Omeprazole, a proton pump inhibitor, is a medication commonly prescribed for humans to treat gastrointestinal conditions such as acid reflux, ulcers, and gastritis. However, omeprazole has also found utility in veterinary medicine, particularly in the treatment of similar gastrointestinal issues in dogs. Understanding the uses, dosage, and potential side effects of omeprazole for dogs is essential for pet owners to ensure the well-being of their canine companions.
Uses of Omeprazole for Dogs:
Omeprazole for dogs is primarily used to treat various gastrointestinal disorders, including gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), gastritis, esophagitis, and ulcers. Dogs may experience symptoms such as vomiting, regurgitation, excessive salivation, and discomfort due to these conditions. Omeprazole works by reducing the production of stomach acid, thereby alleviating symptoms and promoting healing of the gastrointestinal lining.
In veterinary medicine, omeprazole is often prescribed to address a spectrum of gastrointestinal issues that can plague dogs, from mild discomfort to severe conditions. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), commonly seen in canines, occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation and discomfort. This condition can manifest in symptoms like regurgitation, heartburn, and difficulty swallowing, leading to significant discomfort for affected dogs. Gastritis, characterized by inflammation of the stomach lining, is another common ailment that can cause vomiting, abdominal pain, and loss of appetite in dogs. Omeprazole’s ability to reduce stomach acid production can help alleviate these symptoms and promote healing of the inflamed tissues.
Esophagitis, an inflammation of the esophagus often caused by acid reflux or other irritants, can also benefit from omeprazole therapy. Dogs suffering from esophagitis may exhibit symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, drooling, and reluctance to eat due to the discomfort associated with swallowing. Omeprazole can help reduce esophageal inflammation and provide relief from these symptoms, improving the dog’s overall quality of life.
Furthermore, omeprazole is commonly used to treat ulcers in dogs, which can develop in the stomach or small intestine due to various factors such as prolonged use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), infections, or systemic diseases. Ulcers can cause abdominal pain, vomiting, and dark, tarry stools in dogs, necessitating prompt treatment to prevent complications such as perforation or bleeding. By inhibiting stomach acid production, omeprazole helps promote ulcer healing and prevents recurrence, allowing affected dogs to recover more quickly and comfortably.
Overall, omeprazole’s efficacy in addressing a wide range of gastrointestinal disorders makes it a valuable tool in veterinary medicine. Its ability to alleviate symptoms, promote healing, and improve the quality of life for dogs suffering from GERD, gastritis, esophagitis, and ulcers highlights its importance as a therapeutic option in the management of canine gastrointestinal health.
Dosage of Omeprazole for Dogs
The dosage of omeprazole for dogs varies depending on the severity of the gastrointestinal condition, the size of the dog, and the veterinarian’s recommendations. Generally, omeprazole is administered orally in the form of tablets or capsules. The typical dosage ranges from 0.25 to 0.5 mg per pound of body weight, given once daily. It is essential to follow the veterinarian’s instructions regarding dosage and administration to ensure optimal efficacy and safety.
Side Effects of Omeprazole for Dogs
While omeprazole is generally well-tolerated in dogs, some potential side effects may occur, including:
1. Gastrointestinal Upset
Dogs may experience mild gastrointestinal upset, such as nausea, diarrhea, or constipation, particularly when initiating omeprazole treatment. These symptoms typically resolve on their own or with adjustments to the dosage.
2. Changes in Appetite
Some dogs may exhibit changes in appetite, either increased or decreased while taking omeprazole. Monitoring food intake and adjusting feeding schedules may help manage appetite changes.
3. Rare Side Effects

In rare cases, dogs may experience more severe side effects such as allergic reactions, liver dysfunction, or neurological symptoms. If any unusual or concerning symptoms occur, it is crucial to seek veterinary attention promptly.
Precautions and Considerations
Before administering omeprazole to dogs, several precautions and considerations should be taken into account:
1. Veterinary Consultation
Always consult with a veterinarian before giving omeprazole to dogs, as they can assess the dog’s health status, determine the appropriate dosage, and monitor for potential side effects.
2. Underlying Conditions

Omeprazole may not be suitable for dogs with certain underlying conditions, such as liver or kidney disease. Inform the veterinarian of any pre-existing health issues to ensure the safe administration of omeprazole.
3. Drug Interactions
Omeprazole may interact with other medications, including antacids, antibiotics, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Inform the veterinarian about any medications or supplements the dog is currently taking to avoid potential drug interactions.
