Introduction:
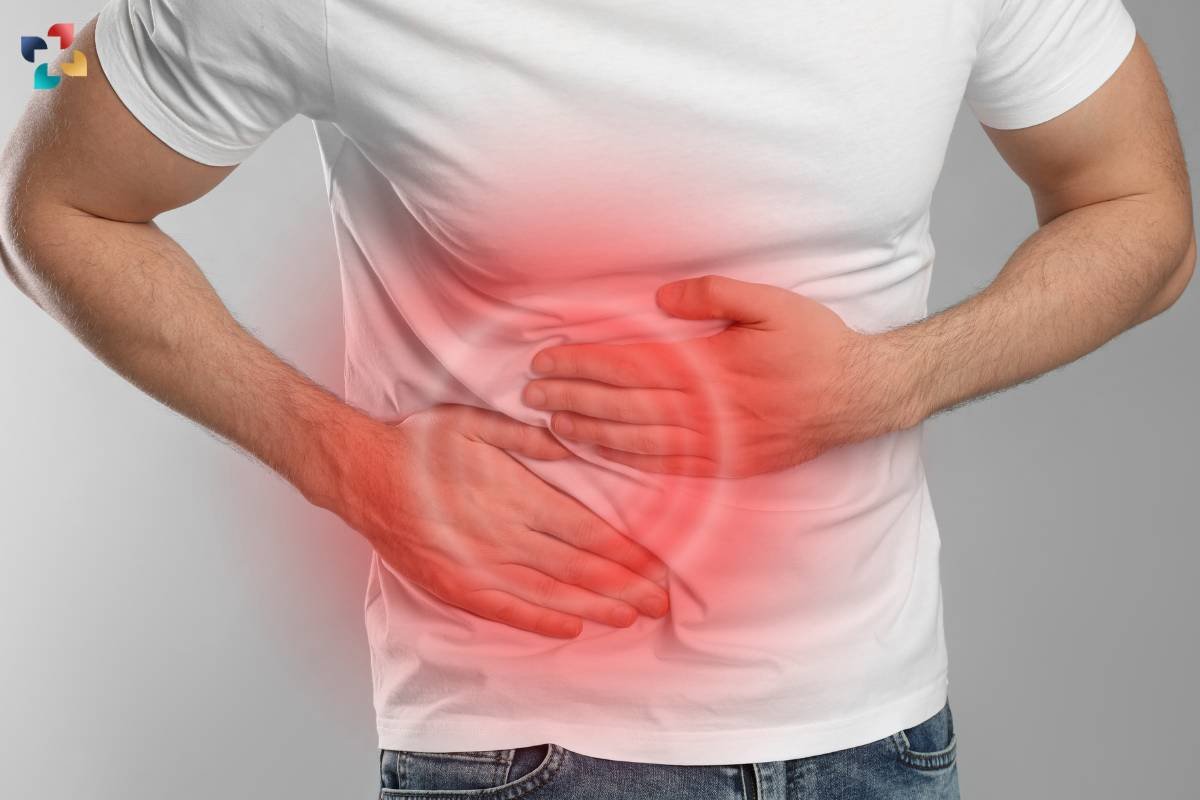
Appendicitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the appendix, a small pouch located in the lower right abdomen. While appendicitis can occur at any age, it is most common in individuals between the ages of 10 and 30. Prompt recognition of the signs of appendicitis is crucial for timely medical intervention and prevention of complications. In this article, we will explore the various signs and symptoms of appendicitis, common diagnostic methods, and the importance of seeking medical attention when these signs arise.
Understanding Appendicitis:
Before discussing the signs of appendicitis, it’s essential to understand the function of the appendix and how appendicitis develops. The appendix is a small, finger-shaped pouch attached to the large intestine. Although its exact function is not fully understood, it is believed to play a role in immune system function. When the appendix becomes inflamed, typically due to blockage by stool, foreign objects, or infection, appendicitis occurs.
Signs of Appendicitis:
Appendicitis is a medical emergency characterized by inflammation of the appendix, a small pouch located in the lower right abdomen. Recognizing the signs of appendicitis is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent potential complications such as a ruptured appendix. This condition typically affects individuals between the ages of 10 and 30, although it can occur at any age. Understanding the signs and symptoms of appendicitis is essential for distinguishing it from other abdominal conditions and seeking appropriate medical care.

