The pharmaceutical industry is heavily cautious and functions in a controlled environment. In this industry, the product’s safety, value, and compliance are the first priority. Under these strict circumstances, a pharmaceutical quality management system (QMS) plays an essential role. This means that in every stage of drug development and manufacturing process, all the rules and regulations are thoroughly followed. By implementing a strong QMS, the pharmaceutical companies get the support to maintain consistency, reduce risk factors, and also ensure the safety of patients.
In this article, we will explore what is a pharmaceutical Quality Management System and also understand the important factors and challenges. We will also understand how organizations can optimize the QMS to enhance their efficiency and compliance.
What Is a Pharmaceutical Quality Management System?
A pharmaceutical quality management system (QMS) is a structured framework that ensures all processes involved in drug manufacturing adhere to regulatory guidelines and quality standards. It integrates policies, procedures, and documentation systems to monitor and control the quality of pharmaceutical products from raw materials to final distribution.
Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Medicines Agency (EMA), and the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) mandate pharmaceutical companies to have a well-defined QMS. Compliance with these regulations not only ensures product safety but also protects manufacturers from legal issues, recalls, and reputational damage.
Key Components of QMS in Pharmaceuticals
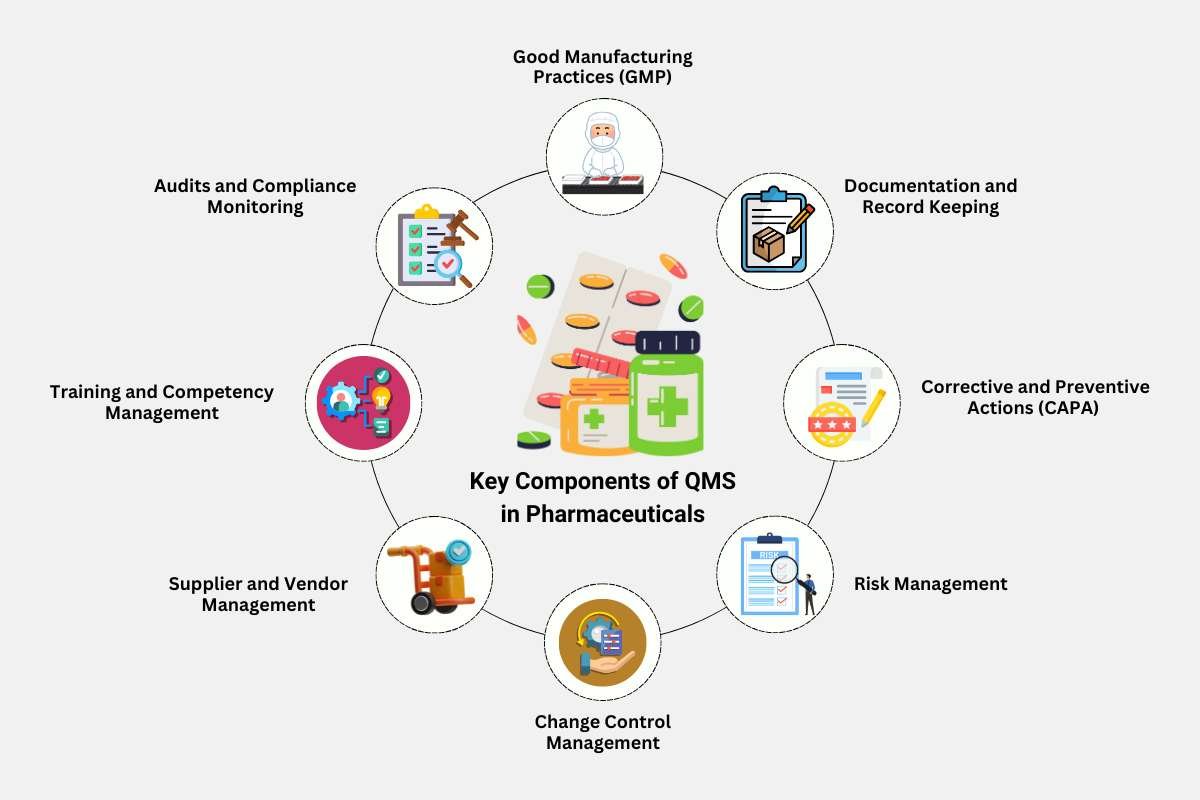
A Pharmaceutical Quality Management system comprises several critical components that work together to maintain product integrity. Below are the key elements that form the foundation of an effective QMS:
1. Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)
GMP guidelines establish strict protocols for manufacturing, testing, and quality control. Compliance with GMP ensures that drugs are consistently produced to meet predetermined quality standards.
2. Documentation and Record Keeping
Accurate and well-maintained documentation is essential for regulatory audits and traceability. Standard operating procedures (SOPs), batch records, and validation reports are critical documents in a QMS.
3. Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA)
The CAPA system identifies deviations, investigates root causes, and implements corrective measures to prevent recurring issues. This proactive approach enhances process efficiency and product safety.
4. Risk Management
Risk-based approaches help pharmaceutical companies identify potential hazards in manufacturing processes and implement mitigation strategies. The ICH Q9 guidelines provide a structured approach to quality risk management.
5. Change Control Management
Any modifications in raw materials, processes, or equipment must go through a structured change control process to ensure they do not compromise product quality or regulatory compliance.
6. Supplier and Vendor Management
Pharmaceutical companies rely on third-party suppliers for raw materials and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). A QMS ensures proper supplier qualification, audits, and quality agreements to maintain supply chain integrity.
7. Training and Competency Management
Employees must undergo regular training to stay updated with current regulations, GMP requirements, and best practices. A well-trained workforce minimizes human errors and ensures compliance.
