Source-Verywell-Health
Introduction:
Foot bones anatomy is a fundamental aspect of understanding the intricate structure and functionality of the human foot. With 26 bones intricately connected by ligaments, tendons, and muscles, the foot is a marvel of biomechanical engineering. This article aims to provide an in-depth examination of foot bones anatomy, exploring its composition, functions, common ailments, diagnostic techniques, treatment options, preventive measures, and the significance of proper foot care in maintaining overall health and well-being.
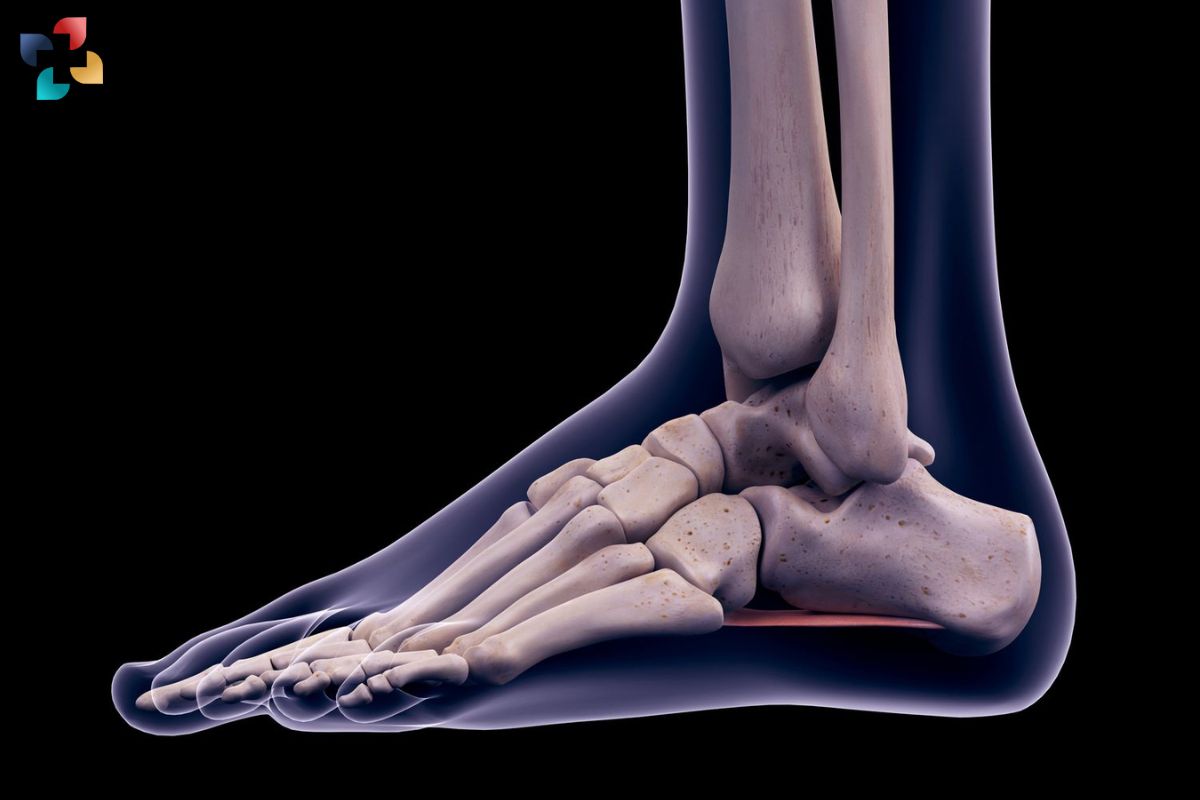
Foot Bones Anatomy:
The foot is divided into three main regions: the hindfoot, midfoot, and forefoot. The hind foot consists of the talus and calcaneus bones, forming the ankle joint and providing stability during weight-bearing activities. The midfoot includes the navicular, cuboid, and three cuneiform bones, contributing to the arches of the foot and facilitating shock absorption. The forefoot comprises the metatarsals and phalanges, forming the toes and enabling propulsion during walking and running. Understanding the intricate interplay between these bones is essential for comprehending the biomechanics of the foot and its role in locomotion.