In this article, we will explore the various signs and symptoms of appendicitis in detail. From abdominal pain and loss of appetite to fever and changes in bowel habits, we will discuss the key indicators that may suggest the presence of appendicitis. Additionally, we will cover the importance of seeking medical attention when these signs arise and the diagnostic methods used to confirm a diagnosis of appendicitis. By being aware of the signs of appendicitis, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their health and well-being.
1. Abdominal Pain
One of the hallmark signs of appendicitis is abdominal pain that starts near the navel and migrates to the lower right abdomen. The pain may worsen over time and become severe, especially with movement or coughing.
2. Loss of Appetite
Individuals with appendicitis often experience a sudden loss of appetite, accompanied by nausea and vomiting. This may be due to the body’s response to inflammation and irritation in the abdominal area.
3. Fever and Chills
Appendicitis can cause a low-grade fever, typically ranging from 99°F to 100.5°F. In some cases, individuals may also experience chills or shaking, indicating an inflammatory response in the body.
4. Abdominal Tenderness
Upon examination, healthcare providers may find that the lower right abdomen is tender to the touch, especially when pressure is applied. This tenderness may be localized to a specific area known as McBurney’s point.
5. Swelling and Bloating

Appendicitis can lead to abdominal swelling and bloating, causing discomfort and a feeling of fullness in the abdomen. This may be accompanied by gas and indigestion.
6. Changes in Bowel Habits
Some individuals with appendicitis may experience changes in bowel habits, such as diarrhea or constipation. This may be due to the disruption of normal digestive processes caused by inflammation in the abdominal area.
7. Rebound Tenderness
Rebound tenderness, also known as Blumberg’s sign, is a phenomenon where pain increases when pressure is released after being applied to the abdomen. This is a classic sign of peritoneal irritation and is often present in cases of appendicitis.
8. Painful Urination
In some cases, appendicitis may cause discomfort or pain during urination. This may be due to inflammation spreading to nearby structures, such as the urinary bladder.
9. Difficulty Passing Gas
Appendicitis can interfere with normal bowel function, leading to difficulty passing gas or experiencing relief from bloating. This symptom is often accompanied by abdominal discomfort and distension.
10. Fatigue and Malaise
Individuals with appendicitis may experience feelings of fatigue, weakness, and overall malaise. This is the body’s natural response to inflammation and infection.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
If you experience any of the signs of appendicitis mentioned above, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, blood tests to check for signs of infection, and imaging tests such as ultrasound or CT scan to visualize the appendix and confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment for appendicitis usually involves surgical removal of the inflamed appendix, a procedure known as an appendectomy. In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and prevent infection before surgery. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent complications such as a ruptured appendix, which can lead to a life-threatening infection called peritonitis.
Conclusion:
Recognizing the signs of appendicitis is essential for timely diagnosis and treatment of this potentially serious condition. If you experience abdominal pain, loss of appetite, fever, or other symptoms associated with appendicitis, seek medical attention promptly. Early intervention can prevent complications and promote a speedy recovery. Remember, when it comes to appendicitis, prompt action can make all the difference in preserving your health and well-being.
FAQs
1. What are the common signs of appendicitis?
Common signs of appendicitis include abdominal pain, particularly in the lower right side, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, low-grade fever, and abdominal tenderness.
2. Is appendicitis always accompanied by severe abdominal pain?
While severe abdominal pain is a hallmark symptom of appendicitis, the intensity of pain may vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience mild discomfort initially, which gradually worsens over time.
3. Can appendicitis cause symptoms other than abdominal pain?
Yes, appendicitis can cause symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, low-grade fever, and changes in bowel habits. However, abdominal pain is the most common and prominent symptom.
4. How long does it take for appendicitis symptoms to develop?
Appendicitis symptoms typically develop over 24 to 48 hours. Initially, individuals may experience mild discomfort or vague abdominal pain, which progressively worsens and becomes localized to the lower right abdomen.
5. When should I seek medical attention for suspected appendicitis?
If you experience persistent abdominal pain, especially if it intensifies or shifts to the lower right side, accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, fever, or abdominal tenderness, seek immediate medical attention. Appendicitis requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications such as a ruptured appendix.