Increased Testing for Rapid Detection
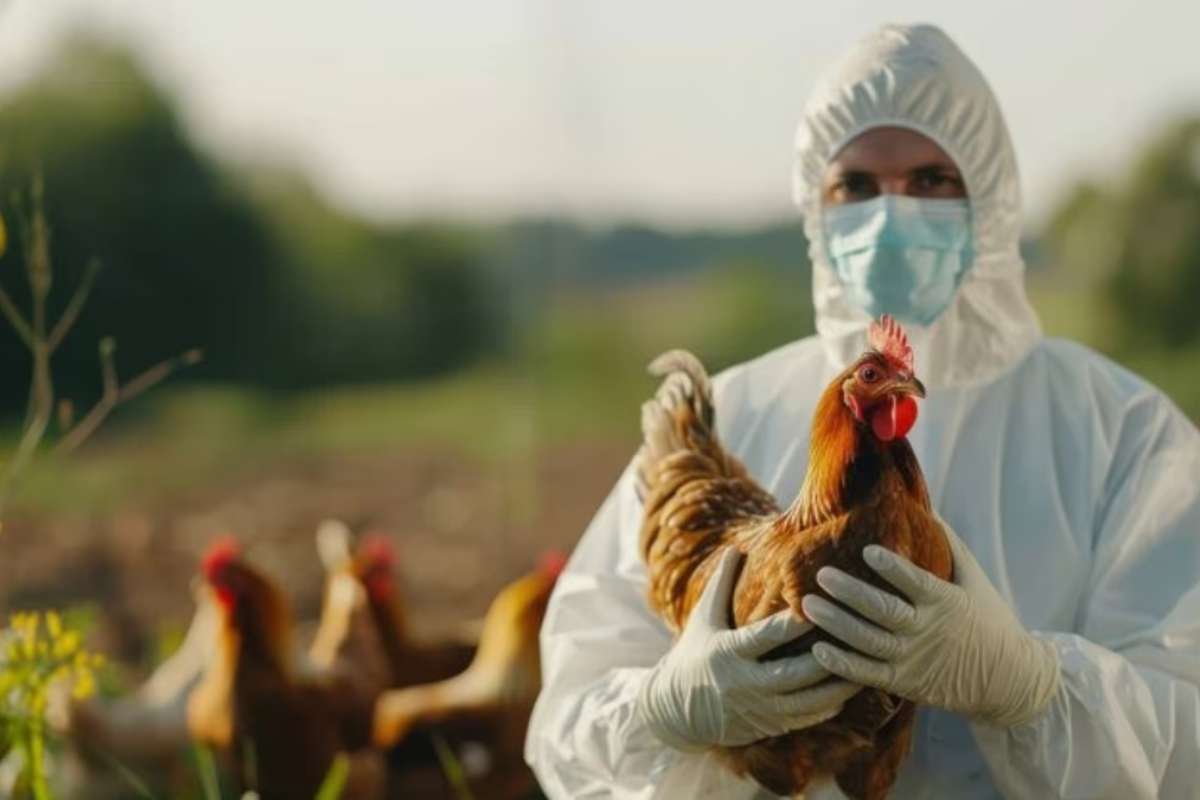
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has issued a call to hospitals and healthcare providers to expedite advanced testing of suspected H5N1 bird flu cases. This initiative follows a few rare H5N1 influenza cases in the US, including a child in San Francisco and an individual in Missouri, where no direct animal exposure was identified. The delayed detection of these infections has complicated efforts to trace exposure sources and prevent further transmission. To enhance surveillance, the CDC has requested state public health labs to conduct additional subtyping tests on all samples that test positive for influenza A, helping identify specific strains like H5N1 more swiftly.
Enhancing Immediate Response and Treatment
CDC officials are emphasizing the importance of rapid subtyping, ideally within 24 hours of patient admission, to distinguish between common seasonal flu strains and novel variants like H5N1. Dr. Nirav Shah, CDC Principal Deputy Director, highlighted the necessity of real-time data to monitor ongoing flu activity. This approach is expected to protect healthcare workers, facilitate timely patient treatment with antivirals, and ensure accurate data collection for potential exposure sources. Moreover, this system aims to detect any shifts in bird flu infection patterns, a crucial step in preventing possible human-to-human transmission.
Strategic Planning and Vaccine Development
As the nation faces a routine flu season with about 100,000 hospitalizations already recorded, the CDC’s urgency for advanced flu testing is further emphasized. In tandem, the Department of Health and Human Services has introduced a strategic playbook to guide future administrations in managing biothreats like H5N1 bird flu. A significant investment of $211 million was announced to develop RNA-based vaccine technology to combat evolving threats. Dr. Eric Deeble from the Department of Agriculture reassured continuity in the bird flu response during the administrative transition, underscoring a collaborative effort to safeguard public health.