Modern medicine has been revolutionized by high-quality medical implants, offering hope and improved mobility to millions worldwide. These implants range from orthopedic screws that help heal broken bones to advanced heart devices that help control heartbeats. The development of these implants highlights the importance of safety, compatibility with the body, and new technologies.
Through this article, we will learn more about what makes an implant “high-quality”, the latest advancements in materials and design, the regulatory standards that ensure safety, and how these elements work together to improve patient outcomes
What Are High-Quality Medical Implants?
These are devices or prosthetics placed inside the body to replace, support, or enhance biological structures. They are distinguished by their durability, biocompatibility, and ability to integrate seamlessly with human tissue, minimizing complications and maximizing function. These implants range from orthopedic devices like hip and knee replacements to cardiac pacemakers, dental implants, and cosmetic enhancements.
Key Characteristics of High-Quality Medical Implants
- Biocompatibility: The implant must not trigger adverse immune responses or toxicity.
- Mechanical Strength: It should withstand the physical stresses and strains of daily activities.
- Corrosion Resistance: Essential for long-term function, especially in moist, biological environments.
- Precision Engineering: Accurate sizing and shaping ensure optimal fit and function.
- Longevity: These implants are designed to last, reducing the need for revision surgeries.
Materials Used in High-Quality Medical Implants
The choice of materials is central to the performance and safety of these implants. The most common materials include:
- Titanium and Titanium Alloys: Titanium, especially the Ti-6Al-4V ELI alloy, is widely used due to its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. Its organic oxide layer further enhances biocompatibility and inhibits corrosion, making it ideal for orthopedic and dental implants.
- Stainless Steel: Frequently used for temporary implants or in situations where cost is a concern. Stainless steel is durable, non-magnetic, and resists infection, but may not offer the same longevity as titanium.
- Cobalt-Chromium Alloys: Not magnetic and highly resistant to wear and high temperatures, cobalt-chromium alloys are often used in joint replacements for their durability.
- Polymers: High-density polyethylene is used for artificial limbs and joint surfaces due to its durability and low cost. Polymers can be reinforced with carbon fiber for additional strength.
- Ceramics: Known for their wear resistance and biocompatibility, ceramics are used in joint replacements, especially for surfaces that experience repeated motion.
- Bioactive Materials: Compounds like hydroxyapatite promote bone growth and integration, enhancing the long-term reliability of implants.
Types of High-Quality Medical Implants
| Implant Type | Typical Materials | Common Uses |
| Orthopedic Screws | Titanium, Stainless Steel | Bone fixation, fracture repair |
| Joint Prostheses | Titanium, Cobalt-Chromium, Ceramics | Hip, knee, shoulder replacements |
| Dental Implants | Titanium | Tooth root replacement |
| Cardiac Devices | Titanium, Polymers | Pacemakers, defibrillators |
| Cosmetic Implants | Silicone, Polymers | Breast, facial, and other enhancements |
Regulatory Standards for High-Quality Medical Implants
Safety and efficacy are paramount in the development and use of these implants. Regulatory bodies such as the FDA and international organizations like ISO set stringent standards:
- ISO 14708 Series: Specifies general and device-specific requirements for active implantable medical devices, including cardiac pacemakers and circulatory support devices. These standards mandate rigorous testing for safety, performance, and labeling.
- ISO 20417: Outlines requirements for information supplied by manufacturers, including identification, labeling, and packaging.
- FDA Approval: In the United States, the FDA evaluates implants for safety, effectiveness, and manufacturing quality before they reach the market.
Compliance with these standards ensures that only high-quality medical implants are used in patient care, minimizing risks and enhancing outcomes.
Advancements in High-Quality Medical Implants
Recent years have witnessed remarkable progress in the field of medical implants, driven by advances in materials science, engineering, and biotechnology:
- Surface Engineering: Innovative surface treatments minimize inflammation and promote bone cell adhesion, improving implant integration and longevity.
- 3D Printing: Custom implants can be designed and manufactured rapidly, tailored to individual patient anatomy for a perfect fit.
- Smart Implants: Devices embedded with sensors can monitor healing, detect infection, and even deliver medication, offering real-time data to clinicians.
- Bioactive Coatings: Coating implants with substances like hydroxyapatite encourages bone growth and secure attachment, reducing the risk of loosening or failure.
