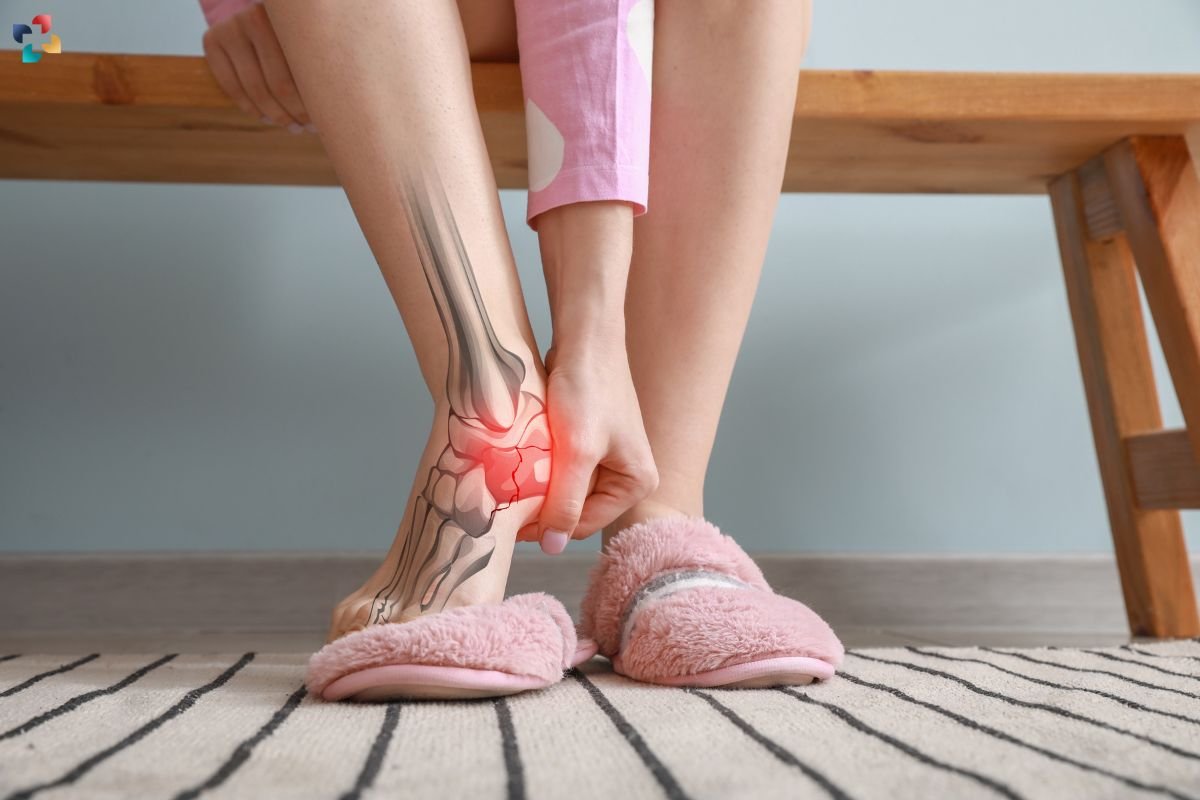
Calcaneal stress fracture, a type of overuse injury affecting the heel bone, is a common concern among athletes and active individuals. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for effective management and prevention.
What is a Calcaneal Stress Fracture?
A calcaneal stress fracture is a small crack in the calcaneus, the large bone forming the heel of the foot. Unlike acute fractures caused by sudden trauma, stress fractures result from repetitive force or overuse. This condition is prevalent among runners, military recruits, and athletes participating in high-impact sports.
Causes of Calcaneal Stress Fracture
The primary cause of a calcaneal stress fracture is repetitive stress or overuse. Here are some key factors that contribute to this injury:
1. Overtraining
Engaging in intense training regimens without adequate rest can lead to a calcaneal stress fracture. Athletes who suddenly increase their activity level or mileage are particularly at risk.
2. Poor Footwear
Wearing improper or worn-out shoes that do not provide adequate support can increase the risk of stress fractures. Footwear that fails to absorb shock effectively places additional stress on the calcaneus.
3. Biomechanical Abnormalities
Structural issues such as flat feet, high arches, or abnormal gait patterns can contribute to uneven distribution of forces across the foot, leading to stress fractures.
4. Osteoporosis
Individuals with osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened bones, are more susceptible to stress fractures, including those in the calcaneus.
