Inflammation is a vital component of the body’s immune response, playing a crucial role in fighting off infections and promoting tissue repair. However, chronic inflammation has been linked to a wide range of health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, autoimmune disorders, and certain cancers. Inflammation blood tests are valuable diagnostic tools used by healthcare providers to assess levels of inflammation in the body and aid in the diagnosis and management of various medical conditions. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the significance, types, and interpretation of inflammation blood tests, shedding light on their role in health assessment and disease management.
Understanding Inflammation:
Inflammation is a complex biological process characterized by the activation of the immune system in response to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, injury, or toxins. When the body detects an infection or injury, immune cells release signaling molecules called cytokines, which trigger inflammation by recruiting immune cells to the site of injury or infection. This inflammatory response helps to eliminate pathogens, clear damaged tissue, and initiate the healing process.
In addition to its role in fighting infections and promoting tissue repair, inflammation plays a vital role in maintaining homeostasis and restoring equilibrium in the body. While acute inflammation is a protective response that resolves once the threat has been neutralized, chronic inflammation can persist over an extended period, leading to tissue damage and contributing to the pathogenesis of various diseases.
Chronic inflammation has been implicated in the development and progression of numerous health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, autoimmune disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and certain cancers. Understanding the underlying mechanisms of inflammation and its contribution to disease pathology is essential for developing targeted therapeutic interventions and preventive strategies aimed at modulating the inflammatory response and mitigating its adverse effects on health.
Types of Inflammation Blood Tests:
There are several inflammation blood tests available, each measuring different markers of inflammation in the bloodstream. Some of the most commonly used inflammation blood tests include:
1. C-reactive protein (CRP) test
CRP is a protein produced by the liver in response to inflammation. Elevated levels of CRP in the blood indicate the presence of acute or chronic inflammation and are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and other inflammatory conditions.
2. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test
ESR measures the rate at which red blood cells settle in a test tube over time. Elevated ESR levels indicate the presence of inflammation in the body, although it is a nonspecific marker and can be influenced by other factors such as age, gender, and certain medications.
3. Complete blood count (CBC) with differential
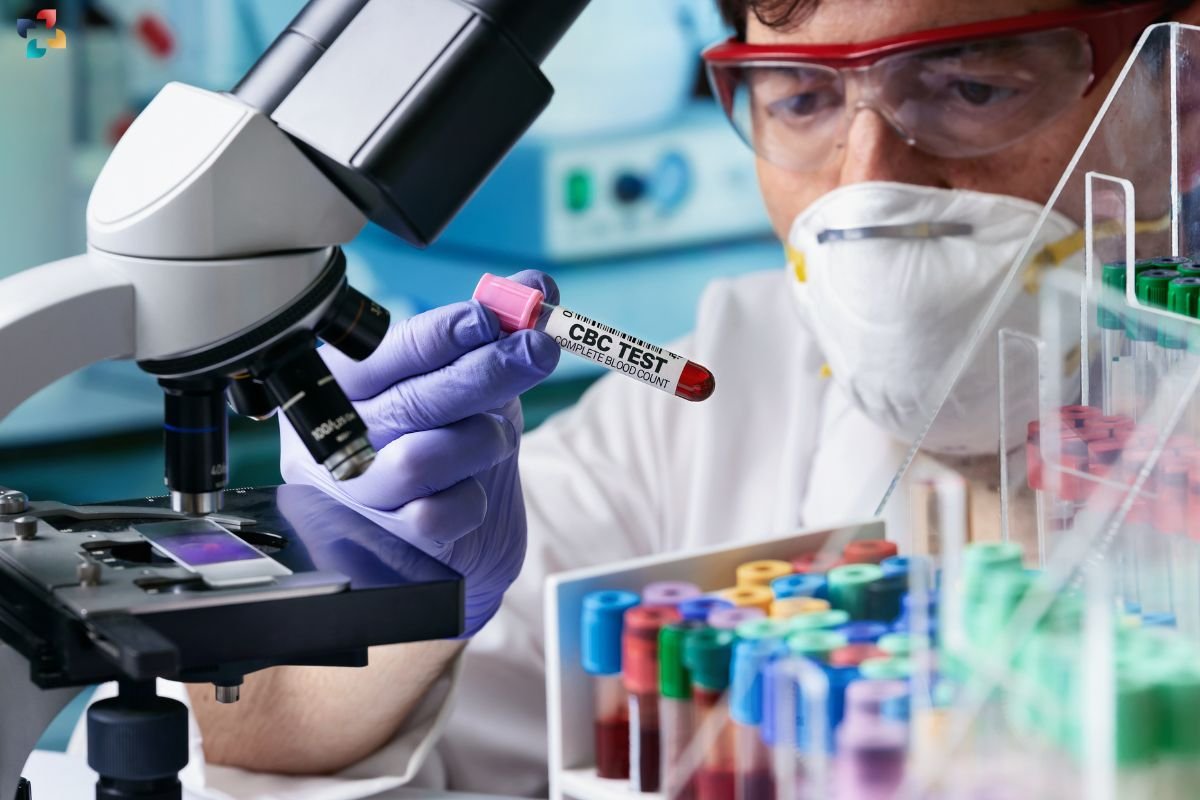

A CBC with differential measures various components of the blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. An abnormal differential count, such as an elevated white blood cell count or an increased percentage of neutrophils, may indicate inflammation or infection.
4. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) test
IL-6 is a cytokine involved in the inflammatory response. Elevated levels of IL-6 in the blood are associated with systemic inflammation and have been implicated in the pathogenesis of various inflammatory diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
5. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) test
TNF-alpha is another cytokine involved in the inflammatory response. Elevated levels of TNF-alpha in the blood are associated with chronic inflammation and are implicated in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis.
Interpretation of Inflammation Blood Tests:
The interpretation of inflammation blood tests depends on the specific marker being measured, as well as the context of the individual patient’s clinical presentation and medical history. Elevated levels of inflammatory markers such as CRP, ESR, IL-6, and TNF-alpha may indicate the presence of acute or chronic inflammation and can help guide further diagnostic evaluation and treatment decisions.
Inflammation blood tests are often used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests and imaging studies to assess the extent and severity of inflammation, monitor disease activity, and evaluate response to treatment. In some cases, repeated testing of inflammatory markers over time may be necessary to track changes in inflammation levels and assess treatment efficacy.
Clinical Applications of Inflammation Blood Tests:
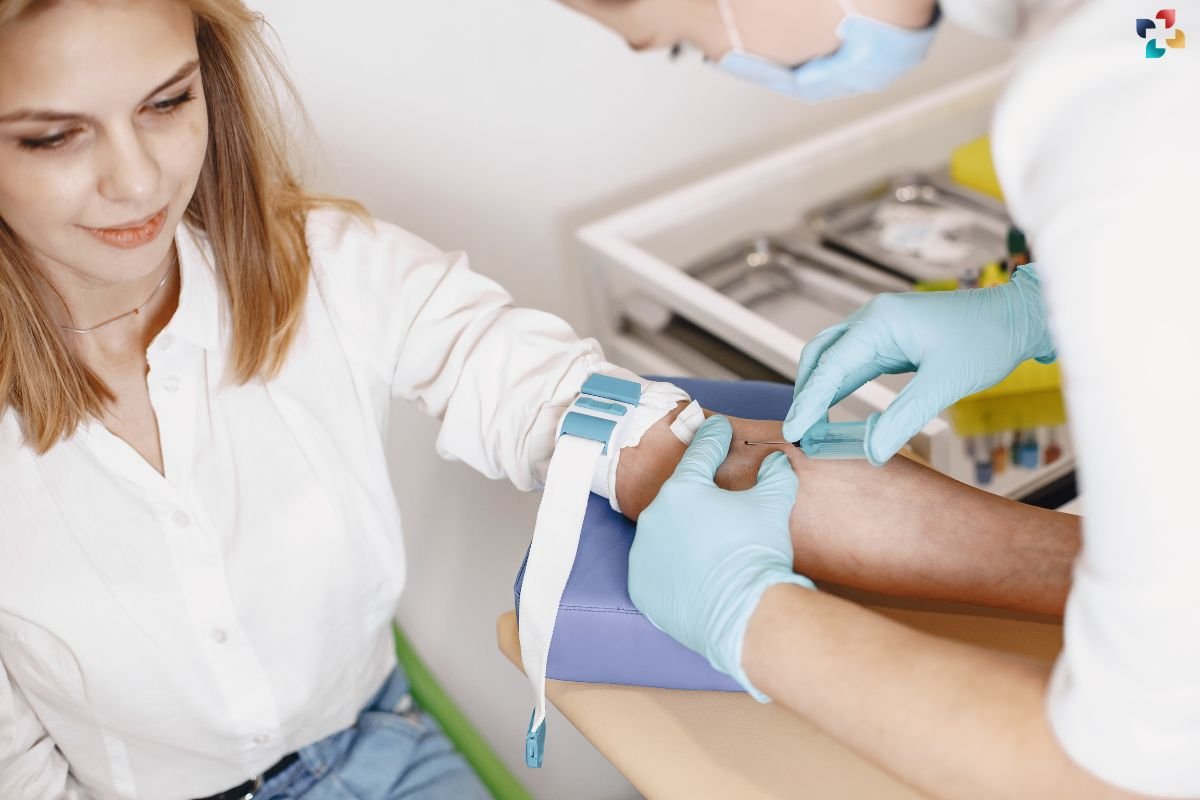
Inflammation blood tests have diverse clinical applications across various medical specialties. In primary care, inflammation blood tests are used to screen for and monitor inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and inflammatory bowel disease. In cardiology, elevated levels of CRP and other inflammatory markers are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular events such as heart attack and stroke, making inflammation blood tests valuable tools for risk stratification and preventive care.
