It has become important for industry to embrace materials that are strong, flexible, and adaptable according to the applications in today’s world. Among various materials, there is one that has been used very often by many industries, which is thermoplastic polyurethane material, also known as TPU. TPU is a revolutionary polymer that is a perfect blend of the best properties of rubber and plastic. TPU is a versatile material that has been used in multiple sectors, from rugged automotive parts to soft and breathable sportswear. But with the increase in demand for this material, the people who aren’t aware of it yet are wondering what makes it a special and preferred choice for manufacturers across the globe.
In this article, we will explore the world of TPU and also find out about its origin, Process, key benefits, and application.
What is Thermoplastic Polyurethane?
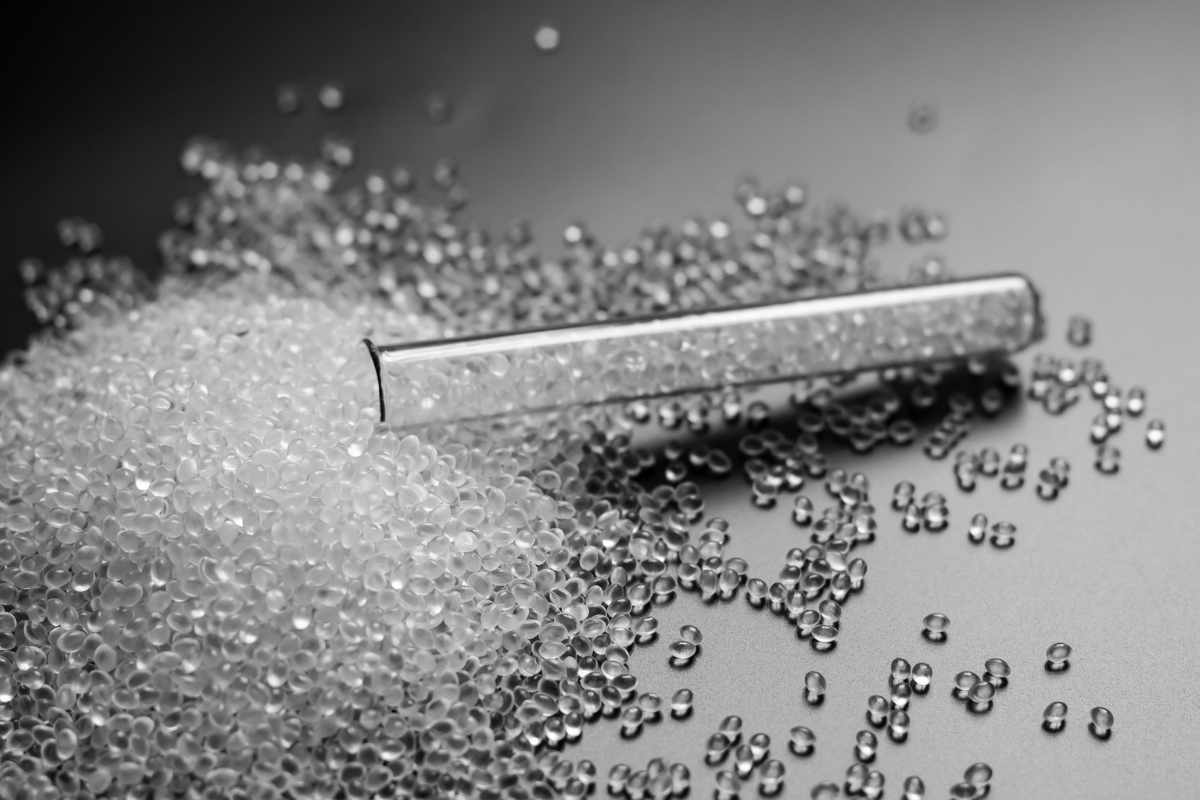
Thermoplastic polyurethane material, commonly known as TPU, is a highly versatile and durable elastomer that combines the properties of plastic and rubber. It is widely recognized for its flexibility, toughness, and resistance to abrasion, making it a preferred choice for various industrial and consumer applications. Unlike traditional plastics, TPU offers superior elasticity, allowing it to be stretched and deformed without losing its original shape.
Who Invented TPU?
