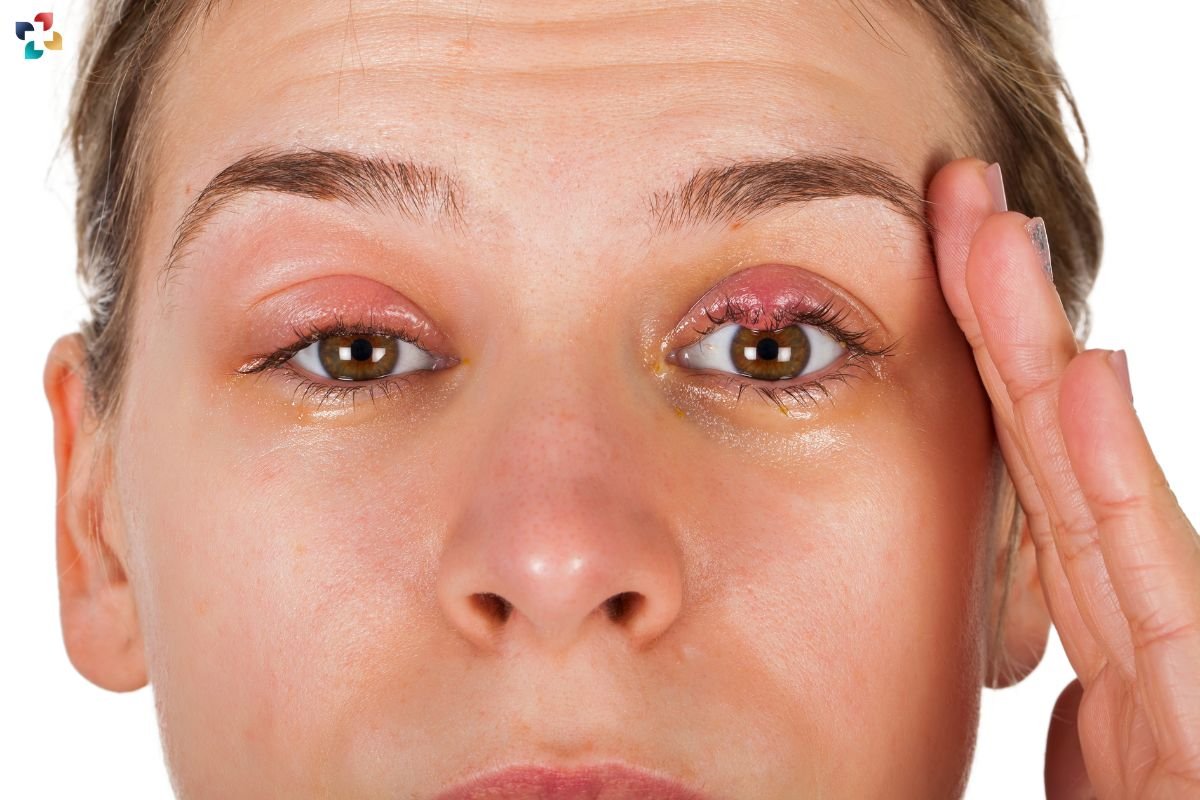
Eye health is a critical aspect of overall well-being, and understanding common eye conditions is essential for maintaining optimal vision. Among the various eye issues that can arise, chalazion and hordeolum are two conditions that often cause confusion due to their similar appearance and symptoms. This article will explore “Chalazion vs. Hordeolum,” providing a comprehensive understanding of their differences, causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Introduction to Chalazion and Hordeolum
Before delving into the differences between a chalazion and a hordeolum, it is crucial to define each condition:
- Chalazion: A chalazion is a non-infectious, chronic inflammatory lesion that develops in the eyelid due to the blockage of the meibomian gland. These glands secrete oil that lubricates the eye’s surface. When a gland becomes blocked, the oil accumulates, leading to inflammation and the formation of a lump.
- Hordeolum (Stye): A hordeolum, commonly known as a stye, is an acute, painful infection of the eyelid glands, usually caused by bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus. There are two types of hordeola: external, which affects the glands of Zeis or Moll, and internal, which involves the meibomian glands.
