Introduction:
In the realm of medicine, understanding blood cell counts is crucial for diagnosing and monitoring various health conditions. One such essential parameter is the Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC), which plays a vital role in assessing a person’s immune health. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the significance of ANC, its interpretation, and its implications for overall health.
What is Absolute Neutrophil Count?
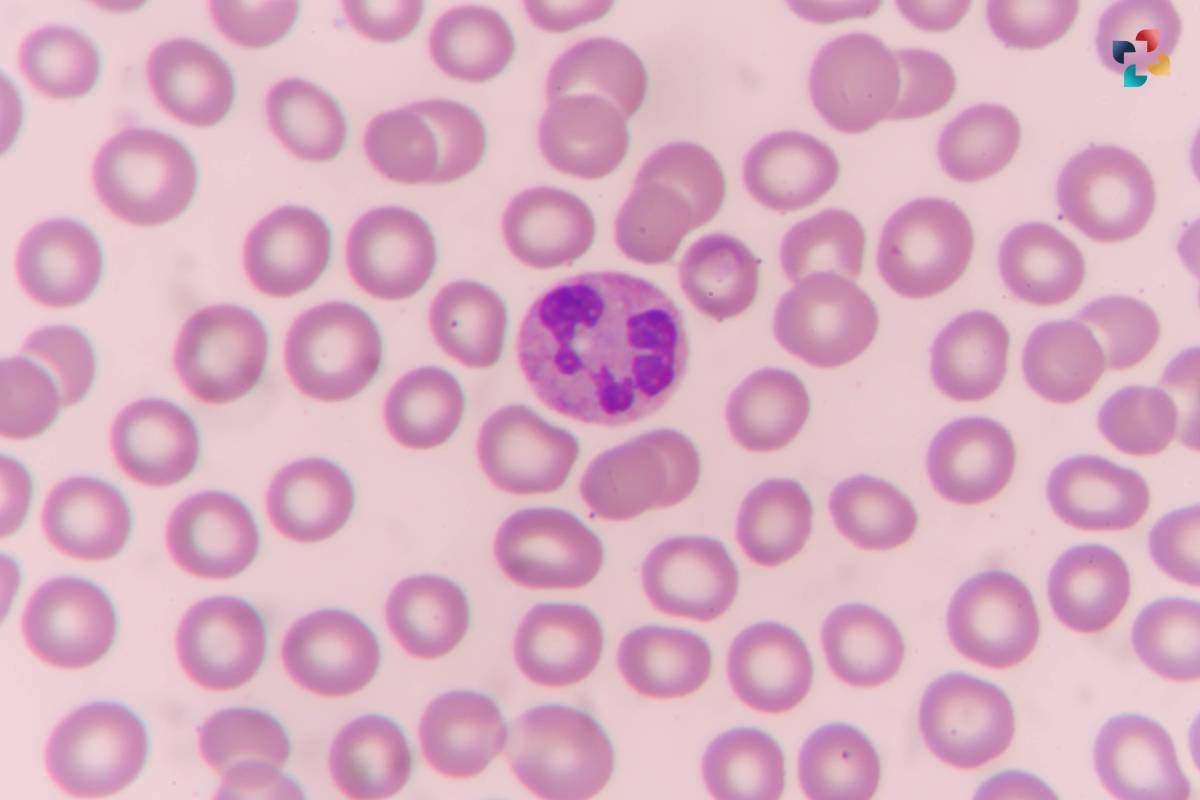
Absolute Neutrophil Count, often abbreviated as ANC, is a measure of the total number of neutrophils in the blood. Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell (WBC) and are a key component of the body’s immune system, primarily responsible for fighting off bacterial and fungal infections. ANC is typically expressed as the number of neutrophils per microliter of blood and is an important indicator of the body’s ability to combat infections.
Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) serves as a critical component in assessing an individual’s immune health and overall well-being. Neutrophils, the most abundant type of white blood cells in the body, play a pivotal role in the immune response against bacterial and fungal infections. As part of the innate immune system, neutrophils are among the first responders to sites of infection, where they engulf and destroy invading pathogens through a process known as phagocytosis.