8. Audits and Compliance Monitoring
Routine internal and external audits help identify gaps in the QMS. Regular monitoring ensures continuous improvement and readiness for regulatory inspections.
Also Read: 20 Best Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Software
Common QMS Challenges in Pharma
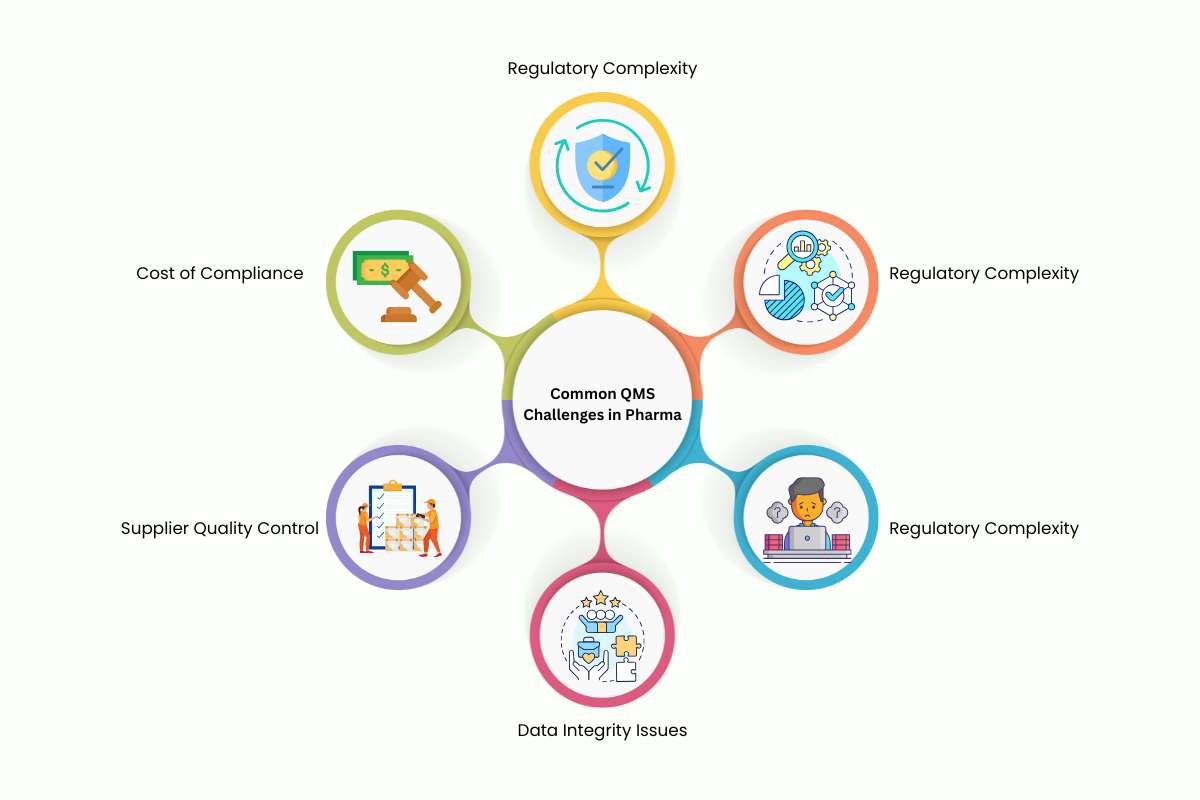
While implementing a QMS is essential, companies often face several challenges in maintaining compliance and efficiency.
1. Regulatory Complexity
Pharmaceutical regulations vary across regions, making compliance a challenging task for multinational companies. Keeping up with evolving guidelines requires constant updates and process modifications.
2. Data Integrity Issues
Ensuring data accuracy, security, and traceability is a major concern. Data integrity violations, such as falsified test results or improper documentation, can lead to severe regulatory penalties.
3. Inefficient Document Management
Paper-based or outdated electronic systems can slow down document retrieval and increase compliance risks. Implementing an automated document management system helps streamline workflows.
4. Quality Culture and Employee Engagement
A strong quality culture is vital for a successful QMS. Resistance to change, lack of awareness, or insufficient training can hinder the effectiveness of quality management initiatives.
5. Supplier Quality Control
Ensuring consistent quality from third-party suppliers is a challenge. Poor-quality raw materials can compromise drug efficacy and lead to recalls.
6. Cost of Compliance
Maintaining a QMS requires significant investment in technology, training, and audits. However, non-compliance can result in greater financial losses due to regulatory fines and product recalls.
Also Read: Best Pharmaceutical Marketing Agencies that Transformed Healthcare Brands
Conclusion
By properly implementing a pharmaceutical quality management system, it becomes a perfect support system to maintain the drug’s value, safety and compliance. The strict integration of quality processes in pharmaceutical companies can make sure that rules are followed thoroughly with a decrease in risk and improvement in patient trust. Regardless of some challenges such as regulatory complexities and data integrity issues, the companies still thrive in the industry by overcoming and bringing continuous improvement, advancement in technology along with employee engagement. By investing in a strong QMS, any company can make sure that the operations are excellent and long-term success is surely achieved in the competitive pharmaceutical industry.
FAQ:
1. What is a quality management system in pharma?
A QMS is a comprehensive collection of policies, processes, and procedures designed to ensure and maintain uniform and high quality in the production of pharmaceutical products.
2. What are the 7 quality management systems?
7 key quality management principles—customer focus, leadership, engagement of people, process approach, improvement, evidence-based decision making and relationship management.
3. What are the six quality systems in pharma?
A model that can help pharmaceutical manufacturers comply with CGMP regulations. The six systems referred to in this inspection model are: quality, production, facilities and equipment, laboratory controls, materials, and packaging and labelling.