Functions and Biomechanics:
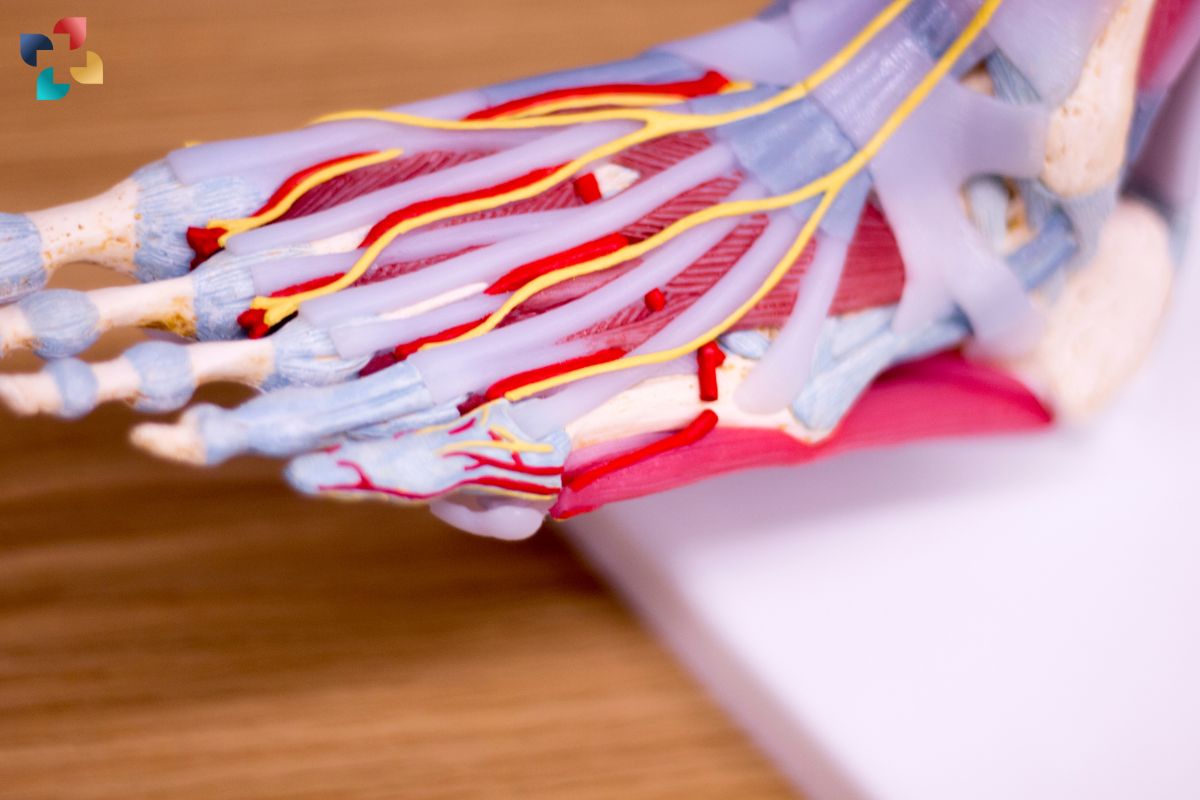
Foot bone anatomy plays a crucial role in supporting body weight, maintaining balance, and facilitating locomotion. The arches of the foot—medial longitudinal, lateral longitudinal, and transverse—distribute weight evenly, absorb shock, and provide dynamic support during movement. Additionally, the alignment of bones and joints allows for a wide range of motion, essential for activities such as standing, walking, running, jumping, and climbing. The intricate network of muscles, tendons, and ligaments surrounding the foot bones further enhances stability and enables fine motor control.
