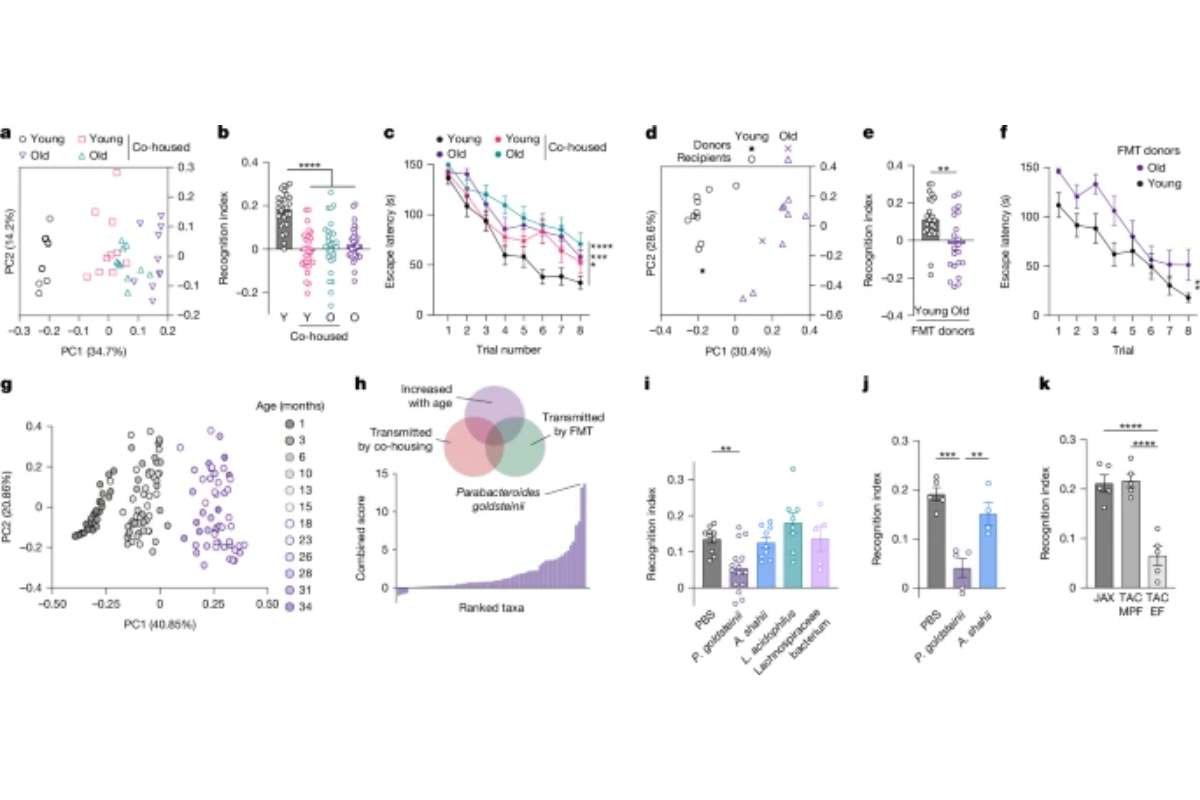
A revolutionary area of biotechnology known as genetic engineering has produced an amazing range of breakthroughs that go beyond what was previously thought to be feasible. This article examines 12 strange genetic engineering instances, ranging from illuminating plants to spider goats, demonstrating the inventiveness and brilliance that occur when scientists work with the basic building blocks of life.
Here are 12 Bizarre Examples of Genetic Engineering:
1. Glowing Plants: Bioluminescence Unleashed
In a mesmerizing display of genetic engineering, scientists have successfully engineered plants to emit light through bioluminescence. By incorporating genes from bioluminescent organisms, such as fireflies, into the plant’s genome, researchers have created plants that glow in the dark. Apart from their aesthetic appeal, these glowing plants hold the potential for environmentally friendly urban lighting.
Beyond their captivating visual allure, these bioluminescent plants have practical implications for sustainable urban planning. The ability to create natural sources of light through genetic engineering opens doors to reducing reliance on traditional energy-consuming lighting systems. Imagine city streets adorned with trees and plants that emit a soft, natural glow, providing ambient illumination without the need for streetlights.
