weight-bearing activities. By contracting and exerting tension on the plantar fascia and other soft tissues, this muscle assists in preventing excessive flattening of the arch, which can lead to conditions such as flat feet or fallen arches.
Furthermore, the Flexor Digitorum Longus contributes to plantar flexion of the foot at the ankle joint, which involves pointing the toes downward toward the ground. This movement is essential for actions such as pushing off during walking or running, as well as for activities like jumping and dancing. Additionally, the muscle aids in inversion of the foot, or turning it inward, which helps stabilize the ankle and maintain proper alignment during movement.
Overall, the multifaceted functions of the Flexor Digitorum Longus highlight its importance in supporting the complex biomechanics of the foot and ankle, making it an integral component of the lower extremity musculature.
Common Injuries Associated with the Flexor Digitorum Longus
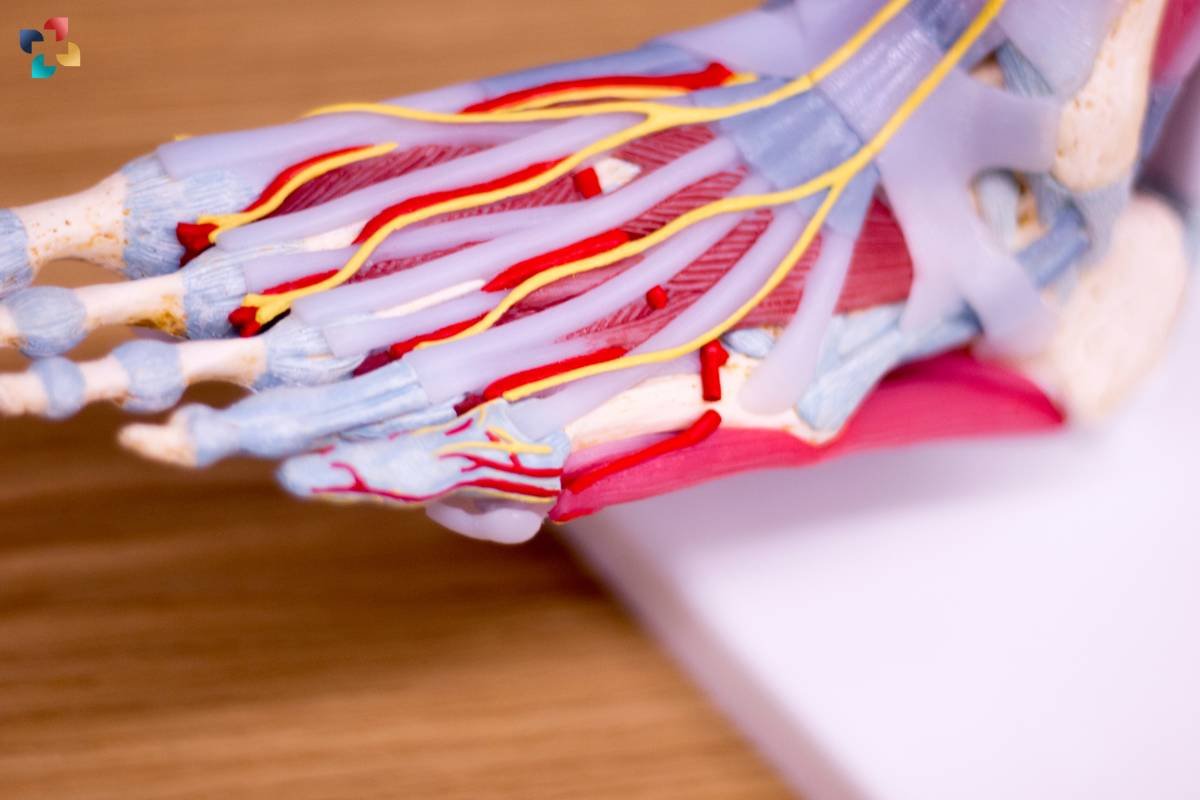
Injuries to the Flexor Digitorum Longus can occur due to overuse, trauma, or improper biomechanics. One common injury is tendonitis, which involves inflammation of the tendon as a result of repetitive stress or a sudden increase in activity. Another injury is a tear or rupture of the tendon, often caused by excessive force or trauma to the foot.
Treatment and Rehabilitation
Treatment for Flexor Digitorum Longus injuries typically involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), along with anti-inflammatory medication and physical therapy. Stretching and strengthening exercises targeted at the muscles of the foot and ankle can help improve flexibility and restore function.
Exercises to Strengthen the Flexor Digitorum Longus
Toe curls: Sit with your foot flat on the ground and place a towel under your toes. Curl your toes to grip the towel and hold for a few seconds before releasing.
- Towel scrunches: Place a towel on the floor and use your toes to scrunch it up towards you.
- Resistance band exercises: Secure a resistance band around the toes and flex them against the resistance.
- Marble pickup: Place marbles on the floor and use your toes to pick them up and place them in a container.
- Toe taps: Sit with your foot flat on the ground and tap your toes up and down rapidly.
Prevention
To prevent injuries to the Flexor Digitorum Longus, it is essential to maintain proper foot biomechanics, wear appropriate footwear, and gradually increase the intensity of physical activity. Additionally, incorporating regular stretching and strengthening exercises into your fitness routine can help improve flexibility and reduce the risk of injury.
Conclusion
The Flexor Digitorum Longus is a critical muscle involved in foot and toe movement, providing stability and support during various activities. Understanding its anatomy, function, and potential injuries can help individuals take proactive steps to maintain foot health and prevent injury. By incorporating targeted exercises and proper biomechanics into their routine, individuals can optimize the function of the Flexor Digitorum Longus and enhance overall foot health and mobility.