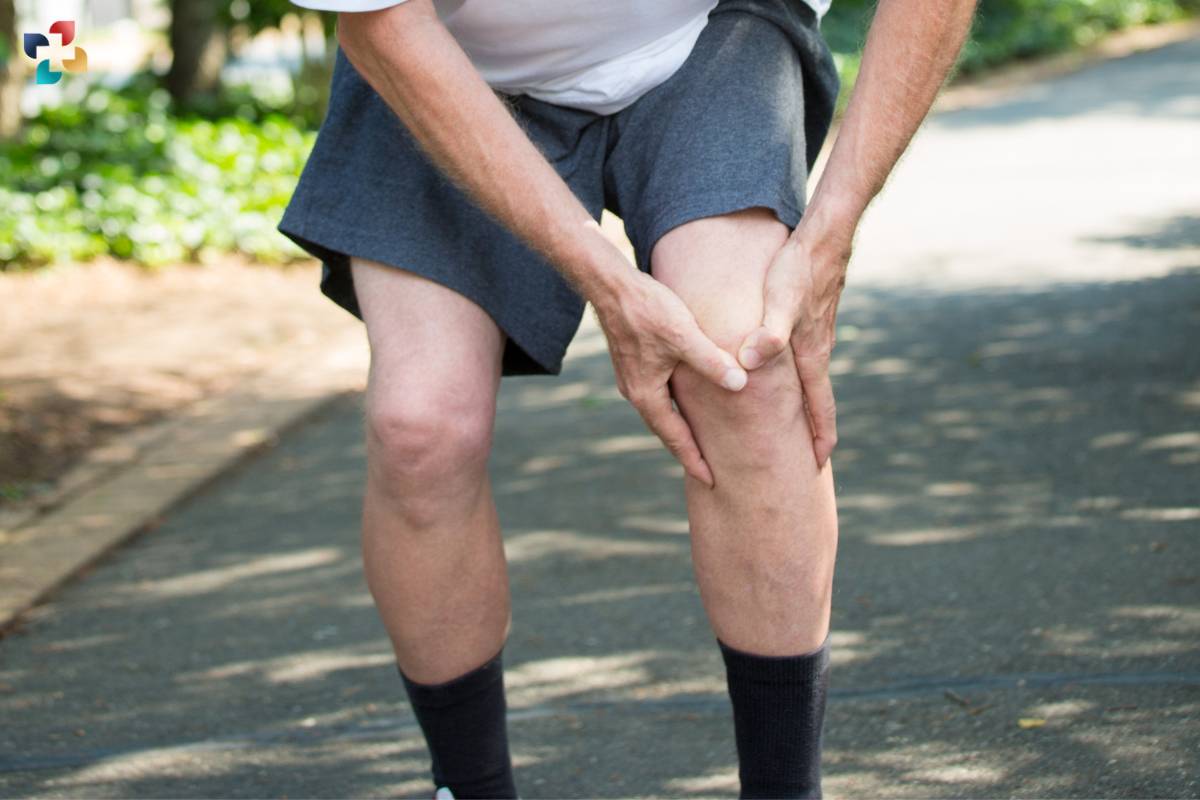
Quadriceps tendon tear is a debilitating injury that affects the knee joint, causing pain, swelling, and limited mobility. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of quadriceps tendon tears, including their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
What is a Quadriceps Tendon Tear?
A quadriceps tendon tear occurs when the tendon that connects the quadriceps muscles to the patella (kneecap) ruptures partially or completely. The quadriceps tendon plays a crucial role in extending the knee joint, allowing activities such as walking, running, and jumping. When the tendon tears, it can severely impair knee function and mobility.
Causes of Quadriceps Tendon Tear
Quadriceps tendon tears can result from various factors, including:
- Traumatic injury: Direct trauma to the knee, such as a fall or sudden impact, can cause the quadriceps tendon to tear.
