Artificial selection, often dubbed “selective breeding,” stands as a testament to humanity’s ability to shape and mold the natural world. From the domestication of plants and animals to the creation of novel breeds, artificial selection exemplifies the power of human intervention in evolutionary processes. In this article, we embark on a journey through diverse realms of life, uncovering fascinating artificial selection examples that underscore the profound impact of human agency on biological diversity.
Here are 10 fascinating artificial selection examples:
1. The Evolution of Canines: Artificial Selection Examples in Dogs
Dogs, our loyal companions for millennia, epitomize the outcomes of artificial selection. From the majestic Great Dane to the diminutive Chihuahua, the staggering diversity in canine breeds is a testament to centuries of selective breeding. Artificial selection examples in dogs range from traits like size, coat color, temperament, and even specialized skills such as herding or hunting. The deliberate breeding practices of humans have sculpted canines into an astonishing array of shapes, sizes, and abilities, showcasing the remarkable adaptability of biological organisms to human desires.
2. Agricultural Marvels: Artificial Selection Examples in Crops
The history of agriculture is replete with artificial selection examples, as humans have transformed wild progenitors into the staple crops that sustain civilizations. Wheat, corn, rice, and countless other agricultural commodities bear little resemblance to their wild ancestors, thanks to millennia of selective breeding. Traits like yield, disease resistance, and nutritional content have been honed through meticulous breeding efforts, ensuring bountiful harvests and food security for billions worldwide. The Green Revolution of the 20th century stands as a testament to the power of artificial selection in revolutionizing agricultural productivity and combating hunger on a global scale.
3. Floral Fantasies: Artificial Selection Examples in Ornamental Plants

Gardens and landscapes are adorned with an exquisite array of ornamental plants, each a testament to the artistry of artificial selection. From vibrant roses to exotic orchids, ornamental plants have been selectively bred for their aesthetic appeal, fragrance, and unique features. Artificial selection examples abound in the horticultural world, where breeders tirelessly work to create novel cultivars with dazzling colors, intricate patterns, and resilient growth habits. Through selective breeding, humans have transformed humble wildflowers into botanical marvels that adorn parks, gardens, and private landscapes worldwide.
4. Feathered Friends: Artificial Selection Examples in Poultry
The domestication of poultry stands as one of the most striking examples of artificial selection in the animal kingdom. Chickens, ducks, and turkeys, once wild birds, have been selectively bred for traits like egg production, meat yield, and docile behavior. Modern poultry breeds exhibit a staggering diversity of plumage colors, egg sizes, and growth rates, all shaped by centuries of human intervention. From the sleek elegance of Leghorn chickens to the majestic plumage of heritage turkey breeds, artificial selection has transformed wild avian ancestors into indispensable sources of food, fiber, and companionship.
5. Fishy Transformations: Artificial Selection Examples in Aquaculture
The realm of aquaculture offers a glimpse into the transformative power of artificial selection in aquatic species. From humble beginnings as wild fish stocks, species like salmon, tilapia, and trout have been selectively bred for traits like growth rate, disease resistance, and fillet quality. Aquaculture operations around the world rely on genetically improved stocks bred through generations of artificial selection, ensuring sustainable seafood production to meet the demands of a growing global population. The evolution of aquaculture serves as a testament to the adaptive potential of artificial selection in harnessing nature’s bounty for human benefit.
6. The Blossoming Beauty: Artificial Selection Examples in Flowers