This not only enhances the aesthetic charm of urban landscapes but also contributes to energy conservation and a diminished carbon footprint. The mesmerizing radiance of these genetically engineered plants might just be the beacon guiding us toward a greener and more environmentally conscious future.
2. Spider-Goats: Nature’s Silk Producers
Combining the genes of spiders and goats may sound like the premise of a science fiction story, but it’s a reality in the realm of genetic engineering. Scientists have engineered goats to produce spider silk proteins in their milk. This silk, known for its strength and elasticity, can be harvested and used for various applications, including lightweight and durable materials.
3. Enviropigs: Eco-Friendly Swine
Enviropigs are genetically modified pigs designed to produce lower levels of phosphorus in their manure. Excessive phosphorus runoff from conventional pig farming contributes to water pollution. Enviropigs address this environmental concern by efficiently utilizing phosphorus in their diet, resulting in reduced phosphorus content in their waste.
4. Flavr Savr Tomato: Prolonging Freshness

The Flavr Savr tomato holds the distinction of being the first commercially approved genetically modified (GM) food. Engineered to have an extended shelf life, this tomato was designed to ripen more slowly, allowing for greater flexibility in harvesting and transportation without sacrificing flavor.
Moreover, the Flavr Savr tomato represents a milestone in the evolution of genetic modification in agriculture. Its approval marked a paradigm shift in how we approach food production and distribution. By extending the tomato’s freshness, it addressed challenges in the supply chain, reducing food wastage and enhancing accessibility.
The success of the Flavr Savr tomato paved the way for further research and development in genetically modified crops, fostering discussions about the intersection of technology, agriculture, and global food security. This pioneering tomato not only graced our tables with its enduring freshness but also catalyzed a broader dialogue on the future of sustainable and resilient food systems.
5. AquAdvantage Salmon: Fast-Growing Fish
AquAdvantage Salmon, a genetically modified salmon, is designed to grow faster than its non-modified counterparts. By incorporating a growth hormone gene from Chinook salmon and a regulatory gene from the ocean pout, this engineered salmon reaches market size more rapidly, offering potential benefits for sustainable aquaculture.
Related: Decoding Genetics: Exploring Examples of Single Gene Disorders
6. Dolly the Sheep: Cloning Breakthrough
Dolly the Sheep made history as the first mammal to be cloned from an adult somatic cell using a technique called somatic cell nuclear transfer. This groundbreaking achievement in genetic engineering opened new possibilities for cloning and reproductive technologies.
7. BioSteel® Spider Silk: Strength in Fibers
Inspired by the strength and resilience of spider silk, scientists have engineered bacteria to produce silk proteins similar to those found in spider silk. This BioSteel® material offers remarkable strength and elasticity, with potential applications in textiles, medical devices, and more.