Common Foot Bone Conditions and Injuries:
Despite their resilience, foot bones are susceptible to various conditions and injuries that can affect mobility and quality of life. Some common ailments include:
1. Fractures
From stress fractures to traumatic breaks, fractures can occur in any of the foot bones and often require prompt medical attention and immobilization.
2. Sprains and strains
Injuries to the ligaments and tendons surrounding the foot bones can result from sudden twists or overuse, causing pain, swelling, and instability.
3. Tendonitis
Inflammation of the tendons, such as the Achilles tendon or the peroneal tendons, can lead to discomfort and limited mobility.
4. Osteoarthritis
Degenerative joint disease can affect the foot bones, particularly the big toe joint (hallux rigidus), causing pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion.
5. Neuropathies
Conditions such as diabetic neuropathy or Morton’s neuroma can result in nerve damage and pain in the foot.
6. Structural abnormalities
Bunions, hammertoes, and flat feet are examples of structural deformities that can affect foot function and lead to discomfort. Identifying and addressing these conditions through the foot bone anatomy can prevent further complications and improve outcomes.
Diagnostic Techniques in Foot Bones Anatomy:
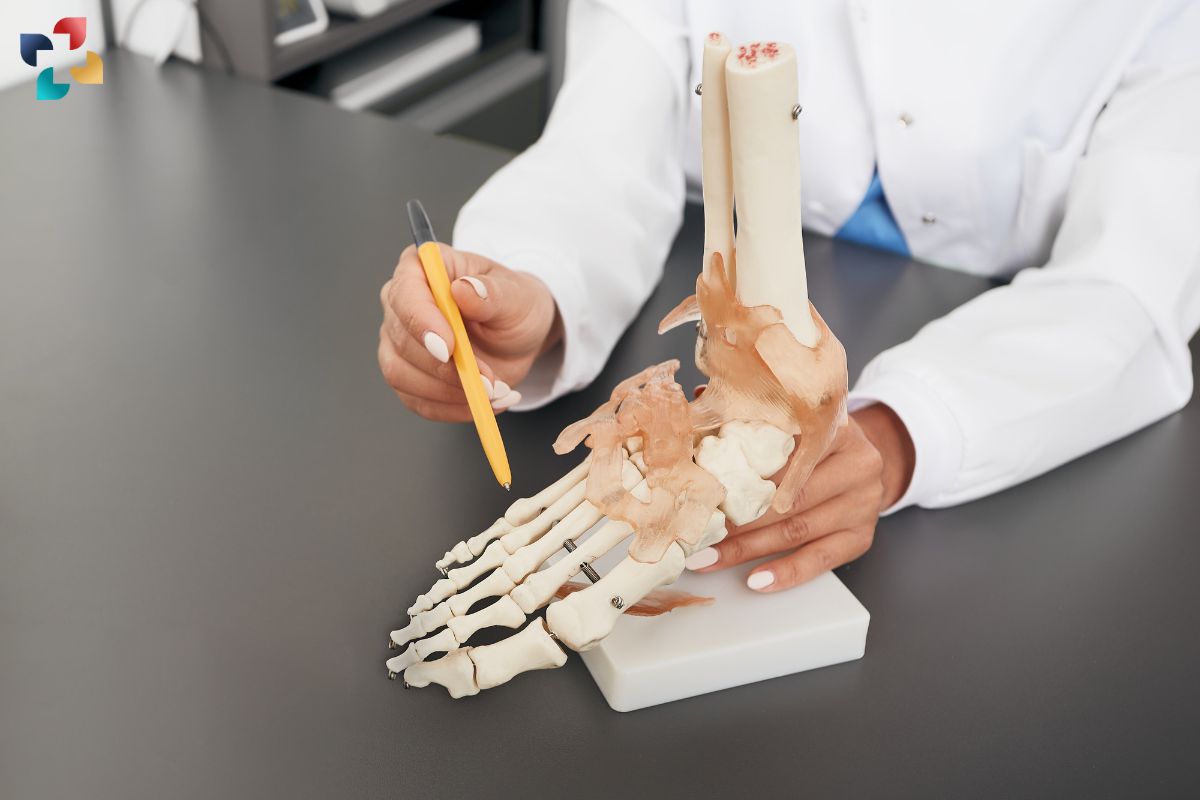
Diagnosing foot bone conditions often requires a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and diagnostic tests. Healthcare professionals may perform physical examinations to assess range of motion, strength, and stability. Imaging modalities such as X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, and ultrasound may be used to visualize bone structure, soft tissue abnormalities, and signs of inflammation or injury. Additionally, diagnostic tests such as nerve conduction studies or electromyography (EMG) may be utilized to evaluate nerve function in cases of neuropathy or nerve compression. The accurate diagnosis of foot bone conditions through foot bones anatomy is essential for developing an effective treatment plan and preventing long-term complications.