Causes of Chalazion vs. Hordeolum
Understanding the causes of “Chalazion vs. Hordeolum” helps in differentiating the two conditions:
- Chalazion: The primary cause of a chalazion is the obstruction of the meibomian gland duct. This blockage can result from various factors, including:
- Chronic blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelid margin)
- Skin conditions like rosacea and seborrheic dermatitis
- Previous hordeolum that has not fully resolved
- Hordeolum: A hordeolum is caused by a bacterial infection, primarily by Staphylococcus aureus. The infection leads to the formation of a painful, pus-filled abscess. Factors that increase the risk of developing a hordeolum include:
- Poor eyelid hygiene
- Contact lens use without proper cleaning
- Chronic blepharitis
- Touching the eyes with dirty hands
Symptoms of Chalazion vs. Hordeolum
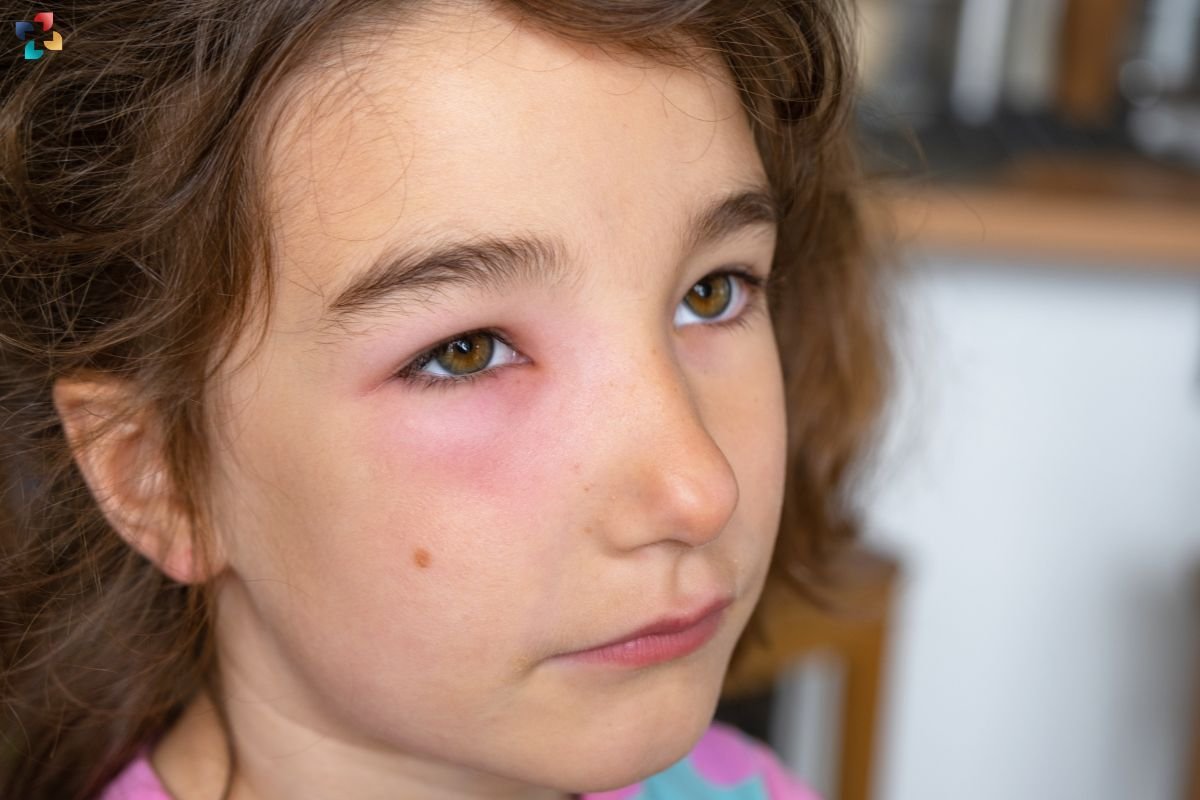
The symptoms of “Chalazion vs. Hordeolum” can overlap, but there are distinct differences that help in identifying each condition:
- Chalazion:
- Gradual onset of a painless lump on the eyelid
- Mild tenderness or sensitivity in the affected area
- Swelling and redness of the eyelid
- Blurred vision if the chalazion presses against the eyeball
- The lump may grow over weeks to months
- Hordeolum:
- Sudden onset of a painful, red lump on the eyelid
- Significant tenderness and sensitivity
- Swelling and redness of the eyelid
- Formation of a pus-filled abscess
- Discomfort when blinking
- The lump typically resolves within a few days to a week
Diagnosis of Chalazion vs. Hordeolum
A proper diagnosis of “Chalazion vs. Hordeolum” requires a thorough examination by an eye care professional. The diagnostic process usually includes:
- Medical History: The doctor will ask about the patient’s symptoms, duration, and any previous occurrences of similar issues.