Omeprazole Dosing Chart
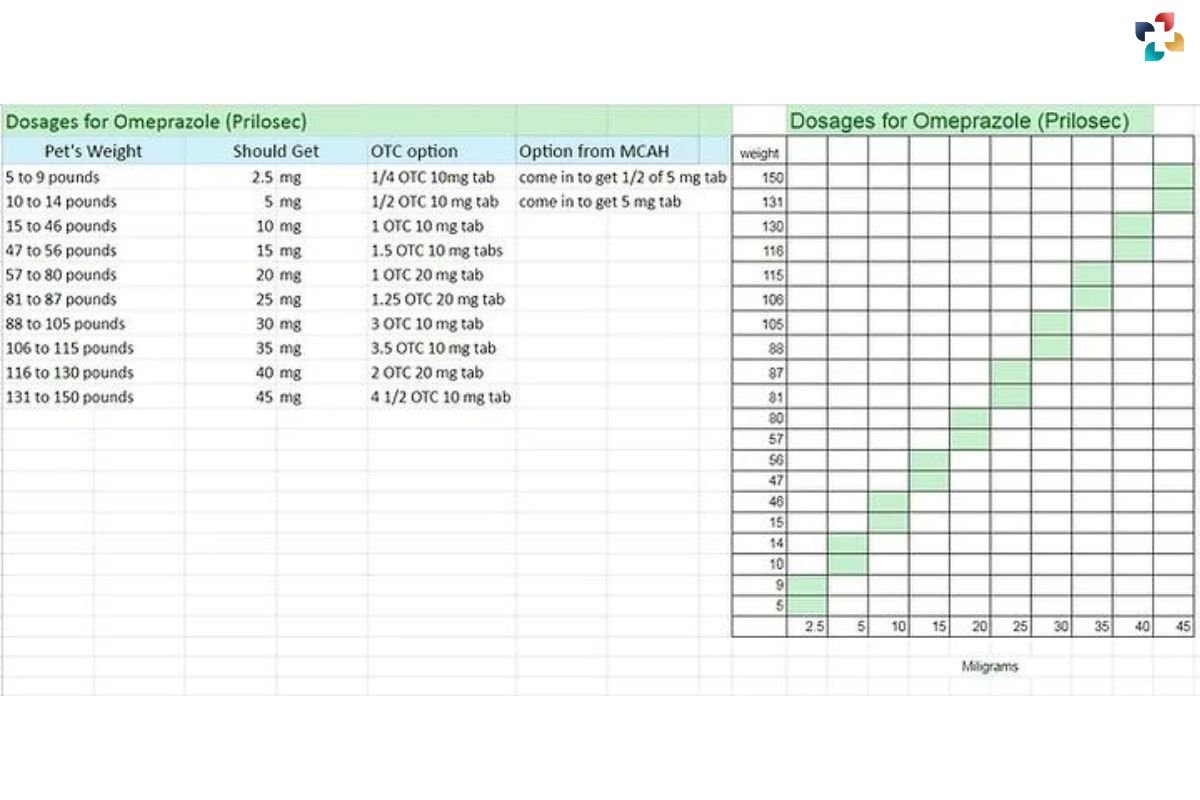
Conclusion
Omeprazole for dogs is a valuable medication for treating gastrointestinal disorders such as acid reflux, ulcers, and gastritis. Understanding the uses, dosage, and potential side effects of omeprazole is essential for pet owners to ensure the well-being of their canine companions. By working closely with a veterinarian and following their recommendations, pet owners can effectively manage gastrointestinal issues and improve the quality of life for their dogs.
FAQs
1. What is omeprazole, and how does it work for dogs?
Omeprazole is a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) that reduces the production of stomach acid in dogs. It works by inhibiting the action of proton pumps in the stomach lining, thereby decreasing acid secretion and alleviating symptoms associated with gastrointestinal disorders.
2. What conditions in dogs can omeprazole treat?
Omeprazole is commonly prescribed to treat gastrointestinal disorders in dogs, including gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), gastritis, esophagitis, and ulcers. It helps reduce symptoms such as vomiting, regurgitation, abdominal pain, and discomfort.
3. How is omeprazole administered to dogs?
Omeprazole for dogs is typically available in tablet or capsule form and is administered orally. The dosage and frequency of administration vary depending on the dog’s weight, the condition being treated, and the veterinarian’s recommendations. It can be given with or without food, but consistency in administration is essential for optimal effectiveness.
4. Are there any side effects of omeprazole in dogs?
While omeprazole is generally well-tolerated in dogs, some may experience mild side effects such as diarrhea, vomiting, or changes in appetite. Serious adverse reactions are rare but may include allergic reactions or liver dysfunction. It’s crucial to monitor dogs closely for any adverse effects and consult a veterinarian if concerns arise.
5. Can omeprazole interact with other medications or supplements?
Omeprazole may interact with certain medications or supplements, particularly those that rely on stomach acid for absorption. Examples include antacids, sucralfate, and some antibiotics. It’s essential to inform the veterinarian about all medications and supplements your dog is taking to avoid potential interactions and ensure safe and effective treatment.