Carpal bones are essential components of the human hand’s intricate skeletal structure, playing a crucial role in supporting hand movement, flexibility, and stability. Comprising eight small bones arranged in two rows, the carpal bones form the wrist joint and serve as a bridge between the forearm and the hand. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the anatomy, function, and significance of carpal bones in the human hand, shedding light on their importance in everyday activities and clinical contexts.
Anatomy of Carpal Bones:
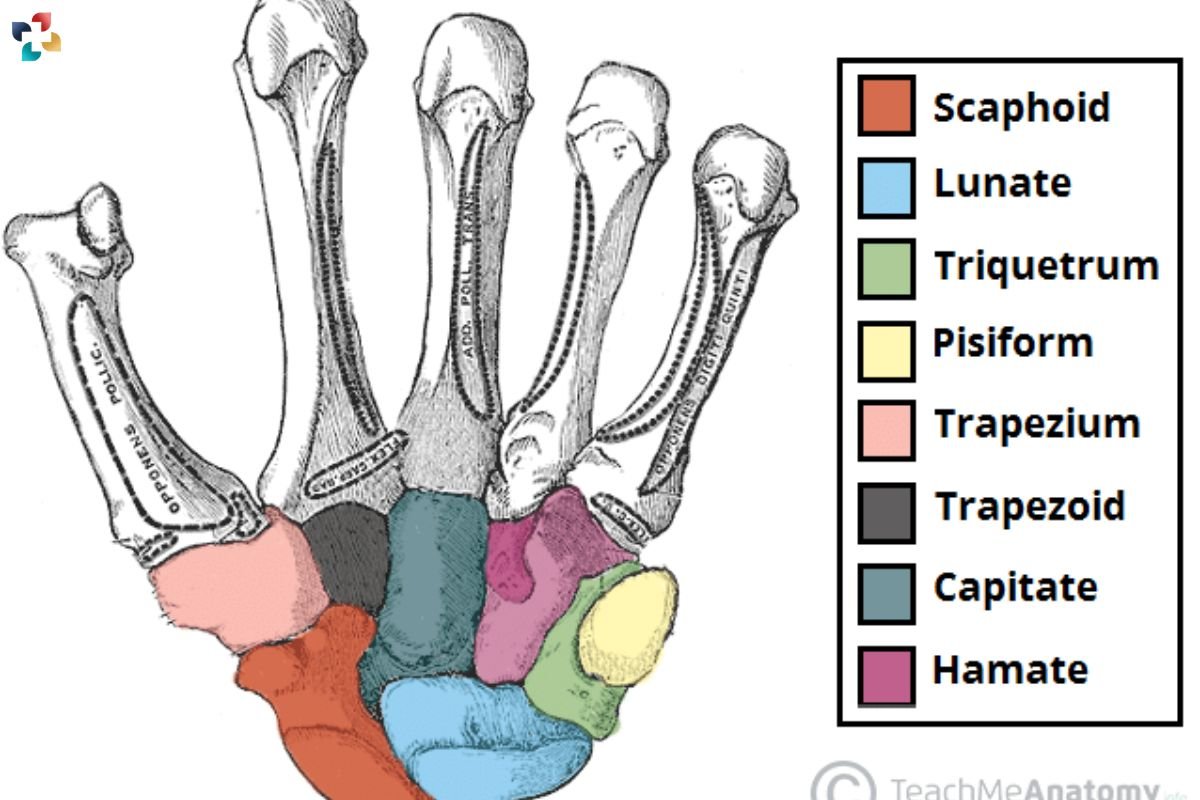
The carpal bones are divided into two rows: the proximal row, which articulates with the radius and ulna of the forearm, and the distal row, which forms the foundation for the palm of the hand. The proximal row consists of the scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, and pisiform bones, while the distal row comprises the trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate bones.
The arrangement of carpal bones allows for the intricate movements of the hand and wrist, providing both stability and flexibility. The proximal row, located closer to the forearm, articulates with the radius and ulna, forming the radiocarpal joint, which allows for flexion, extension, and radial/ulnar deviation of the wrist. The distal row, positioned towards the palm, forms the foundation for the metacarpal bones of the hand, facilitating precise movements and grip strength.

