“Muscles are built in the gym, but they grow in the kitchen.”
If you’re trying to build muscle, protein is your best friend. Every time you lift weights or push through a tough workout, tiny tears form in your muscle fibers. Your body repairs those tears with the help of protein, and that’s how muscles grow stronger and bigger.
Simply put, without enough protein, your hard work in the gym doesn’t pay off.
A recent study by the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition found that people who ate 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily gained up to 25% more lean muscle than those who didn’t eat enough. That’s a huge difference and proof that protein isn’t just a trend; it’s science.
But here’s where things get confusing. Walk into any supplement store and you’ll see hundreds of options: whey, casein, soy, pea, hemp, and more. They all promise muscle growth, but not all proteins work the same way. Some digest fast and are great after workouts, while others work slowly and help your body recover overnight.
In this blog, we’ll break down the best protein for building muscle, backed by science and explained in simple terms. You’ll learn which type of protein fits your lifestyle, when to take it, and how much your body really needs to see results.
So, if you’re ready to stop guessing and start growing, let’s dive into the truth behind protein and how it can transform your fitness journey.
Understanding How the Best Protein For Building Muscle Works
When you hit the gym, your muscles go through stress; those heavy lifts and resistance workouts cause tiny tears in your muscle fibers. This might sound bad, but it’s actually the key to growth. Your body repairs these microtears using amino acids, the building blocks of protein. Over time, this repair process makes your muscles stronger, thicker, and more defined.
Think of protein as the “construction material” your body needs to rebuild what the workout breaks down. Without enough of it, you’ll recover more slowly, feel more sore, and miss out on the gains you worked so hard for.
The Science Behind the Best Protein For Building Muscle

When you eat protein, whether from food or a supplement, your body breaks it down into amino acids. These amino acids then trigger muscle protein synthesis (MPS), which is your body’s process of repairing and growing muscle tissue.
Research shows that after a workout, your muscles are like sponges; they absorb nutrients faster than usual. This is often called the “anabolic window.” Eating or drinking a protein source within 30–60 minutes after your workout helps kickstart recovery and maximize growth.
How Much Protein Do You Really Need?
The ideal protein intake depends on your body weight and activity level. Here’s a quick look:
| Activity Level | Protein Needed per kg of Body Weight | Example (70 kg Person) |
| Sedentary (Little activity) | 0.8g | 56g/day |
| Regular workouts (3–4 days/week) | 1.2–1.6g | 84–112g/day |