The development of thermoplastic polyurethane material can be traced back to the 1930s when German chemist Otto Bayer first introduced polyurethane chemistry. However, it wasn’t until the 1950s that TPU was commercially developed and refined. Bayer’s research laid the foundation for the modern TPU materials used today in multiple industries, including automotive, textiles, and medical applications.
How is TPU Produced?

The production of thermoplastic polyurethane material involves a reaction between diisocyanates and polyols, along with chain extenders. This process forms long-chain molecules that exhibit both soft and hard segment properties, giving TPU its unique characteristics. TPU can be formulated with varying degrees of hardness, flexibility, and elasticity, depending on the specific application requirements.
The key steps in TPU production include:
- Polymerization: The reaction of diisocyanates (such as MDI or TDI) with polyols and chain extenders to form TPU.
- Extrusion or Injection Molding: The resulting TPU is then processed into granules, sheets, or films for manufacturing various products.
- Modification: Additives can be introduced to enhance TPU’s properties, such as UV resistance, flame retardancy, or increased durability.
Do You Know All Its Applications?
Thermoplastic polyurethane material is widely used across numerous industries due to its adaptability and strength. Some of its common applications include:
- Automotive: Used in gaskets, hoses, seat covers, and suspension bushings for its wear resistance and durability.
- Footwear: Found in sports shoes, sandals, and protective footwear due to its flexibility and comfort.
- Medical Industry: TPU is used in medical tubing, catheters, and surgical gloves because of its biocompatibility.
- Electronics: Protective phone cases, cables, and flexible components utilize TPU for shock absorption.
- Textile Industry: TPU-coated fabrics offer water resistance and breathability for outdoor and sportswear.
Uses of TPU
The versatility of thermoplastic polyurethane material makes it ideal for a broad range of applications. Some of its most prominent uses include:
- Industrial Belts and Seals: TPU’s wear resistance ensures long-lasting conveyor belts and sealing components.
- 3D Printing: TPU filaments allow for the creation of flexible and impact-resistant 3D-printed parts.
- Sporting Goods: From inflatable rafts to ski boots, TPU provides strength and flexibility.
- Protective Films: Used in automotive paint protection films and screen protectors for scratch resistance.
Benefits of TPU
Thermoplastic polyurethane material offers numerous advantages over conventional plastics and rubbers. Some of its key benefits include:
- High Elasticity: TPU retains its shape even after repeated stretching and compression.
- Chemical and Oil Resistance: Ideal for applications exposed to harsh environments.
- Abrasion Resistance: Ensures durability in industrial and consumer products.
- Transparency: Available in clear grades for aesthetic and functional applications.
- Recyclability: TPU can be reprocessed and reused, reducing environmental impact.
Composition of TPU
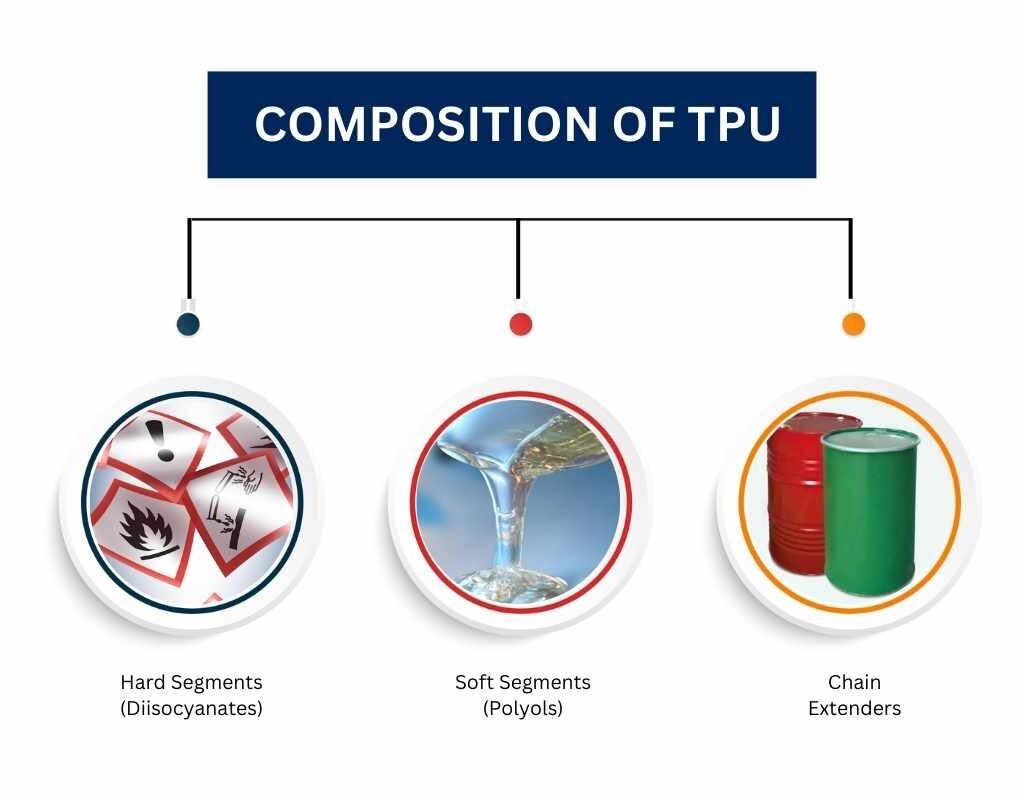
TPU is composed of three main components:
- Hard Segments (Diisocyanates): Provide rigidity and strength to TPU.