Patient Outcomes and Benefits
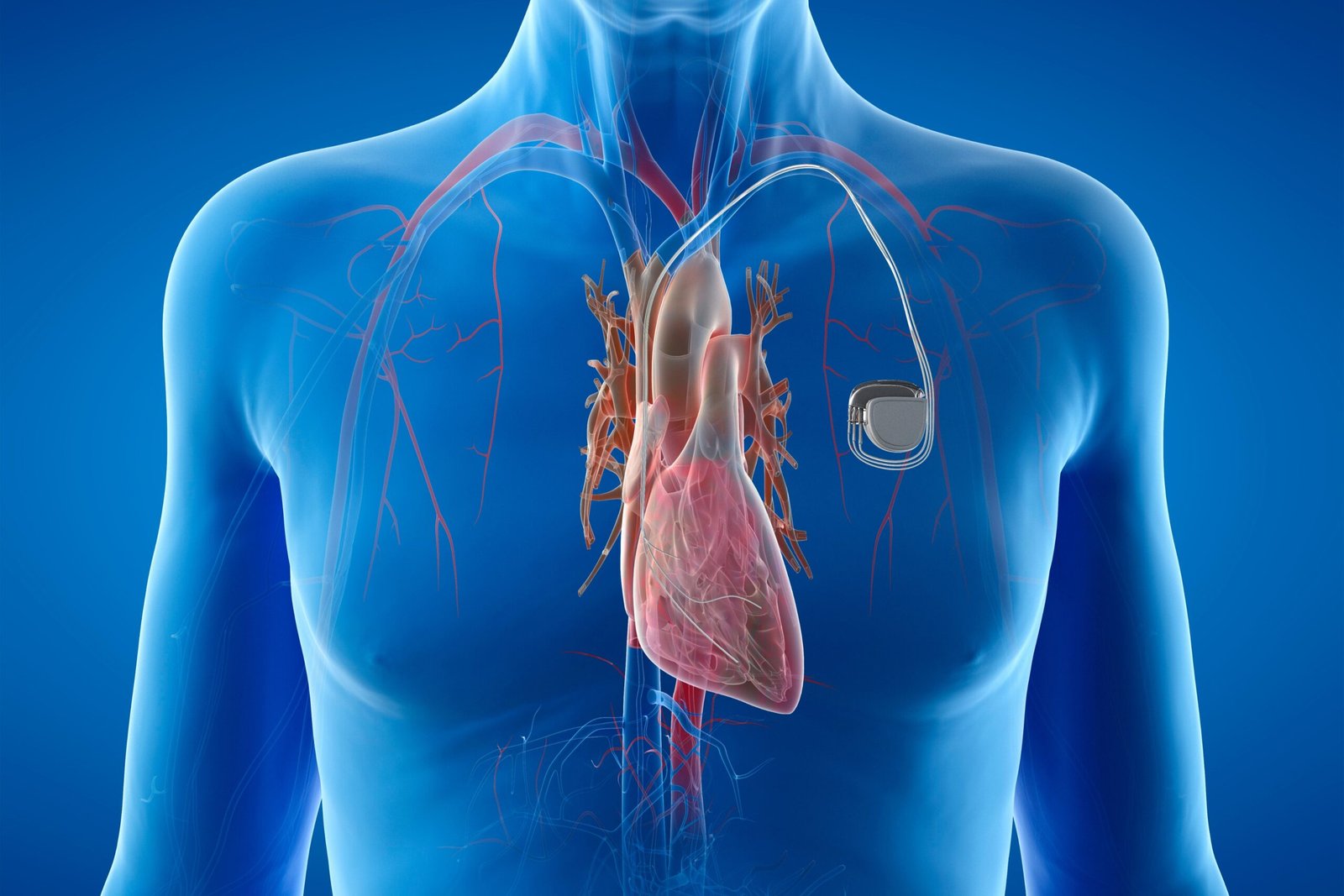
The hallmark of these implants is their impact on patient health and quality of life.
Key benefits include:
- Improved Mobility: Joint replacements and orthopedic implants restore movement and independence to patients with arthritis or traumatic injuries.
- Pain Relief: By stabilizing bones or replacing damaged structures, implants can significantly reduce chronic pain.
- Enhanced Longevity: Durable materials and advanced engineering mean implants last longer, decreasing the likelihood of revision surgeries.
- Lower Complication Rates: Biocompatible materials and stringent manufacturing standards reduce the risk of infection, rejection, and device failure.
The Future of High-Quality Medical Implants
The field of high-quality medical implants continues to evolve, with research focused on:
- Personalized Medicine: Custom implants tailored to individual anatomy and needs.
- Regenerative Implants: Devices that not only replace but also stimulate the body’s own repair mechanisms.
- Integration with Digital Health: Smart implants that communicate with external devices for monitoring and adjustment.
As technology advances, patients can expect even safer, more effective, and longer-lasting solutions for a wide range of medical conditions.
Also Read:
- Orthopedic Implants: Types, Materials, Innovations, and Their Transformative Role in Modern Medicine
- I Bet You Didn’t Know These Interesting Facts about Orthopedic Technology
- Cardiovascular Solutions: Comprehensive Strategies for a Healthy Heart
Conclusion
High-quality medical implants are a major achievement in modern medicine. They change lives by providing innovative solutions that prioritize safety and lead to better health outcomes.
Whether you are a patient looking for information, a healthcare provider, or a manufacturer, it is important to understand what makes these implants high-quality. This knowledge helps you make better choices and provide the best care possible.
Keeping up with new developments in materials, safety standards, and marketing strategies can help medical practices stay on top in this ever-changing field.
These implants are not just tools; they are a sign of human creativity and care, helping many people regain their health, movement, and self-confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions About High-Quality Medical Implants
1. What makes an implant “high-quality”?
A high-quality medical implant combines biocompatibility, mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and precision engineering. It is manufactured and tested according to rigorous international standards to ensure safety and efficacy.
2. How long do high-quality medical implants last?
The lifespan varies by type and material. Orthopedic implants can last 15-25 years or more, while dental implants may last decades with proper care. Advances in materials and design continue to extend implant longevity.
3. Are there risks associated with medical implants?
All surgical procedures carry risks, but these implants are designed to minimize complications such as infection, rejection, or mechanical failure. Choosing an experienced surgeon and following post-operative care guidelines further reduces risks.
4. What materials are safest for implants?
Titanium and its alloys are considered among the safest due to their excellent biocompatibility and mechanical properties. Cobalt-chromium alloys, ceramics, and certain polymers are also widely used and approved for specific applications.