Flowers, with their kaleidoscope of colors and fragrances, represent another domain where artificial selection has left an indelible mark. From the iconic beauty of the rose to the delicate charm of the daisy, floral diversity owes much to human intervention through selective breeding. Artificial selection examples in flowers extend beyond mere aesthetics, encompassing traits like bloom size, petal shape, and flowering time. Horticulturists and botanists have meticulously crafted new varieties and hybrids through generations of breeding efforts, enriching our gardens and floricultural industries with an endless array of floral treasures.
7. Equine Excellence: Artificial Selection Examples in Horses
The majestic horse, a symbol of power and grace, exemplifies the outcomes of artificial selection in the animal kingdom. From the swift Thoroughbred to the sturdy Percheron, horse breeds showcase a remarkable diversity of shapes, sizes, and capabilities, all shaped by human breeding practices. Traits like speed, strength, and temperament have been selectively honed through centuries of breeding for various purposes, from racing and riding to draft work and leisure pursuits. The history of horsemanship stands as a testament to the enduring partnership between humans and horses, forged through the art and science of artificial selection.
8. Cultivated Marvels: Artificial Selection Examples in Fruits
Fruits, nature’s sweet offerings, have undergone profound transformations through the lens of artificial selection. From the wild progenitors of apples and bananas to the cultivated varieties found in supermarkets worldwide, fruit crops bear the hallmarks of human intervention. Artificial selection examples in fruits encompass traits like size, flavor, shelf life, and resistance to pests and diseases. Plant breeders have employed innovative techniques to create new cultivars with enhanced nutritional profiles, improved taste, and extended seasonality, ensuring a constant supply of fresh and flavorful fruits to consumers year-round.
9. Dairy Dynasties: Artificial Selection Examples in Cattle
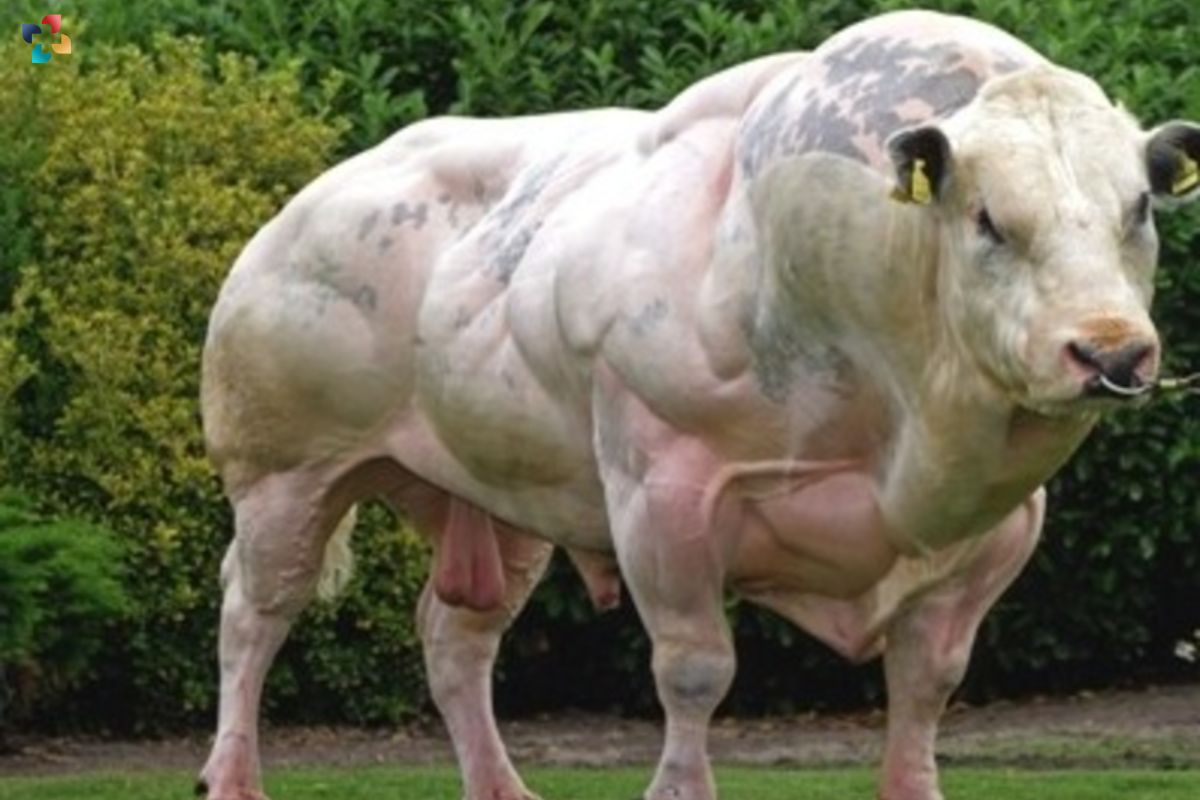

The dairy industry owes much of its success to centuries of artificial selection in cattle breeding. From the ancient aurochs to modern dairy breeds like Holstein and Jersey, cattle have been selectively bred for milk production, conformation, and adaptability to various climates. Artificial selection examples in dairy cattle include traits like milk yield, butterfat content, and udder conformation, all optimized through careful breeding programs. The dairy sector relies on genetically superior cattle bred for efficiency and productivity, ensuring a steady supply of milk and dairy products to meet consumer demand.
10. Floral Fantasy: Artificial Selection Examples in Orchids
Orchids, with their exquisite blooms and diverse forms, represent a pinnacle of artificial selection in the plant kingdom. From the towering spikes of Cattleya hybrids to the delicate allure of Phalaenopsis varieties, orchid enthusiasts have cultivated an astonishing array of cultivars through selective breeding. Artificial selection examples in orchids span traits like flower size, color, fragrance, and even bloom duration. Orchid breeders employ sophisticated techniques like hybridization and tissue culture to create new varieties with unique characteristics, fueling a vibrant orchid industry catering to collectors, enthusiasts, and commercial growers worldwide.
Conclusion
Artificial selection examples abound in every facet of the natural world, underscoring humanity’s profound impact on the evolutionary trajectory of life on Earth. From the humblest wildflower to the most majestic thoroughbred, the fingerprints of human intervention are evident in the staggering diversity of species shaped by selective breeding. As we marvel at nature’s wonders, let us recognize the role of artificial selection in unlocking the genetic potential of organisms, enriching our lives and livelihoods with a bounty of agricultural, horticultural, and zoological treasures.
For More Visit The Lifesciences Magazine