Treatment Options and Management:
The management of foot bone conditions depends on the underlying cause, severity of symptoms, and individual patient factors. Treatment options may include:
- Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) for acute injuries and inflammation.
- Immobilization with splints, braces, or casts to promote healing of fractures or sprains.
- Physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and proprioception.
- Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, or pain relievers to alleviate symptoms.
- Orthotic devices, shoe modifications, or custom-made footwear to support the arches and correct biomechanical abnormalities.
- Injections of corticosteroids, platelet-rich plasma (PRP), or hyaluronic acid for targeted pain relief and tissue regeneration.
- Surgical interventions, including fracture fixation, tendon repair, joint fusion, or joint replacement, may be considered for severe or refractory cases. Collaborating with a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including orthopedic surgeons, podiatrists, physical therapists, and rehabilitation specialists, can optimize treatment outcomes and facilitate a comprehensive approach to care.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Recommendations:
Maintaining foot health requires proactive measures and lifestyle modifications to prevent injuries and minimize the risk of developing foot bone conditions. Some preventive measures that foot bones anatomy suggest, include:
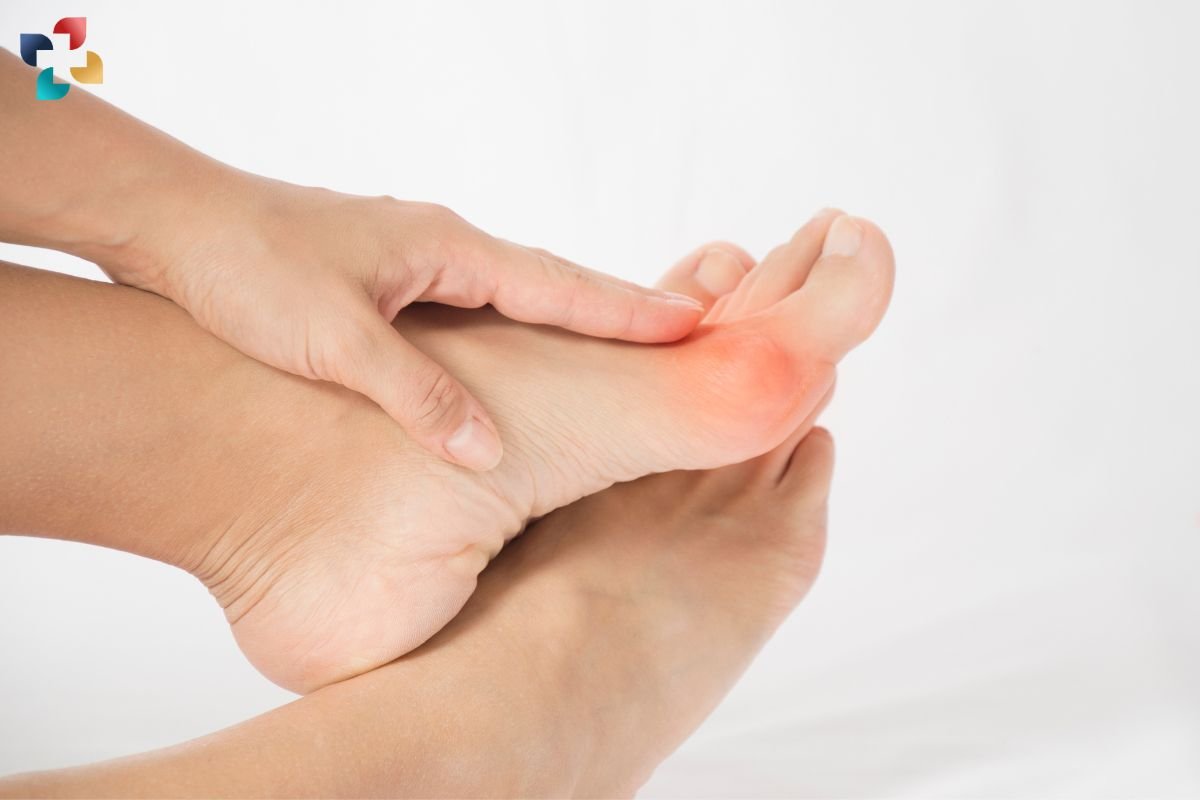
- Wearing properly fitting footwear with adequate support, cushioning, and room for the toes to prevent friction, pressure, and rubbing. Choosing shoes designed for specific activities, such as running shoes for jogging or hiking boots for outdoor adventures, can further enhance comfort and protection.
- Gradually increasing the intensity and duration of physical activities to avoid overuse injuries and stress fractures. Incorporating cross-training activities, such as swimming, cycling, or yoga, can reduce repetitive strain on the feet and promote overall fitness and flexibility.
- Incorporating strength and flexibility exercises into a regular fitness routine to improve foot and ankle stability, mobility, and proprioception. Exercises targeting the intrinsic muscles of the foot, such as toe curls, arch lifts, and ankle circles, can enhance balance and coordination.