5. Sudden Changes in Activity
Abrupt changes in physical activity, such as transitioning from a sedentary lifestyle to vigorous exercise, can overload the calcaneus and result in a stress fracture.
6. Running on Hard Surfaces
Consistently running on hard surfaces like concrete increases the impact on the feet, raising the likelihood of developing a calcaneal stress fracture.
Symptoms of Calcaneal Stress Fracture
Recognizing the symptoms of a calcaneal stress fracture is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms include:
1. Heel Pain
Persistent pain in the heel, especially during weight-bearing activities, is a hallmark symptom of a calcaneal stress fracture. The pain often worsens with activity and improves with rest.
2. Swelling
Swelling around the heel may occur due to inflammation caused by the fracture. This swelling can be mild to moderate and is typically accompanied by tenderness.
3. Bruising
Some individuals may notice bruising around the heel, indicating underlying tissue damage.
4. Pain During Exercise
Pain that intensifies during physical activity, particularly running or jumping, is a common sign of a calcaneal stress fracture.
5. Pain When Touching the Heel
Tenderness and pain when pressing on the heel bone are indicative of a stress fracture. This pain is usually localized to the area of the fracture.
Diagnosis of Calcaneal Stress Fracture
Accurate diagnosis of a calcaneal stress fracture involves a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging studies. Here’s how healthcare providers typically diagnose this condition:
1. Medical History
A thorough medical history helps identify risk factors, recent changes in activity, and the onset of symptoms. This information guides the diagnostic process.
2. Physical Examination
During a physical examination, the healthcare provider will assess the foot for tenderness, swelling, and bruising. They may apply pressure to the heel to localize the pain.
3. Imaging Studies
Imaging studies are essential for confirming the diagnosis of a calcaneal stress fracture. The most common imaging techniques include:
a. X-rays
X-rays can reveal fractures, but early-stage stress fractures may not be visible. In such cases, additional imaging is necessary.
b. MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is highly sensitive and can detect stress fractures at an early stage. It provides detailed images of the bone and surrounding tissues.
c. Bone Scan
A bone scan involves injecting a small amount of radioactive material into the bloodstream. Areas of increased bone activity, such as stress fractures, will absorb more of the material and appear as “hot spots” on the scan.
Treatment of Calcaneal Stress Fracture
Effective treatment of a calcaneal stress fracture involves a combination of rest, pain management, and rehabilitation. The goal is to promote healing while preventing further injury. Here are the primary treatment options:
1. Rest and Activity Modification
Rest is crucial for allowing the fracture to heal. Avoiding weight-bearing activities and reducing physical activity can prevent further stress on the calcaneus. In some cases, a period of non-weight-bearing is recommended, which may involve using crutches.
2. Immobilization
Immobilization with a cast or walking boot may be necessary to stabilize the fracture and prevent movement that could delay healing. The duration of immobilization depends on the severity of the fracture.
3. Pain Management
Pain relief can be achieved through over-the-counter pain medications such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These medications help reduce pain and inflammation.
4. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation process. A physical therapist can design a tailored exercise program to improve strength, flexibility, and balance. This helps prevent future injuries and facilitates a safe return to activity.
5. Gradual Return to Activity
Once the fracture has healed, a gradual return to activity is essential. A structured rehabilitation program, guided by a healthcare provider or physical therapist, ensures that the transition back to physical activity is safe and controlled.
6. Orthotics
Custom orthotic devices or shoe inserts can provide additional support and help correct biomechanical abnormalities that contribute to stress fractures. These devices can distribute pressure more evenly across the foot.
7. Nutrition
Proper nutrition is vital for bone health and healing. Ensuring an adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D supports bone strength and recovery.
8. Surgical Intervention
In rare cases where conservative treatments fail, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgery involves the use of screws or plates to stabilize the fracture and promote healing. This option is typically reserved for severe or non-healing fractures.
Prevention of Calcaneal Stress Fracture
Preventing a calcaneal stress fracture involves adopting strategies to reduce stress on the heel bone and promote overall foot health. Here are some preventive measures:
1. Gradual Increase in Activity
Avoid sudden increases in physical activity. Gradually increase the intensity and duration of exercise to allow the body to adapt and strengthen.
2. Proper Footwear
Invest in high-quality, supportive footwear that provides adequate cushioning and shock absorption. Replace worn-out shoes regularly to maintain proper support.
3. Cross-Training
Incorporate cross-training into your exercise routine to reduce repetitive stress on the calcaneus. Activities such as swimming or cycling can provide cardiovascular benefits without impacting the feet.
4. Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening the muscles of the lower leg and foot can improve stability and reduce the risk of stress fractures. Focus on exercises that target the calf muscles, Achilles tendon, and foot arches.
5. Stretching
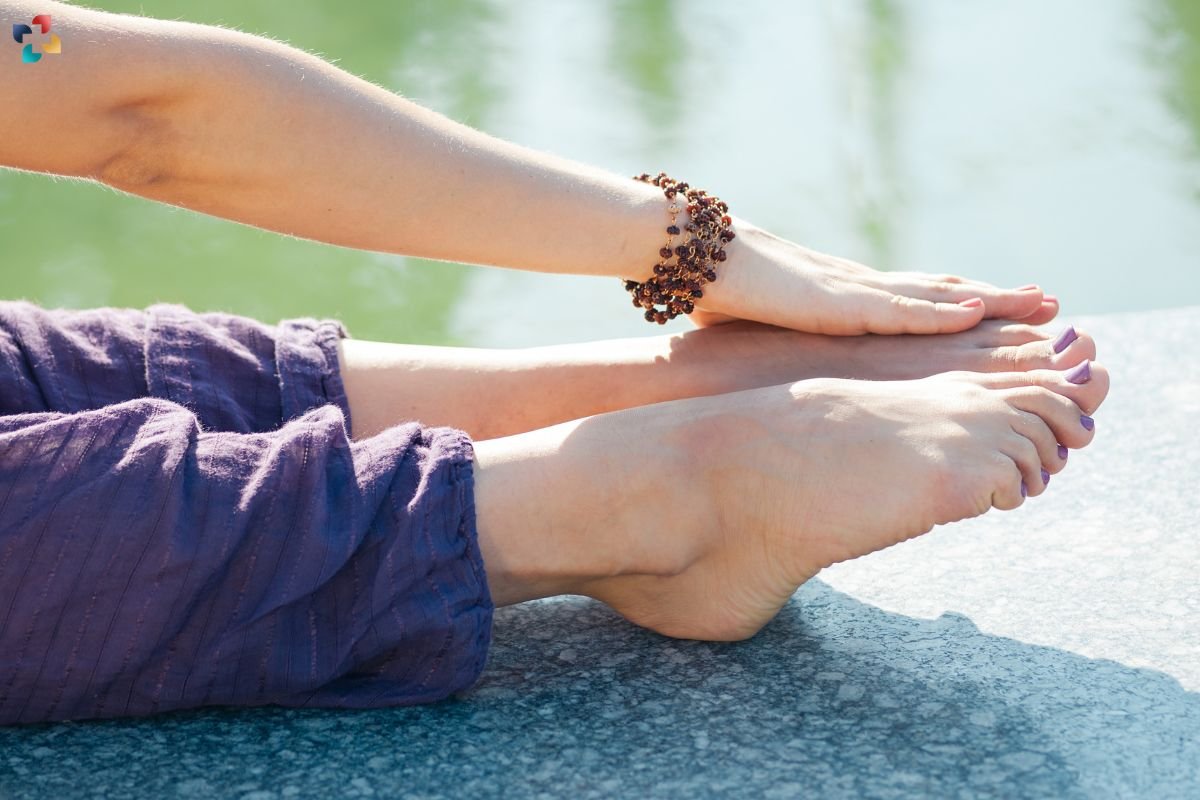

Regular stretching of the calf muscles and Achilles tendon can improve flexibility and reduce tension on the calcaneus. Incorporate stretching exercises into your warm-up and cool-down routines.
6. Bone Health
Maintain good bone health through a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D. Consider supplements if necessary, and engage in weight-bearing exercises to strengthen bones.
7. Addressing Biomechanical Issues
Consult with a healthcare provider or podiatrist to address any biomechanical abnormalities. Custom orthotics or shoe inserts can help correct issues such as flat feet or high arches.
Understanding Bone Spurs on Feet: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
Bone spurs, also known as osteophytes, are bony projections that develop along the edges of bones. This article provides a comprehensive overview of bone spurs on feet, including their causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
Conclusion
A calcaneal stress fracture is a common overuse injury that can significantly impact an individual’s ability to engage in physical activity. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for effective management and prevention. By adopting preventive measures, such as proper footwear, gradual increases in activity, and maintaining good bone health, individuals can reduce the risk of developing a calcaneal stress fracture. If symptoms arise, seeking prompt medical attention and adhering to a comprehensive treatment plan can promote healing and ensure a safe return to physical activity.