| Intense training or bodybuilding | 1.6–2.2g | 112–154g/day |
Most fitness experts agree that staying around 1.6 to 2 grams per kilogram of body weight is the sweet spot for building muscle efficiently.
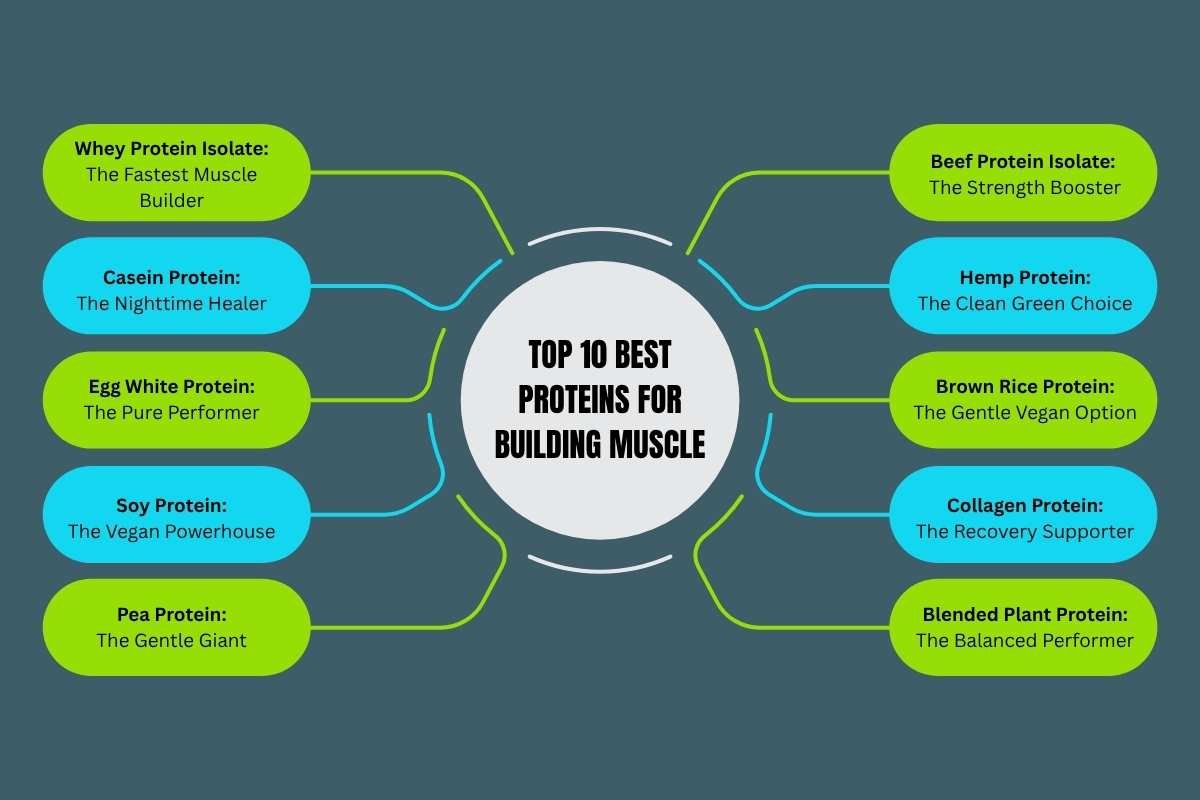
Here are the Top 10 Best Proteins for Building Muscle (2025 Edition)
Now that you understand how protein helps you build muscle, let’s talk about the real question: what’s the best protein for building muscle in 2025?
With so many options out there, finding the right one can feel overwhelming. Some are fast-digesting for quick recovery, others are slow and steady for overnight repair. The trick is to know which fits your goals, diet, and lifestyle.
Here’s a breakdown of the top protein types trusted by athletes, trainers, and nutrition experts around the world:
| Protein Type | Digestibility | Protein % (Approx.) | Best Timeto Take | Ideal For | Unique Benefit |
| Whey Isolate | Fast | 90% | Post-workout | Muscle gain | High leucine content |
| Casein | Slow | 80% | Before bed | Recovery | Overnight muscle repair |
| Egg White | Moderate | 85% | Morning | Lean gain | Pure and lactose-free |
| Soy | Moderate | 80% | Anytime | Vegans | Complete plant protein |
| Pea | Moderate | 75% | Post-workout | Vegans | High in arginine & iron |
| Beef Isolate | Fast | 90% | Post-workout | Strength | Natural creatine content |
| Hemp | Slow | 65% | Morning | Sustainable users | Omega-3s and fiber-rich |
| Brown Rice | Moderate | 70% | Post-meal | Allergy-prone | Gentle digestion |
| Collagen | Fast | 90% | Anytime | Recovery | Joint and tendon support |
| Blended Plant | Moderate | 75–80% | Anytime | Vegans | Balanced amino profile |
No matter which you choose, remember: the best protein for building muscle is the one your body digests well, fits your diet, and keeps you consistent. The real secret isn’t just what protein you take, it’s how regularly you take it. Let’s break down the top 10 proteins that truly deliver results more descriptively:
1. Whey Protein Isolate: The Fastest Muscle Builder
Known as the king of muscle proteins, whey isolate is a gym essential for a reason. It digests quickly in under 30 minutes and contains about 90% pure protein. It’s rich in leucine, the amino acid that kickstarts muscle repair after workouts.
A 2024 Sports Nutrition Review found that athletes using whey isolate post-training experienced 22% faster recovery compared to those using standard whey concentrate.
| Best for | Post-workout recovery and lean muscle gain |
| Why it stands out | Extremely low in carbs and lactose, great for those who want pure results. |
| Pro tip | Take one scoop within 30 minutes after your workout to maximize gains. |
2. Casein Protein: The Nighttime Healer
Casein works opposite to whey; it digests slowly, feeding your muscles gradually for 6–8 hours. This makes it perfect before bedtime. It prevents muscle breakdown during sleep, when your body naturally enters repair mode.
