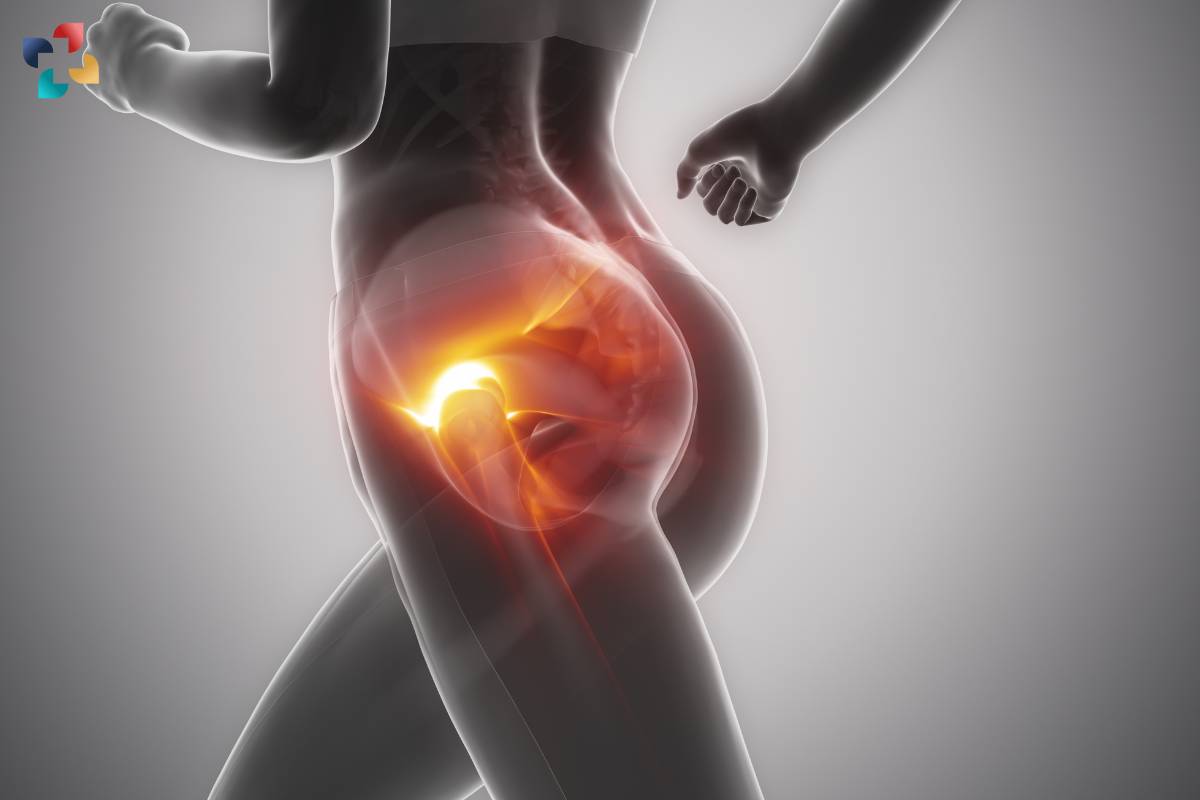
Hip tendonitis, also known as hip tendinitis, is a common orthopedic condition characterized by inflammation or irritation of the tendons surrounding the hip joint. It can cause pain, stiffness, and limited range of motion, impacting daily activities and quality of life. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures for hip tendonitis.
Understanding Hip Tendonitis
Hip tendonitis occurs when the tendons around the hip joint become inflamed due to repetitive stress, overuse, muscle imbalances, or biomechanical issues. The primary tendons affected by hip tendonitis include the iliotibial (IT) band, gluteus medius, and rectus femoris tendons. These tendons play crucial roles in stabilizing the hip joint and facilitating movement, making them prone to injury and inflammation.