- Practicing good foot hygiene, including washing feet regularly, keeping nails trimmed, and moisturizing dry or cracked skin to prevent infections. Using antimicrobial foot powders or sprays can help control odor and fungal growth, particularly in warm and humid environments.
- Avoid high-impact activities or surfaces that may exacerbate foot pain or discomfort, especially in individuals with underlying conditions such as arthritis or neuropathy. Choosing low-impact alternatives, such as swimming, cycling, or using elliptical machines, can reduce stress on the feet and joints while still providing cardiovascular benefits.
- Monitoring foot health and seeking prompt medical attention for any persistent pain, swelling, numbness, tingling, or changes in foot structure or function. Regular foot exams by a healthcare professional, especially for individuals with diabetes or peripheral vascular disease, can help identify potential problems early and prevent complications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, foot bones anatomy is a complex subject that contains the structure, function, pathology, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of conditions affecting the bones and joints of the foot. By gaining a deeper understanding of foot bones anatomy and its implications for overall health and well-being, individuals can take essential steps to maintain foot health, prevent injuries, and optimize mobility and quality of life.
Whether you’re an athlete, a healthcare professional, or someone with a keen interest in anatomy and biomechanics, exploring the complexities of foot-bones anatomy offers valuable insights into the remarkable resilience and adaptability of the human body. Embracing a comprehensive approach to foot care, including proper footwear selection, injury prevention strategies, and early intervention for foot bone conditions, can empower individuals to lead active, pain-free lifestyles and enjoy the countless wonders of movement and mobility.
6 Innovations in Operative Medicine for Foot and Ankle Surgery
Foot and ankle surgeries have been evolving for years with the advancement of technology and modern medical techniques. Here are six innovations in operative medicine for foot and ankle surgery.