- Soft Segments (Polyols): Ensure flexibility and elasticity.
- Chain Extenders: Help control the polymer’s hardness and processing characteristics.
By adjusting the ratio of these components, manufacturers can produce TPU with different levels of hardness and elasticity, making it suitable for a wide range of uses.
Soft Touch/High Comfort of Use for Ergonomic Applications
One of the standout features of thermoplastic polyurethane material is its soft-touch property, making it ideal for ergonomic applications. TPU is commonly used in wearable devices, handles, grips, and medical instruments due to its comfortable texture. This property enhances the user experience, ensuring a firm yet comfortable grip without causing discomfort during prolonged use.
UV Resistance
Thermoplastic polyurethane material exhibits excellent UV resistance, making it a top choice for outdoor applications. Unlike conventional plastics that degrade when exposed to sunlight, TPU retains its structural integrity and color. This quality makes it ideal for automotive trims, outdoor sports gear, and protective coatings that require long-term exposure to sunlight.
What are the Main Types of TPU Films?
TPU films are widely used in protective coatings, laminates, and flexible packaging. The main types of TPU films include:
- Aliphatic TPU Films: Known for their superior UV stability and clarity, they are commonly used in automotive and architectural applications.
- Aromatic TPU Films: Offer excellent mechanical properties and cost-effectiveness but tend to yellow over time when exposed to UV light.
- Breathable TPU Films: Used in sportswear and medical applications where moisture control is essential.
- Flame-Retardant TPU Films: Designed for aerospace and industrial safety applications requiring fire resistance.
What are the Environmental Benefits of TPU?
Thermoplastic polyurethane material is considered an eco-friendly alternative to many traditional plastics. Some of its environmental benefits include:
- Recyclability: TPU can be melted and reprocessed multiple times without significant loss in quality.
- Biodegradable Options: Certain TPU formulations are designed to break down more easily in landfills.
- Reduced Waste: Its durability leads to longer product life cycles, reducing plastic waste.
- Low VOC Emissions: TPU produces fewer volatile organic compounds compared to conventional plastics, making it safer for indoor use.
What are the Limitations of TPUs?
While thermoplastic polyurethane material offers numerous advantages, it also has some limitations:
- Higher Cost: TPU is generally more expensive than standard plastics like PVC or polyethylene.
- Processing Complexity: Requires precise temperature control during molding and extrusion.
- Moisture Sensitivity: TPU can absorb moisture, which may affect its mechanical properties if not stored properly.
- UV Stability in Aromatic Grades: Some TPU types may discolor or degrade under prolonged UV exposure.
Conclusion
The thermoplastic polyurethane material has changed the world of polymers, as these materials offer unique blends of flexibility, strength, and durability to the user. TPU has been a vital element in many industries because of its superior properties, and it’s used in automotive components and medical devices as well. It does have some drawbacks in certain terms, but the number of benefits is countless to trump setbacks such as recyclability and UV resistance, making TPU the preferred choice for many manufacturers.
Today, industries are openly exploring and accepting sustainable materials for their products. So, thermoplastic polyurethane material has gained attention because of its environmentally friendly properties and high performance for the better future of industry. Regardless of what industry you are in, such as manufacturing, fashion, or technology, TPU has proven to be an exceptional material that improves both functionality and sustainability in product design.