Bone marrow mononuclear cells (BM-MNCs) are the most fascinating factor of the body’s cellular system. It plays a vital role in terms of immunity and tissue regeneration. The bone marrow mononuclear cells are a diverse mixture of stem cells such as lymphocytes, monocytes, and hematopoietic progenitor cells.
They have contributed to the medical and research field in various ways, from combatting infections to repairing tissues. These cells gave a new direction to the research and development of many therapies for many diseases and injuries. The bone marrow mononuclear cells are helping advance and change the way healthcare assistance works by becoming a key player in stem cell therapy. The BM-MNCs help in various bodily functions, mainly related to our immune system and blood cell production.
In this article, we will dive into the world of these distinct cells and study their function and application in the research field.
What are Bone Marrow Mononuclear cells?
Bone Marrow mononuclear cells are heterogeneous mixtures of stem cells present in the marrow that have various bodily functions. It is a population of stem cells isolated from bone marrow. The reason why these cells are known as mononuclear is because they only consist of one nucleus, setting them apart from multinucleated cells. The bone marrow is a large source of many types of stem cells, such as Hematopoietic stem cells and Mesenchymal stem cells. These two stem cells are present in the bone marrow mononuclear cell fractions. Hematopoietic stem cells are responsible for producing blood cells. Mesenchymal stem cells repair any injuries, infections, or damage in our body. The Bone Marrow Mononuclear cells include various types of cells:
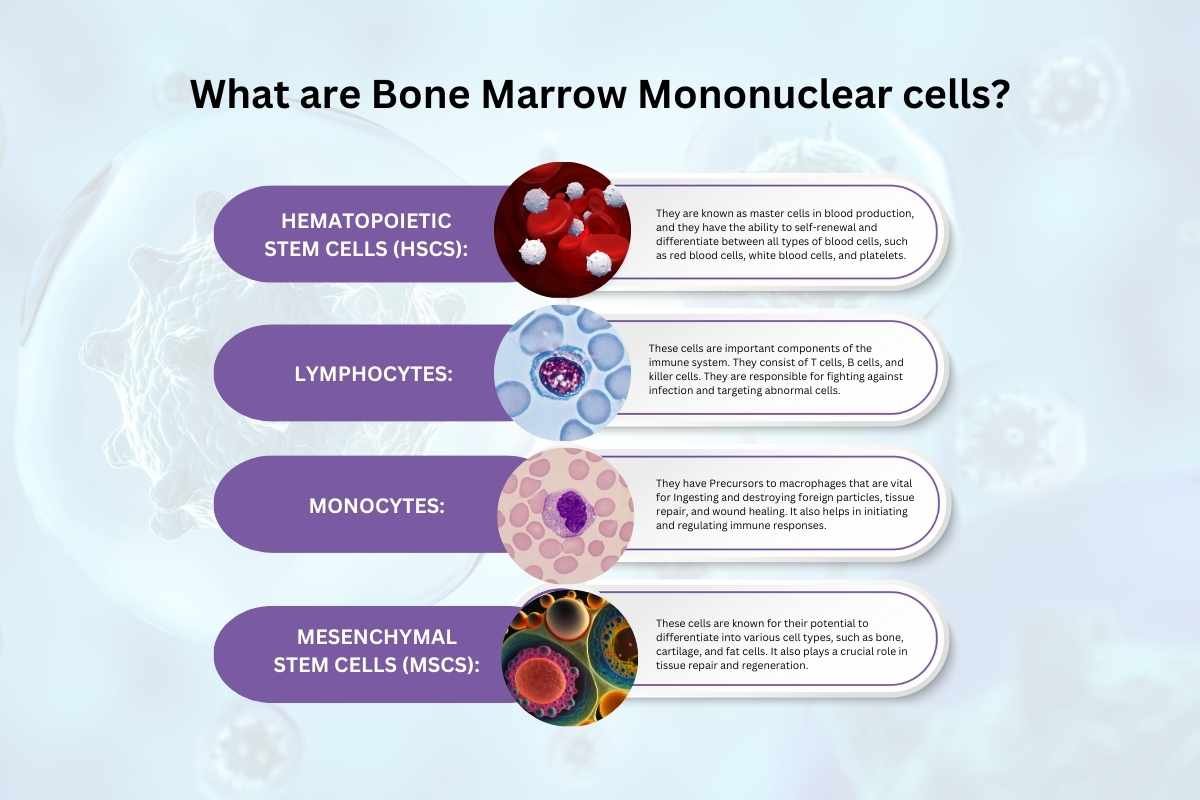
1. Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs)
They are known as master cells in blood production, and they have the ability to self-renewal and differentiate between all types of blood cells, such as red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
2. Lymphocytes
These cells are important components of the immune system. They consist of T cells, B cells, and killer cells. They are responsible for fighting against infection and targeting abnormal cells.