Causes of Hip Tendonitis:
Several factors can contribute to the development of hip tendonitis, including:
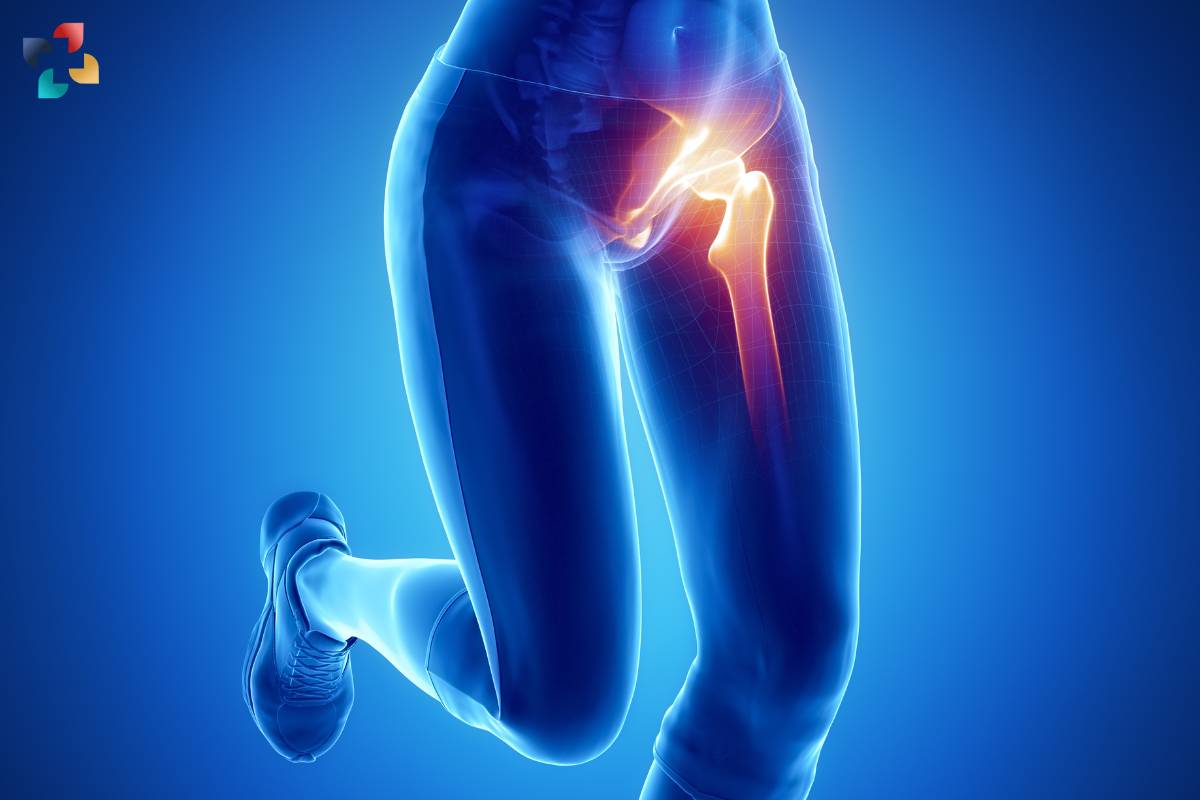
1. Overuse or repetitive movements: Activities such as running, cycling, or excessive sitting can strain the hip tendons over time, leading to inflammation.
2. Muscle imbalances: Weakness or tightness in the hip muscles can alter biomechanics and increase stress on the tendons, predisposing them to injury.
3. Poor posture: Incorrect posture or alignment can place excessive pressure on the hip tendons, causing irritation and inflammation.
4. Trauma or injury: Direct trauma or sudden movements can damage the hip tendons, triggering an inflammatory response.
5. Aging: As we age, the tendons may become less resilient and more susceptible to wear and tear, increasing the risk of hip tendonitis.
Symptoms of Hip Tendonitis:
The symptoms of hip tendonitis may vary depending on the specific tendon involved and the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
- Pain or tenderness around the hip joint, especially during movement or activity.
- Stiffness or reduced range of motion in the hip.
- Swelling or warmth in the affected area.
- Weakness or instability in the hip muscles.
- Clicking or snapping sensations during movement.
Diagnosis of Hip Tendonitis:
Diagnosing hip tendonitis typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional, including:
1. Medical history: The healthcare provider will inquire about the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and activity level.
2. Physical examination: A thorough physical examination will assess a hip’s range of motion, strength, flexibility, and tenderness.
3. Imaging tests: X-rays, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be ordered to visualize the hip joint and surrounding structures and rule out other potential causes of hip pain.
4. Diagnostic injections: In some cases, diagnostic injections may be performed to confirm the diagnosis by temporarily relieving pain and inflammation in the affected area.
5. Treatment Options for Hip Tendonitis: Treatment for hip tendonitis aims to reduce pain and inflammation, improve hip function, and prevent recurrence. Common treatment options include:
6. Rest and activity modification: Avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms and modifying daily activities to reduce stress on the hip tendons.
7. Ice therapy: Applying ice packs to the affected area can help reduce pain and inflammation.
8. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter or prescription medications such as ibuprofen or naproxen may help alleviate pain and inflammation.