ANC is expressed as the number of neutrophils per microliter of blood and is often measured as part of a complete blood count (CBC) test. This simple yet informative test provides healthcare providers with valuable insights into the body’s ability to combat infections and mount an effective immune response. An ANC within the normal range indicates that the body’s immune system is functioning optimally, while deviations from the norm may signal underlying health conditions or immune system disorders.
Maintaining an optimal ANC is crucial for protecting the body against infectious agents and maintaining overall health. Low ANC, a condition known as neutropenia, increases the risk of infections, leaving individuals vulnerable to bacterial and fungal invaders. Conversely, high ANC, or neutrophilia, may indicate inflammation, infection, or other underlying health issues that require further evaluation and management.
In summary, Absolute Neutrophil Count provides valuable information about the body’s immune health and its ability to combat infections. Regular monitoring of ANC levels, along with appropriate medical interventions, can help identify potential health issues early and ensure optimal immune function and overall well-being.
Significance of Absolute Neutrophil Count:
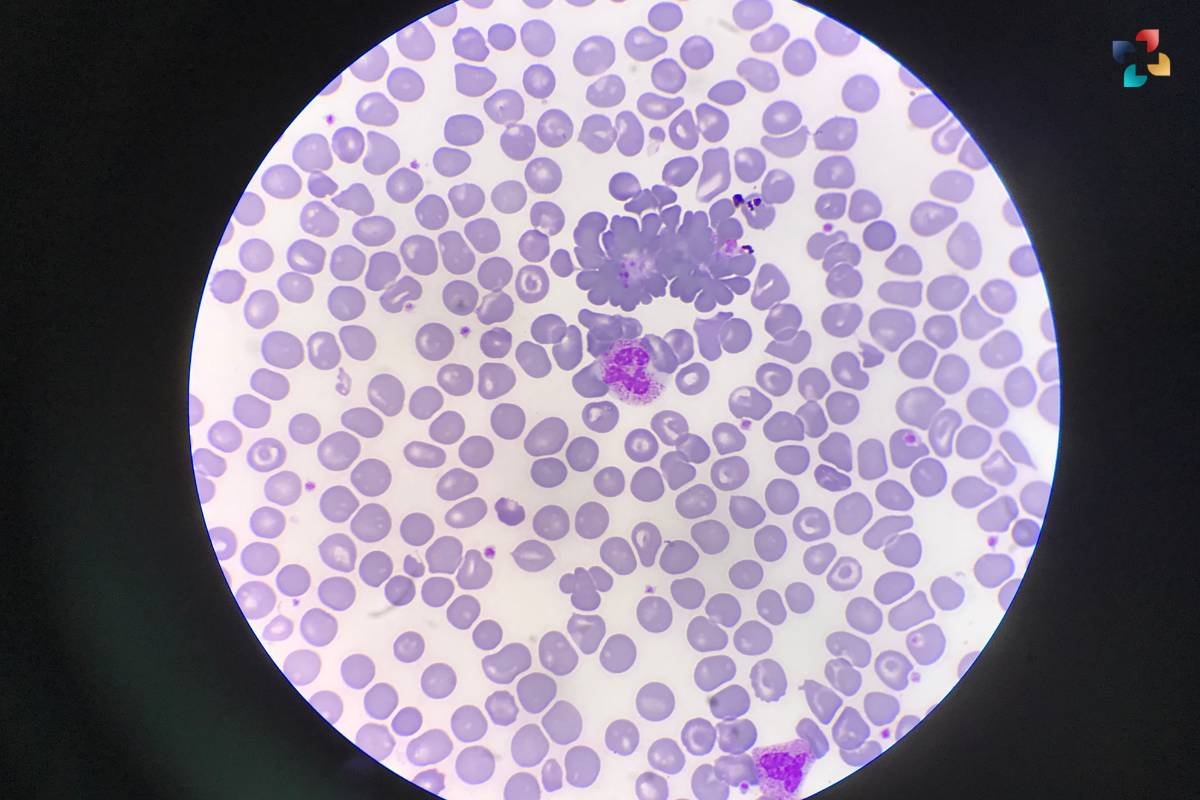
An optimal Absolute Neutrophil Count is crucial for maintaining a healthy immune response. Neutropenia, or a low ANC, can leave individuals susceptible to infections, while neutrophilia, or a high ANC, may indicate inflammation, infection, or other underlying health issues. Monitoring ANC levels is particularly important for individuals undergoing chemotherapy or other treatments that suppress the immune system, as they are at increased risk of infections.