3. Monocytes
They have Precursors to macrophages that are vital for Ingesting and destroying foreign particles, tissue repair, and wound healing. It also helps in initiating and regulating immune responses.
4. Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs)
These cells are known for their potential to differentiate into various cell types, such as bone, cartilage, and fat cells. It also plays a crucial role in tissue repair and regeneration.
Function and Application of Bone marrow mononuclear cells:
Function of BM-MNCs:
As mentioned, these cells are important and contribute to various bodily functions, as well as the production of blood cells. Their functions can be broken down in this way:
1. Hematopoiesis
This is the main function of BM-MNCs; they have the hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs). They are used for generating all types of blood cells, such as red blood cells (help in transporting oxygen through the body), white blood cells (fight any kind of infection and are vital for the immune system), and platelets (help in blood clotting).
2. Immune Response
The BM-MNCs contain various immune cells like lymphocytes and monocytes. These cells work together to eliminate foreign invaders and develop future immunity to fight against bacteria. It also helps regulate immune responses to prevent excessive inflammation or autoimmune reactions.
3. Tissue Repair and Regeneration
The Bone marrow mononuclear cells help in tissue repair and also in the regeneration of many organs and tissues. They can secrete the growth factors and signaling molecules that contribute to cell growth and differentiation. They are capable of differentiating into specific cell types needed for tissue repair, such as endothelial cells (lining blood vessels) or muscle cells.
Application:
1. Regenerative Medicine
They help in cardiac repair, as the bone marrow mononuclear cells consist of cardiac progenitor cells that help in treating heart damage. They also help in improving heart function by promoting new blood vessel growth. These cells have also shown promising outcomes when it comes to treating neurological disorders such as stroke, spinal cord injury, Parkinson’s, and Alzheimer’s. They are also boosting bone healing in fractures and treating cartilage damage in joints.
2. Hematopoietic Disorders
The BM-MNCs are vital for bone marrow transplants, as they are used to treat blood cancers like leukemia and lymphoma, along with other blood-related disorders. These cells are also used to restore the immune function in patients with immunodeficiency disorders by replenishing depleted immune cell populations.
3. Drug Discovery and Development

BM-MNCs are used for screening and testing new drugs for their efficacy and safety. It can also be used to develop personalized therapies for individual patients, taking into account their unique genetic and immunological profiles.
4. Research
It is considered a valuable tool in studying and understanding basic biological processes like hematopoiesis (blood cell formation), immune function, and stem cell biology.
Conclusion
Bone marrow mononuclear cells have brought various changes in the stem cell therapy field. And gave birth to phenomenal experiences that led to many discoveries. The world of cells is mysterious, but if you are willing to look inside, they can give answers to many questions that could help in the medical field to save lives. It can be used as a powerful tool to enhance the genetic makeup of someone’s body. It can help in curing many diseases. BM-MNC study takes a lot of patience, but if we understand the concept and how to use it, we can make wonders out of it. Tissue repair and regeneration to treating many Hematopoietic disorders.
FAQ:
How many mononuclear cells are in bone marrow?
The average BMMNC per mL in patients of age group 0–20 years was 4.71 million; in 21–40 years it was 4.03 million; in 41–60 years it was 3.67 million; in 61–80 it was 3.02 million. The average BMMNC per mL in all the 332 patients ranged from a minimum of 1.47 million to a maximum of 15.36 million.
What are mononuclear cells of bone?
Mononuclear cells are a mixture of cells isolated after Ficoll density gradient separation of the bone marrow aspirate. This procedure removes most of the erythrocytes and polymorphonuclear cells. The resulting mononuclear cell fraction is a mixture of lymphoid, myeloid, erythroid, and stem cell populations.
What are examples of mononuclear cells?
A peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) is any peripheral blood cell having a round nucleus. These cells consist of lymphocytes (T cells, B cells, NK cells) and monocytes, whereas erythrocytes and platelets have no nuclei, and granulocytes (neutrophils, basophils, and eosinophils) have multi-lobed nuclei.