Studies show that consuming 40g of casein before bed enhances overnight muscle synthesis by nearly 34%.
| Best for | Overnight recovery and preventing muscle loss |
| Why it stands out | Sustained release keeps your muscles nourished while you rest. |
| Pro tip | Mix it with milk or oats for a creamy, slow-digesting shake. |
3. Egg White Protein: The Pure Performer
Egg whites are one of nature’s most complete protein sources. They have a biological value of 100, meaning your body uses them almost entirely for muscle growth. They’re also naturally fat-free and lactose-free. In fact, research shows that egg protein stimulates nearly the same muscle-building response as whey.
Egg protein ranks high among the best proteins for building muscle because of its perfect amino acid balance and high biological value. It’s cholesterol-free, lactose-free, and ideal for individuals who want a clean protein source with excellent digestibility. Moreover, it contains leucine, one of the most crucial amino acids for muscle growth.
| Best for | Lean muscle gain and lactose-intolerant individuals |
| Why it stands out | All-natural, pure, and easily absorbed. |
| Pro tip | Ideal for early mornings or between meals. |
4. Soy Protein: The Vegan Powerhouse
Soy protein is one of the few plant-based options that’s a complete protein; it has all nine essential amino acids. It’s rich in BCAAs and supports both muscle recovery and heart health.
A 2023 study in the Nutrients Journal found that soy protein helped athletes gain muscle comparable to whey when taken in equal amounts.
| Best for | Vegans and vegetarians looking for a balanced source |
| Why it stands out | High in antioxidants and cholesterol-friendly. |
| Pro tip | Combine it with regular resistance training for optimal results. |
5. Pea Protein: The Gentle Giant
Pea protein is quickly becoming a favorite in the fitness world. It’s high in arginine, which boosts blood flow and muscle pumps, and contains plenty of iron for energy. Plus, it’s very easy to digest and allergen-free.
A 2024 study by Sports Medicine Today showed pea protein users gained the same muscle thickness as those consuming whey after 12 weeks of training.
| Best for | Vegans, beginners, and those with sensitive stomachs |
| Why it stands out | Eco-friendly and clean, without additives. |
| Pro tip | Combine it with rice protein for a complete amino acid profile. |
6. Beef Protein Isolate: The Strength Booster
If you want animal-based power without dairy, this one’s for you. Beef protein isolate offers high protein content with collagen peptides that support both muscle and joint recovery. It’s Paleo-friendly and easy to digest.
Beef protein ranks among the best proteins for building muscle due to its dense nutrient content and naturally occurring creatine. It fuels muscle cells for high-intensity performance and strength gains. Unlike whey, it’s lactose-free, making it suitable for individuals sensitive to dairy-based proteins.
| Best for | Strength trainers and dairy-free athletes |
| Why it stands out | Contains natural creatine — helping boost energy and endurance. |
| Pro tip | Each serving packs nearly the same amino profile as a 4-oz steak! |
7. Hemp Protein: The Clean Green Choice
Hemp protein is made from nutrient-rich hemp seeds, making it one of the cleanest, most sustainable proteins out there. It’s packed with omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and magnesium, all great for recovery and heart health.
Among the best proteins for building muscle, hemp protein stands out for its natural omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, fiber, and minerals. While slightly lower in protein concentration, it provides powerful anti-inflammatory benefits that accelerate muscle recovery and joint health. Its nutrient profile also enhances overall energy metabolism and stamina.
| Best for | Eco-conscious and health-focused individuals |
| Why it stands out | Boosts energy and reduces inflammation naturally. |
| Pro tip | Great for adding to smoothies or breakfast bowls. |
8. Brown Rice Protein: The Gentle Vegan Option
Brown rice protein is hypoallergenic, meaning it’s safe for people with dairy, gluten, or soy allergies. It’s easy to digest and supports consistent muscle repair. When combined with pea protein, it becomes a complete protein source.
| Best for | Sensitive stomachs and allergy-prone users |
| Why it stands out | Low in fat and naturally gluten-free. |
| Pro tip | Use it as a post-meal shake to maintain muscle recovery. |
9. Collagen Protein: The Recovery Supporter
While collagen isn’t a direct muscle builder, it’s vital for overall recovery. It strengthens tendons, ligaments, and connective tissue, all of which support heavier training and prevent injury.
| Best for | Recovery, joint strength, and long-term muscle support |
| Why it stands out | Helps you train harder and recover faster. |
| Pro tip | Mix it with other proteins like whey or casein for a complete blend. |
10. Blended Plant Protein: The Balanced Performer
Blended proteins combine pea, rice, chia, and hemp, giving you the best of all worlds. They deliver a balanced amino acid profile and steady energy. They’re also easy to digest and ideal for long-term use.
| Best for | Vegans and anyone seeking an all-in-one formula |
| Why it stands out | Balanced nutrition with natural vitamins and minerals. |
| Pro tip | Look for blends with 20–25g protein per serving and low sugar content. |
Also Read:
- 15 Best Tasting Protein Shakes That Make Dieting Feel Like Having Dessert
- Can Protein Supplements for Vegetarians Help Build Muscles? The Answer Might Shock You!