Interpretation of Absolute Neutrophil Count:
Interpreting Absolute Neutrophil Count requires understanding normal reference ranges and considering individual patient factors. In general, a normal ANC typically falls within the range of 1500 to 8000 neutrophils per microliter of blood. ANC levels below 1500 indicate neutropenia, while levels above 8000 suggest neutrophilia. However, interpretation may vary based on age, underlying health conditions, and medications.
When interpreting Absolute Neutrophil Count, it’s essential to consider various factors that may influence neutrophil levels. For instance, certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs or immunosuppressants, can cause neutropenia by suppressing the bone marrow’s ability to produce neutrophils. Additionally, individuals with underlying health conditions like autoimmune disorders, viral infections, or bone marrow disorders may also experience fluctuations in ANC levels.
Furthermore, age can play a role in ANC interpretation, as normal reference ranges may differ in pediatric and elderly populations. Pediatric patients typically have higher ANC levels compared to adults, while the elderly may have lower baseline levels due to age-related changes in immune function.
Overall, interpreting Absolute Neutrophil Count requires a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s medical history, current health status, and any underlying conditions or medications that may affect neutrophil production. Healthcare providers use this information to make informed decisions regarding diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of immune-related disorders.
Implications of Absolute Neutrophil Count:
An abnormal Absolute Neutrophil Count can have significant implications for health. Neutropenia increases the risk of severe infections, while neutrophilia may indicate inflammatory conditions, autoimmune disorders, or even leukemia. Regular monitoring of ANC levels is essential for early detection of infections or underlying health issues, allowing for prompt intervention and treatment.
In the clinical setting, abnormalities in Absolute Neutrophil Count can guide healthcare providers in diagnosing and managing various medical conditions. Neutropenia, characterized by low ANC levels, can predispose individuals to recurrent and severe bacterial or fungal infections, particularly in the respiratory tract, skin, and mucous membranes. Patients with neutropenia may require close monitoring and prophylactic treatment with antibiotics or antifungal medications to prevent infections.
On the other hand, neutrophilia, or elevated ANC levels, can indicate a heightened immune response to infection, inflammation, or tissue injury. While transient neutrophilia is a normal response to acute stressors like infection or trauma, persistent neutrophilia may suggest underlying inflammatory disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, or vasculitis. In some cases, neutrophilia can also be a sign of certain cancers, particularly leukemias or myeloproliferative disorders, where the bone marrow produces excessive numbers of white blood cells, including neutrophils.
Overall, understanding the implications of Absolute Neutrophil Count is crucial for clinicians to effectively manage patients’ health and implement appropriate treatment strategies. Regular monitoring of ANC levels, along with clinical assessment and other laboratory tests, allows healthcare providers to promptly identify and address underlying health issues, optimize patient outcomes, and minimize the risk of complications associated with neutropenia or neutrophilia.
Conclusion:
Absolute Neutrophil Count is a critical parameter in assessing immune health and detecting potential health issues. Understanding ANC levels and their implications can aid healthcare providers in diagnosing and managing various conditions, ultimately contributing to better patient outcomes and overall well-being. Regular monitoring of ANC levels, along with appropriate medical interventions, plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal immune function and overall health.
Understanding Red Cell Distribution Width: Importance, Interpretation, and Clinical Significance
We shall examine the importance of RDW, its interpretation, clinical uses, and consequences for different medical disorders in this article.