Each carpal bone has unique features and functions. For example, the scaphoid and lunate bones are critical for wrist stability and coordination, while the capitate and hamate bones provide support for the palm and assist in transferring forces from the forearm to the hand during gripping and grasping activities. Understanding the anatomy and function of these bones is essential for healthcare professionals involved in diagnosing and treating conditions affecting the hand and wrist.
Function of Carpal Bones:
Carpal bones play a pivotal role in facilitating various movements of the hand and wrist, including flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and circumduction. Additionally, they provide stability and support to the wrist joint, allowing for precise and coordinated movements during everyday activities such as grasping, gripping, and manipulating objects. The unique arrangement of carpal bones enables the hand to perform a wide range of tasks with remarkable dexterity and precision.
Furthermore, the carpal bones serve as attachment sites for ligaments, tendons, and muscles that contribute to hand and wrist movement. Ligaments connect the these bones to each other and to the radius, ulna, and metacarpal bones, providing stability to the wrist joint and preventing excessive movement. Tendons of the forearm muscles pass through the carpal tunnel, a narrow passageway formed by the carpal bones and the transverse carpal ligament, to insert onto the hand and finger bones, allowing for the transmission of forces and generation of grip strength.
In addition to supporting movement and stability, the carpal bones also play a crucial role in distributing forces across the hand and wrist during activities such as weight-bearing or impact loading. By distributing forces evenly and dissipating mechanical stress, the carpal bones help prevent injury and maintain the structural integrity of the hand and wrist complex.
Overall, the functional significance of carpal bones cannot be overstated. Their unique anatomy and biomechanical properties enable the hand to perform intricate tasks with precision and efficiency while providing stability and support to the wrist joint. Understanding the role of carpal bones in hand and wrist function is essential for healthcare professionals involved in diagnosing and treating conditions affecting these structures, as well as for individuals seeking to optimize hand health and performance in everyday activities.
Significance of Carpal Bones:
The proper alignment and function of carpal bones are essential for maintaining hand and wrist health and preventing musculoskeletal disorders such as carpal tunnel syndrome, arthritis, and fractures. Understanding the anatomy and biomechanics of carpal bones is crucial for healthcare professionals involved in diagnosing and treating conditions affecting the hand and wrist. Additionally, athletes, musicians, and individuals engaged in repetitive hand movements can benefit from knowledge about carpal bone anatomy to prevent injuries and optimize performance.
Clinical Relevance of Carpal Bones:
Carpal bone injuries and disorders are common in clinical practice and can significantly impact hand function and quality of life. Fractures, dislocations, ligament injuries, and degenerative conditions affecting the carpal bones require prompt diagnosis and appropriate management to prevent complications and facilitate optimal recovery. Imaging modalities such as X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and computed tomography (CT) scans play a crucial role in evaluating carpal bone injuries and guiding treatment decisions.

Prompt and accurate diagnosis of carpal bone injuries and disorders is essential for effective management and optimal outcomes. Fractures, which can occur as a result of trauma or repetitive stress, may require immobilization, splinting, or surgical intervention, depending on the severity and location of the fracture. Dislocations, where the bones of the wrist become displaced from their normal position, often necessitate immediate reduction and stabilization to restore normal joint alignment and function.
Ligament injuries, such as sprains or tears, can lead to instability and functional impairment of the wrist joint. Rehabilitation and targeted exercises may be prescribed to restore strength and mobility, while severe cases may require surgical repair or reconstruction. Degenerative conditions affecting the carpal bones, such as osteoarthritis or Kienböck’s disease, may result in chronic pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion. Treatment options may include medication, physical therapy, splinting, or surgery to alleviate symptoms and preserve joint function.
Overall, effective management of carpal bone injuries and disorders requires a multidisciplinary approach involving orthopedic surgeons, hand therapists, radiologists, and other healthcare professionals. By leveraging advanced imaging techniques and evidence-based treatment strategies, clinicians can optimize outcomes and improve the quality of life for individuals affected by carpal bone conditions.

Unlocking the Power of Biceps Brachii: A Comprehensive Guide
In this comprehensive guide, we delve deep into the anatomy, function, exercises, and common injuries associated with the biceps brachii.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, carpal bones are indispensable components of the human hand’s skeletal framework, contributing to its remarkable flexibility, stability, and functionality. Understanding the anatomy, function, and clinical significance of carpal bones is essential for healthcare professionals involved in diagnosing and treating conditions affecting the hand and wrist. By appreciating the intricate interplay between carpal bones and surrounding structures, we can better comprehend the complexities of hand movement and effectively manage conditions that impact hand health and function.