In rheumatology, inflammation blood tests are used to diagnose and monitor autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and vasculitis. In gastroenterology, inflammation blood tests help assess disease activity and guide treatment decisions in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, inflammation blood tests are essential diagnostic tools used by healthcare providers to assess levels of inflammation in the body and aid in the diagnosis and management of various medical conditions. By measuring markers such as CRP, ESR, IL-6, and TNF-alpha, inflammation blood tests provide valuable insights into the inflammatory status of patients and help guide clinical decision-making. Incorporating inflammation blood tests into routine health assessments can facilitate early detection of inflammatory conditions, optimize treatment strategies, and improve patient outcomes. As our understanding of inflammation continues to evolve, inflammation blood tests will remain invaluable tools in the arsenal of modern medicine, enabling clinicians to identify and address inflammation-related health concerns more effectively.
FAQs
What are inflammation blood tests?
Inflammation blood tests are diagnostic tests that measure markers of inflammation in the bloodstream, providing valuable insights into the body’s immune response and inflammatory status.
What are some common markers measured in inflammation blood tests?
Common markers measured in inflammation blood tests include C-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), and white blood cell count (WBC).
What conditions can inflammation blood tests help diagnose or monitor?
Inflammation blood tests can help diagnose and monitor a wide range of inflammatory conditions, including infections, autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and rheumatologic disorders.
How are inflammation blood tests performed?
Inflammation blood tests are typically performed using a blood sample obtained through venipuncture. The sample is then analyzed in a laboratory to measure levels of specific inflammatory markers.
What do elevated levels of inflammatory markers indicate?
Elevated levels of inflammatory markers in blood tests may indicate the presence of acute or chronic inflammation in the body, which could be associated with infections, autoimmune diseases, tissue damage, or other inflammatory conditions. These markers help healthcare providers assess disease activity, guide treatment decisions, and monitor response to therapy.