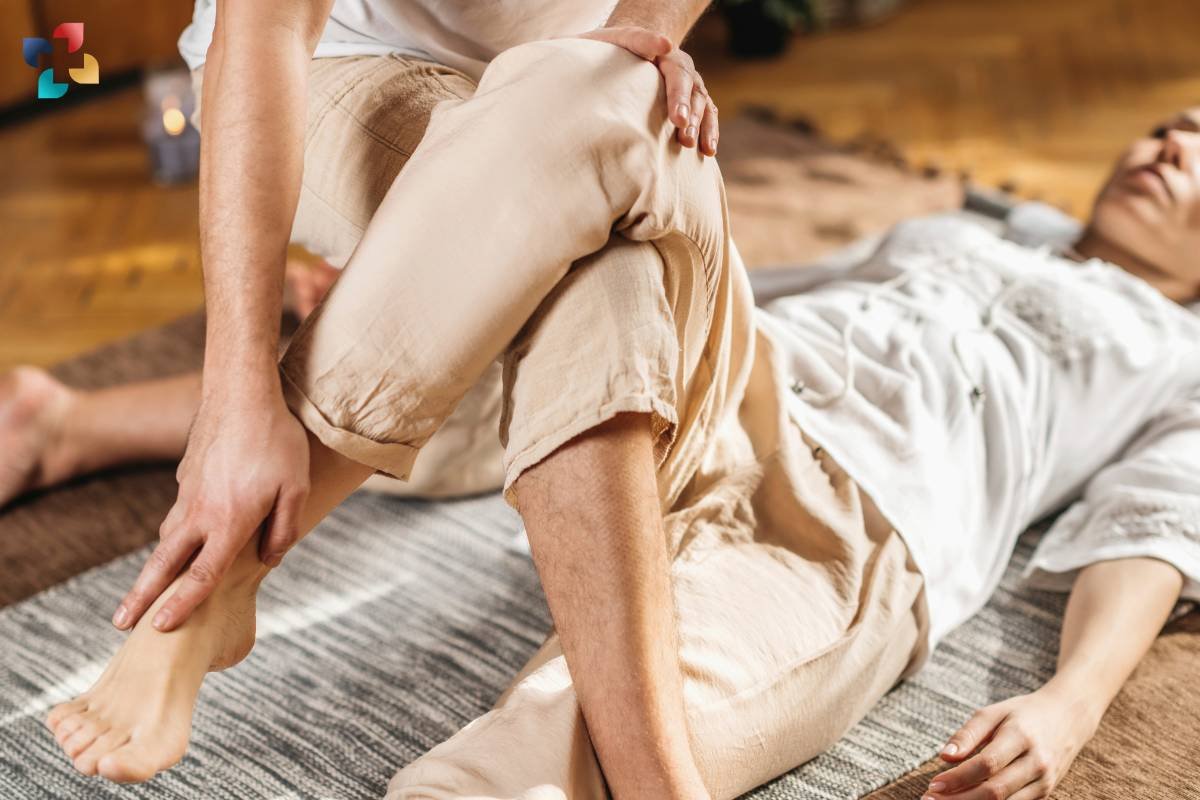
9. Physical therapy: Specific exercises and stretches can help strengthen the hip muscles, improve flexibility, and correct muscle imbalances.
10. Corticosteroid injections: Injections of corticosteroids directly into the hip joint can provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation.
11. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT): ESWT uses shockwave energy to stimulate healing in the affected tendons and reduce pain.

12. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy: PRP therapy involves injecting concentrated platelets from the patient’s own blood into the affected area to promote tissue repair and regeneration.
13. Surgical intervention: In severe cases of hip tendonitis that do not respond to conservative treatment, surgery may be recommended to repair or remove damaged tendon tissue.
Preventive Measures for Hip Tendonitis:
Preventing hip tendinitis involves adopting healthy lifestyle habits and minimizing risk factors for tendon injury. Some preventive measures include:
1. Gradual progression of activity: Avoid sudden increases in physical activity intensity or duration to prevent overuse injuries.
2. Proper warm-up and stretching: Always warm up before exercise and incorporate dynamic stretching exercises to prepare the hip muscles and tendons for activity.
3. Strength training: Regular strength training exercises targeting the hip muscles can help improve muscle strength, stability, and resilience.
4. Correct biomechanics: Maintain proper posture and alignment during daily activities and sports to reduce stress on the hip tendons.
5. Adequate rest and recovery: Allow sufficient time for rest and recovery between workouts to prevent overuse injuries and promote tissue repair.
Conclusion
Hip tendonitis is a common orthopedic condition characterized by inflammation or irritation of the tendons surrounding the hip joint. It can cause pain, stiffness, and limited range of motion, impacting daily activities and quality of life. However, with proper diagnosis, treatment, and preventive measures, individuals can effectively manage hip tendinitis and return to an active lifestyle.
By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures for hip tendinitis, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their hip health and reduce the risk of injury. If experiencing symptoms of hip pain or discomfort, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan tailored to individual needs.
With proper care and management, individuals can overcome hip tendinitis and enjoy improved hip function, reduced pain, and enhanced overall well-being.
FAQs
1. What causes hip tendonitis?
Hip tendonitis can be caused by factors such as overuse or repetitive movements, muscle imbalances, poor posture, trauma or injury, and aging.
2. What are the symptoms of hip tendonitis?
Common symptoms of hip tendinitis include pain or tenderness around the hip joint, stiffness or reduced range of motion, swelling or warmth in the affected area, weakness or instability in the hip muscles, and clicking or snapping sensations during movement.
3. How is hip tendonitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis of hip tendonitis typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional, including a medical history review, physical examination, imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI, and sometimes diagnostic injections to confirm the diagnosis.
4. What are the treatment options for hip tendonitis?
Treatment for hip tendinitis may include rest and activity modification, ice therapy, NSAIDs, physical therapy, corticosteroid injections, shockwave therapy, PRP therapy, and in severe cases, surgical intervention.
5. How can hip tendonitis be prevented?
Preventive measures forhip tendinitis include gradual progression of activity, proper warm-up and stretching, strength training exercises, maintaining correct biomechanics, and allowing adequate rest and recovery between workouts.