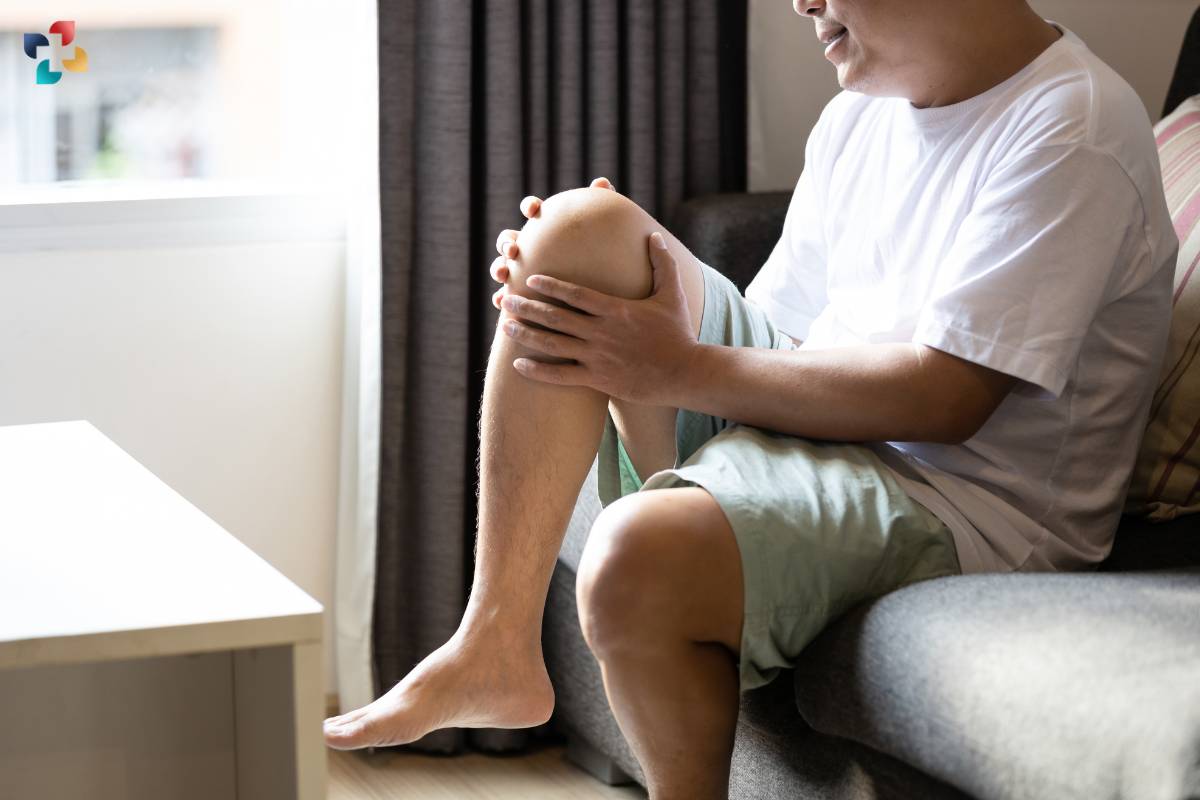

- Degenerative changes: Overuse, repetitive stress, and degenerative conditions such as tendinitis can weaken the quadriceps tendon over time, increasing the risk of tears.
- Pre-existing conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, obesity, and chronic kidney disease, can weaken the tendons and predispose them to injury.
Symptoms of Quadriceps Tendon Tear
The symptoms of a quadriceps tendon tear may vary depending on the severity of the injury but often include:
- Sudden, sharp pain in the front of the knee or upper thigh.
- Swelling and bruising around the knee joint.
- Difficulty or inability to straighten the knee or bear weight on the affected leg.
- A visible gap or depression above the kneecap where the tendon has torn.
- Weakness and instability in the knee joint. If left untreated, a quadriceps tendon tear can lead to long-term complications and functional limitations.
Diagnosis of Quadriceps Tendon Tear
Diagnosing a quadriceps tendon tear is crucial for initiating appropriate treatment and preventing further complications. Healthcare providers employ a multifaceted approach that encompasses thorough physical examination, careful review of the patient’s medical history, and specialized imaging techniques.
This comprehensive diagnostic process aims to accurately assess the extent of the injury, identify associated symptoms, and formulate an individualized treatment plan tailored to the patient’s needs. By conducting a detailed physical examination, healthcare professionals can evaluate the range of motion, stability, and strength of the knee joint, as well as assess for signs of swelling, bruising, or deformity.
Additionally, gathering information about the patient’s medical history, including previous injuries, chronic medical conditions, and activity level, helps to contextualize the injury and identify potential risk factors. Imaging tests, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound, and X-rays, play a pivotal role in confirming the diagnosis and visualizing the structural integrity of the quadriceps tendon. Together, these diagnostic modalities enable healthcare providers to make informed decisions regarding the most appropriate course of treatment for quadriceps tendon tears, ensuring optimal outcomes for patients.
1. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI scans can provide detailed images of the knee structures, allowing healthcare providers to visualize the extent of the tendon tear and assess for associated injuries.