- High-Protein Diet Plan: Benefits, Foods, and How to Get Started
Major Types of Proteins and Their Fascinating Functions
Before diving deeper into how proteins impact our health and daily life, let’s take a quick look at the main types of proteins that drive essential biological processes in the human body.
Each of these proteins serves a unique purpose, from building muscle fibers to carrying oxygen and defending against pathogens.
Key Types of Proteins and Their Core Functions:
| Protein Type | Primary Function | Examples | Interesting Fact |
| Structural Proteins | Provide strength and support to cells and tissues | Collagen, Keratin, Elastin | Collagen makes up about 30% of the body’s total protein; it’s literally the body’s glue! |
| Enzymatic Proteins | Speed up chemical reactions in the body | Amylase, Lipase, Pepsin | Without enzymes, digestion would take weeks instead of hours. |
| Transport Proteins | Carry essential molecules like oxygen and nutrients | Hemoglobin, Albumin, Myoglobin | Hemoglobin can carry four oxygen molecules at once, a true biological powerhouse. |
| Defensive Proteins | Protect the body from infections and foreign invaders | Antibodies, Complement Proteins | Antibodies remember past infections; that’s how vaccines help build immunity. |
| Contractile Proteins | Enable movement by contracting and relaxing muscle fibers | Actin, Myosin | Every heartbeat is powered by these proteins working in perfect coordination. |
| Storage Proteins | Store vital nutrients and minerals | Ferritin, Casein, Ovalbumen | Ferritin stores iron in the liver, ensuring your body never runs short of it. |
| Signaling Proteins | Help transmit messages between cells | Insulin, Growth Hormones | Insulin not only regulates sugar, it communicates directly with your body’s energy system. |
These protein categories together form the biological backbone of life, ensuring our systems function in perfect harmony, from cellular repair to immunity and energy metabolism.
The Role of Proteins in Human Health
Proteins are not just building blocks; they’re active participants in nearly every biological process that defines human life. From repairing damaged tissues to fueling metabolic functions, these molecules are what keep the body balanced, energized, and resilient.
1. Muscle Growth and Repair
Whenever you lift weights, go for a run, or even perform simple physical tasks, tiny muscle fibers experience micro-tears. Proteins, especially those rich in amino acids like myosin and actin, immediately step in to rebuild and strengthen these fibers. This is why athletes and fitness enthusiasts prioritize high-protein diets: it’s nature’s own recovery formula. The human body recycles nearly 250 grams of protein every day, constantly breaking down and rebuilding muscle tissues.
2. Hormonal Balance and Communication
Certain proteins act as messengers that maintain communication between organs and systems. For instance, insulin, a signaling protein, regulates glucose levels and ensures that cells receive the energy they need. Similarly, growth hormones play a central role in cellular regeneration and physical development. Without these protein-based messengers, the body’s internal communication network would collapse, leading to metabolic imbalances and fatigue.
3. Immunity and Defense Mechanisms
Your immune system’s frontline warriors, antibodies, are all made of proteins. They identify harmful pathogens, such as bacteria and viruses, and neutralize them before they cause damage. These antibodies also develop “memory,” which is how vaccines provide long-term protection against diseases. Studies reveal that people with low protein intake are more prone to infections, slower recovery rates, and overall weakened immunity.
4. Enzyme Activity and Digestion
Every metabolic reaction in your body relies on enzymes, which are specialized proteins. Enzymes like amylase, lipase, and pepsin help break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into absorbable nutrients. Without enzymes, digestion would take weeks, quite literally! Even beyond digestion, enzymes regulate everything from DNA replication to energy conversion at the cellular level, making them indispensable for survival.