- Physical Examination: A detailed examination of the eyelid using a slit lamp (a specialized microscope) helps in identifying the nature of the lump and distinguishing between a chalazion and a hordeolum.
- Additional Tests: In rare cases, if the diagnosis is uncertain or if the lump does not respond to treatment, a biopsy may be performed to rule out other conditions such as sebaceous gland carcinoma.
Treatment Options for Chalazion vs. Hordeolum
Effective treatment for “Chalazion vs. Hordeolum” depends on the accurate identification of the condition. Here are the treatment options for each:
- Chalazion:
- Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to the affected eyelid several times a day can help soften the hardened oil and promote drainage.
- Massage: Gently massaging the eyelid after applying warm compresses can aid in opening the blocked gland.
- Topical Medications: In some cases, antibiotic or steroid ointments may be prescribed to reduce inflammation.
- Intralesional Steroid Injection: For persistent chalazia, an injection of a corticosteroid directly into the lesion may help reduce inflammation and size.
- Surgical Removal: If conservative treatments fail, a minor surgical procedure called incision and curettage may be performed to remove the chalazion.
- Hordeolum:
- Warm Compresses: Similar to chalazion treatment, warm compresses applied to the affected area several times a day can help the stye come to a head and drain.
- Topical Antibiotics: Antibiotic ointments or drops may be prescribed to treat the bacterial infection.
- Oral Antibiotics: In more severe cases, oral antibiotics may be necessary to treat the infection.
- Incision and Drainage: If the hordeolum does not respond to other treatments or if it is particularly large and painful, a minor surgical procedure may be required to drain the abscess.
Prevention of Chalazion vs. Hordeolum

Preventing “Chalazion vs. Hordeolum” involves maintaining good eyelid hygiene and adopting healthy habits:
- For Chalazion:
- Practice regular eyelid hygiene, such as cleaning the eyelids with a gentle, non-irritating cleanser.
- Manage underlying conditions like blepharitis or rosacea effectively.
- Avoid rubbing the eyes, which can exacerbate gland blockages.
- For Hordeolum:
- Maintain proper eyelid hygiene, including regular cleaning of the eyelids.
- Avoid touching the eyes with unclean hands.
- Ensure contact lenses are cleaned and stored properly.
- Replace eye makeup regularly to prevent bacterial buildup.
When to See a Doctor?
It is essential to seek medical attention if you experience any of the following symptoms with “Chalazion vs. Hordeolum”:
- Persistent or worsening pain
- Increased swelling and redness
- Vision changes
- Recurrence of the condition
- No improvement with home treatment after a week

Understanding Watery Eyes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
This article delves into the various causes, symptoms, and treatments for watery eyes, providing a comprehensive understanding of this common yet often misunderstood condition.
Complications of Chalazion vs. Hordeolum
While both chalazion and hordeolum are generally benign and self-limiting, complications can arise if they are not treated properly:
- Chalazion:
- Persistent chalazion can lead to chronic inflammation and discomfort.
- Large chalazia may press on the cornea, causing astigmatism and blurred vision.
- Recurrent chalazia may indicate underlying conditions that require medical attention.
- Hordeolum:
- Untreated hordeolum can lead to the formation of a chalazion.
- In rare cases, the infection can spread to surrounding tissues, causing preseptal cellulitis or orbital cellulitis, which are serious conditions requiring prompt medical intervention.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions and similarities between “Chalazion vs. Hordeolum” is crucial for effective management and treatment. While both conditions involve lumps on the eyelid, their causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches differ significantly. By recognizing these differences and following appropriate preventive measures, individuals can maintain good eyelid health and reduce the risk of recurrence. If you experience persistent or severe symptoms, it is essential to consult an eye care professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.