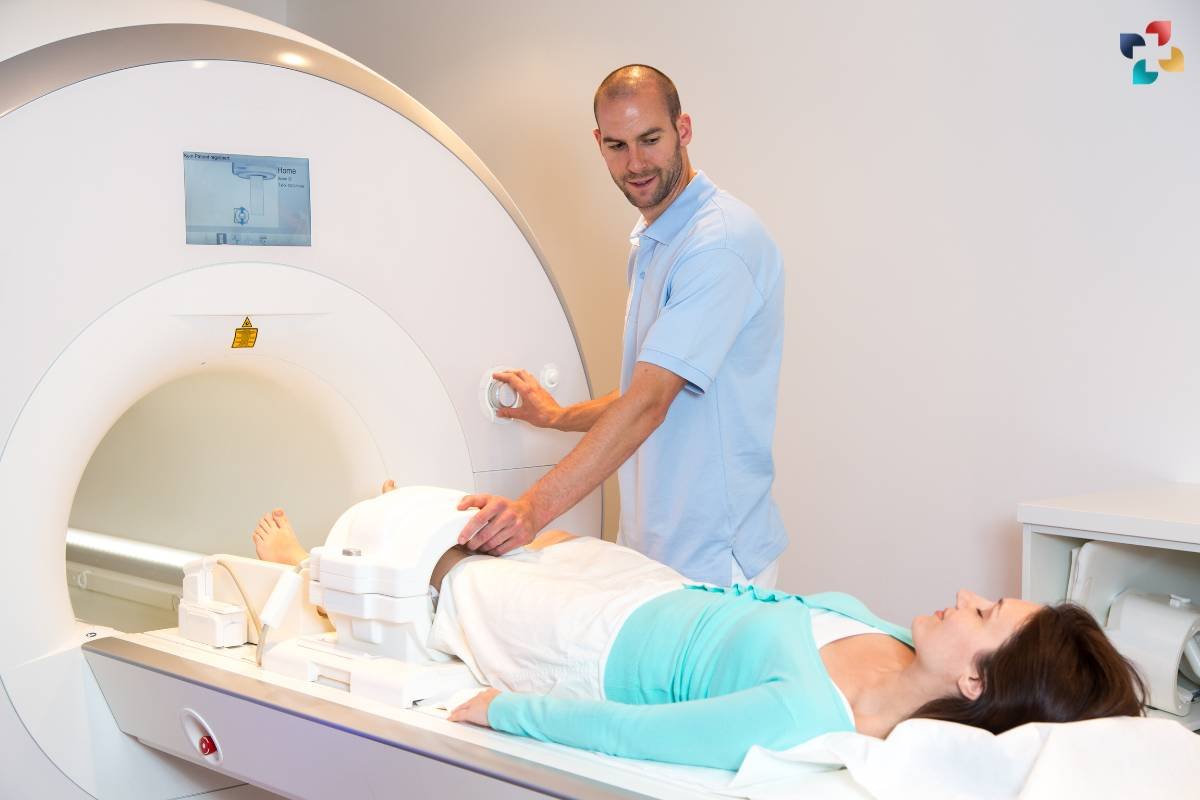
2. Ultrasound: Ultrasound imaging may be used to evaluate tendon integrity and detect abnormalities, such as tears or inflammation.
3. X-rays: X-rays can help rule out other potential causes of knee pain and assess for fractures or degenerative changes in the knee joint.
Treatment Options for Quadriceps Tendon Tear
The treatment approach for quadriceps tendon tears depends on the severity of the injury, the patient’s age, activity level, and overall health. Treatment options may include:
1. Conservative management: Mild to moderate quadriceps tendon tears may be treated conservatively with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), along with physical therapy to strengthen the surrounding muscles and improve the range of motion.
2. Immobilization: Severe quadriceps tendon tears may require immobilization of the knee joint using a brace or splint to prevent further damage and promote healing.
3. Surgical repair: In cases of complete tendon rupture or significant functional impairment, surgical repair may be necessary to reattach the torn tendon to the patella. This typically involves a minimally invasive procedure known as arthroscopic surgery, where small incisions are made to access the knee joint and repair the tendon using sutures or anchors.
4. Rehabilitation: Following surgical repair or conservative treatment, rehabilitation plays a crucial role in restoring knee function and mobility. Physical therapy exercises focus on strengthening the quadriceps and surrounding muscles, improving flexibility, and gradually reintroducing weight-bearing activities.
Conclusion
A quadriceps tendon tear is a serious knee injury that can significantly impact an individual’s mobility and quality of life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for quadriceps tendon tears, healthcare providers can effectively manage these injuries and help patients achieve optimal recovery and functional outcomes. Early recognition and prompt intervention are key to successful treatment and rehabilitation of quadriceps tendon tears, ensuring a speedy return to normal activities and sports participation.
FAQs
1. What causes a quadriceps tendon tear?
Quadriceps tendon tears often result from sudden, forceful contractions of the quadriceps muscles, typically during activities involving jumping, running, or lifting heavy objects. They can also occur due to degenerative changes in the tendon over time, particularly in older individuals.
2. What are the symptoms of a quadriceps tendon tear?
Common symptoms include severe pain and swelling around the knee, difficulty straightening the leg, a noticeable gap or indentation above the kneecap, and weakness or instability when bearing weight on the affected leg.
3. How is a quadriceps tendon tear diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, where a healthcare provider assesses the range of motion, stability, and strength of the knee joint. Imaging tests such as MRI, ultrasound, or X-ray may also be used to confirm the diagnosis and evaluate the extent of the injury.
4. What treatment options are available for a quadriceps tendon tear?
Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the tear. Conservative approaches may include rest, ice, physical therapy, and bracing. In more severe cases or complete tears, surgical repair may be necessary to reattach the tendon to the kneecap or patella.
5. What is the recovery time for a quadriceps tendon tear?
Recovery time can vary depending on the severity of the tear, the chosen treatment approach, and individual factors such as age and overall health. In general, recovery may take several weeks to months, with physical therapy playing a crucial role in restoring strength and function to the affected knee.