8. Blue Roses: A Floral Hue Transformation
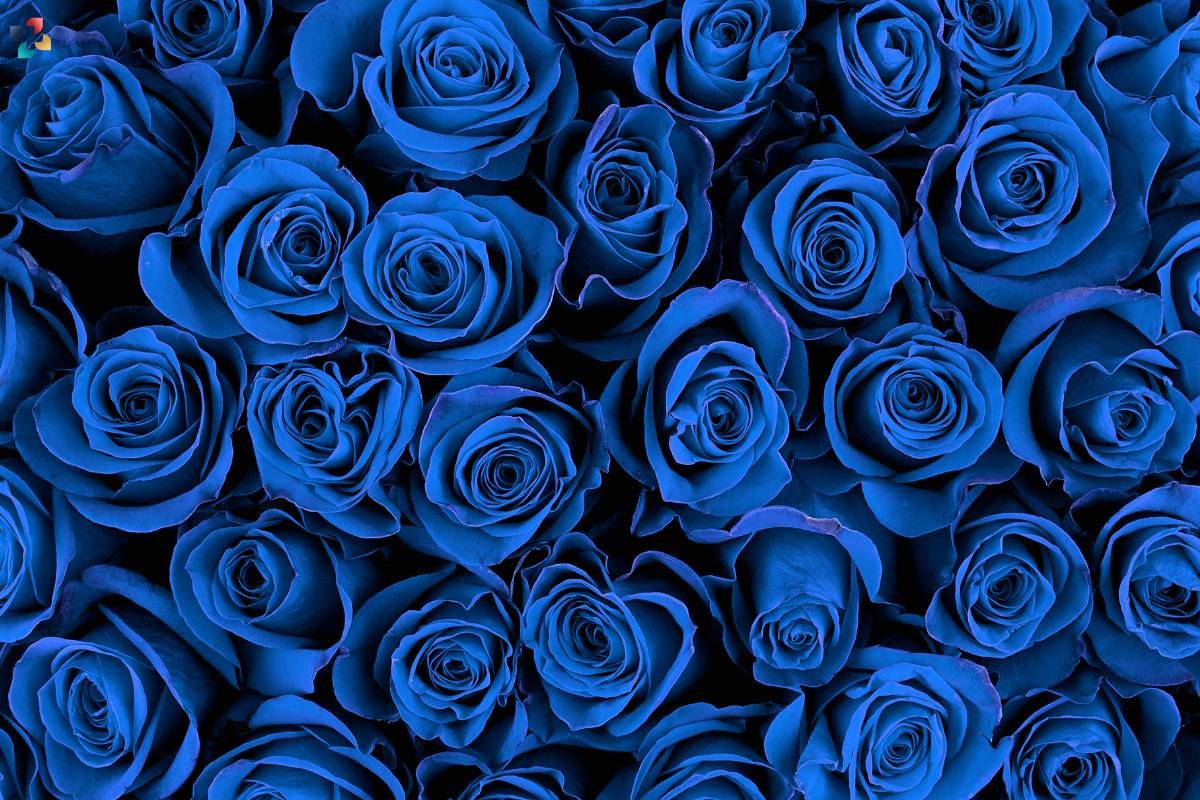

The quest for the elusive blue rose led to genetic engineering solutions. By introducing genes responsible for blue pigment synthesis from other plants, researchers have successfully engineered roses to exhibit a striking blue hue. This serves as a testament to the creative possibilities unlocked by manipulating plant genomes.
9. Altered Apples: Browning Resistance
Genetic engineering has been employed to enhance the shelf life and aesthetic appeal of apples by reducing browning. By suppressing the expression of genes involved in browning reactions, genetically modified apples resist enzymatic browning, offering consumers a visually appealing and longer-lasting fruit.
10. Venomous Cabbages: Targeting Crop Pests
In a bid to protect crops from insect pests, scientists have engineered cabbage plants to produce a toxin found in scorpion venom. This toxin acts as a natural insecticide, deterring pests and reducing the need for chemical pesticides in agriculture.
11. Heat-Tolerant Chickens: Climate-Resilient Poultry
As climate change poses challenges to poultry farming, researchers have turned to genetic engineering to develop heat-tolerant chickens. By identifying genes associated with heat resistance, scientists aim to create poultry that can thrive in warmer climates, ensuring the sustainability of poultry production.
12. Muscle-Enhanced Super Dogs: A Leap in Canine Genetics

In the realm of canine genetics, scientists have explored the possibility of enhancing muscle mass in dogs through genetic engineering. While primarily an area of research, the concept raises ethical considerations and discussions about the responsible use of genetic engineering in animals.
Ethical Considerations and Future Perspectives
There are many ethical questions that arise as genetic engineering pushes boundaries. Intentional modification of living things brings up issues related to misuse, unexpected results, and environmental effects. Achieving an equilibrium between scientific advancement and ethical accountability is crucial as we explore the unexplored realm of genetic engineering.
Genetic engineering has the potential to solve urgent issues in the future, from producing climate change-resistant crops to establishing ground-breaking medicinal therapies. As this subject develops, ethical frameworks, regulatory supervision, and public discussion will be critical in determining how genetic engineering is applied responsibly and advantageously in our society.