5. Energy and Nutrient Storage
When your body runs low on carbohydrates or fats, it turns to proteins as an alternate energy source. Storage proteins like ferritin and casein also act as nutrient reservoirs, ensuring essential minerals and amino acids are available when needed. During prolonged fasting, the body’s metabolism intelligently shifts to use stored proteins for energy to preserve vital organ function.
6. Maintaining Structural Integrity
From the elasticity of your skin to the strength of your tendons, structural proteins like collagen and keratin hold everything together. Collagen, for example, forms about 75% of your skin’s dry weight, contributing to firmness and youthfulness. As we age, collagen production declines, leading to wrinkles and joint stiffness, which is why many health experts recommend collagen-rich foods or supplements to support healthy aging.
7. Cellular Transport and Oxygen Delivery
Hemoglobin, the iron-rich protein in red blood cells, carries oxygen from the lungs to every cell in your body. Without it, your tissues would be starved of oxygen, and energy production would plummet. In addition, albumin helps transport hormones, vitamins, and drugs through the bloodstream, making it one of the most versatile proteins in the human system.
Dietary Sources of the Best Protein For Building Muscle
Now that you understand how crucial protein is for building and maintaining muscle, let’s look at where you can actually get it. Whether you’re a non-vegetarian, vegetarian, or vegan, there’s a protein source for everyone, and knowing which ones give you the best “muscle return” for your meal is key.
The Top Protein Sources are mentioned in the table below:

| Food Source | Protein (per 100g) | Notable Benefit |
| Chicken Breast | 31g | Lean muscle building |
| Salmon | 25g | Anti-inflammatory, omega-3 boost |
| Eggs | 13g | Complete protein, fast absorption |
| Greek Yogurt | 10g | Digestive health, recovery |
| Lentils | 9g | Vegetarian, high in fiber |
| Cottage Cheese | 11g | Slow-digesting protein |
| Nuts & Seeds | 6–8g (per 30g) | Energy and healthy fats |
| Tofu & Tempeh | 8–15g | Complete vegan protein |
| Milk | 8g (per 250ml) | Balanced recovery support |
| Lean Beef | 26g | Iron and creatine source |
1. Chicken Breast — The Classic Muscle Fuel
Chicken breast has long been the gold standard for anyone serious about gaining lean muscle. It’s low in fat, high in protein, and extremely versatile. A single chicken breast can provide almost half of your daily protein requirement for an average adult.
2. Salmon — Protein Meets Omega-3 Power
Salmon not only delivers high-quality protein but also offers omega-3 fatty acids, which reduce inflammation and improve muscle repair after workouts. According to a study in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, omega-3s can increase muscle protein synthesis by up to 30% post-exercise.
3. Eggs — The Perfect Protein
Eggs are one of the most bioavailable sources of protein, meaning your body can absorb and use them efficiently. The protein in eggs has a biological value of 100, which is considered the gold standard against which other proteins are measured.
4. Greek Yogurt — Creamy, Powerful, and Packed
Greek yogurt is an excellent option for those who want both taste and nutrition. It’s higher in protein than regular yogurt and contains probiotics that support digestion.
5. Lentils — A Vegetarian Powerhouse
Don’t underestimate lentils; they’re one of the best plant-based proteins you can eat. Along with protein, they offer fiber, iron, and slow-digesting carbs that provide steady energy.
6. Cottage Cheese — Slow and Steady Muscle Support
Cottage cheese is rich in casein protein, which digests slowly, providing a steady stream of amino acids to muscles, perfect before bedtime.
7. Nuts and Seeds — Tiny But Mighty
Almonds, peanuts, chia seeds, and pumpkin seeds are compact protein bombs loaded with healthy fats and fiber. Soaking nuts overnight can improve nutrient absorption and make them easier to digest.
8. Tofu and Tempeh — The Vegan Muscle Builders
Made from soybeans, tofu, and tempeh are excellent sources of complete plant-based protein, containing all nine essential amino acids.
9. Milk — The Old-School Recovery Drink
Milk provides both whey and casein, making it one of the most balanced protein sources. The whey digests quickly for instant recovery, while casein works slowly for long-term support.
10. Lean Beef — The Strength Staple
Lean beef not only supplies top-quality protein but also delivers creatine and iron, both essential for performance and endurance.
Why the Best Protein For Building Muscle Depends on Timing?
Ever wondered when the perfect time is to have your protein shake or meal? While there’s no single magic minute, timing your protein intake can make a noticeable difference in muscle growth, recovery, and overall results.
Let’s break it down simply:
1. Morning — Kickstart Your Metabolism
After 7–8 hours of sleep, your body is in a mild fasting state. This means your muscles have gone without nutrients for quite a while. Consuming protein first thing in the morning helps stop muscle breakdown and restarts your metabolism.
Best options:
- Scrambled eggs or an omelet
- A protein smoothie with milk, banana, and oats
- Greek yogurt with nuts and berries
Research published in The Journal of Nutrition found that eating a high-protein breakfast (30g or more) helps control hunger, boosts energy, and improves muscle protein synthesis compared to a low-protein one.
2. Pre-Workout — Fuel Your Muscles
Having protein before your workout gives your muscles the amino acids they need during exercise, reducing fatigue and preventing muscle breakdown.
- Ideal window: 1–2 hours before training
- Try this:
- Chicken and brown rice
- Greek yogurt with fruit
- A small protein shake with oats
A 2017 study from Sports Medicine showed that athletes who consumed protein before workouts saw a 10–15% improvement in muscle endurance over time.
3. Post-Workout — The Anabolic Window
This is the most crucial time for muscle repair. After your workout, your muscles act like a sponge, eagerly absorbing nutrients to rebuild and grow stronger.
- Ideal window: Within 30–60 minutes after your session
- Best options:
- Whey protein shake (fast-digesting)
- Chicken or tofu stir-fry with rice
- Scrambled eggs on whole-grain toast
Consuming protein right after training can increase muscle synthesis by up to 30% compared to waiting several hours, according to studies in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
4. Before Bed — Overnight Recovery
While you sleep, your body continues repairing and rebuilding muscle tissues. A slow-digesting protein like casein helps supply amino acids throughout the night, reducing overnight muscle loss.
Best options:
- Cottage cheese
- Casein protein shake
- A glass of milk before bed
Studies from Maastricht University found that consuming 40g of casein protein before sleep enhances overnight recovery and promotes greater muscle mass over time.
5. Throughout the Day — Consistent Gains
Instead of eating large amounts of protein in one go, spreading it evenly throughout the day helps keep your muscles in an “anabolic” or growth-supportive state.
Tip: Aim for 25–30g of protein every 3–4 hours through meals and snacks.
Also Read:
- Best body-building meals to increase your muscle
- How to Build Lean Muscle – The Ultimate Guide
- Fueling Gains: Unlocking the Power of a Vegetarian Diet for Bodybuilding
Busting Myths About the Best Protein For Building Muscle
There’s a lot of noise around protein, from gym locker talk to flashy supplement ads. But not everything you hear about building muscle is true. Let’s clear up some of the most common myths and get the facts straight once and for all.
Myth 1: “More Protein Means More Muscle”
Truth: Your body can only use a certain amount of protein at a time. Eating excess doesn’t mean you’ll suddenly bulk up faster; instead, the extra protein might just be used for energy or stored as fat. Most studies show that consuming 1.6–2.2g of protein per kg of body weight is enough for optimal muscle growth. Going beyond that brings little to no added benefit.
Myth 2: “You Need Protein Shakes to Build Muscle”
Truth: Protein shakes are convenient but not mandatory. You can easily meet your protein goals through whole foods like eggs, chicken, lentils, tofu, and yogurt. Think of protein powders as a supplement, not a replacement. They’re great when you’re short on time or need a quick recovery boost after workouts.
Myth 3: “Vegetarians Can’t Build Muscle”
Truth: Total myth! Plant-based eaters can absolutely build muscle; it’s all about combining the right foods to get all essential amino acids. Lentils, chickpeas, soy, quinoa, and peas are excellent options. A study from the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition found that plant-based athletes gained similar muscle mass as meat eaters when their total protein intake was matched.
Conclusion
Building muscle isn’t just about lifting—it’s about fueling right. The best protein for building muscle provides the amino acids your body needs to repair, recover, and grow stronger. Whether you choose whey, eggs, tofu, or cottage cheese, consistency is what turns effort into transformation.
Aim for 1.6–2.2g of protein per kg of body weight daily, spaced throughout your meals. Combine that with progressive workouts, proper sleep, and hydration, and you’ll see lasting strength and definition.
Remember, the best protein for muscle isn’t a secret—it’s a smart, science-backed choice you make every day.