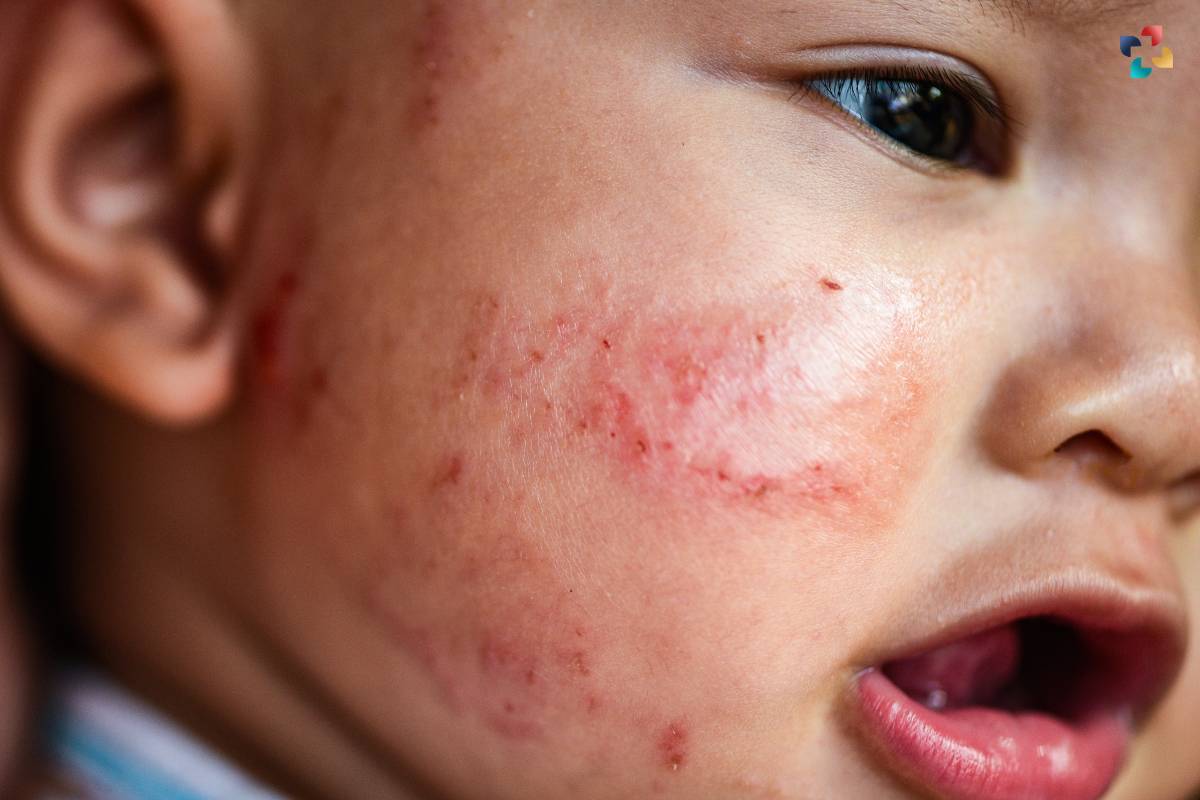
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common skin condition characterized by inflammation, itching, and redness. When eczema affects the face, it can be particularly distressing and challenging to manage due to the visible nature of the symptoms. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for eczema on the face, along with practical tips for managing and alleviating symptoms.
Understanding Eczema on the Face:
Eczema on the face refers to atopic dermatitis that specifically affects the facial skin. It can occur in people of all ages, from infants to adults, and is often triggered by various factors, including genetics, environmental factors, and immune system dysfunction.
Eczema on the face is a challenging condition characterized by redness, itching, dryness, and inflammation of the facial skin. It can manifest as patches of rough, scaly skin, or as fluid-filled blisters that ooze and crust over. The discomfort and visible symptoms of eczema on the face can have a significant impact on one’s appearance, self-esteem, and overall quality of life. Managing eczema on the face requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both the underlying causes and the symptoms to alleviate discomfort and promote skin healing.
The symptoms of eczema on the face can vary in severity and may include:
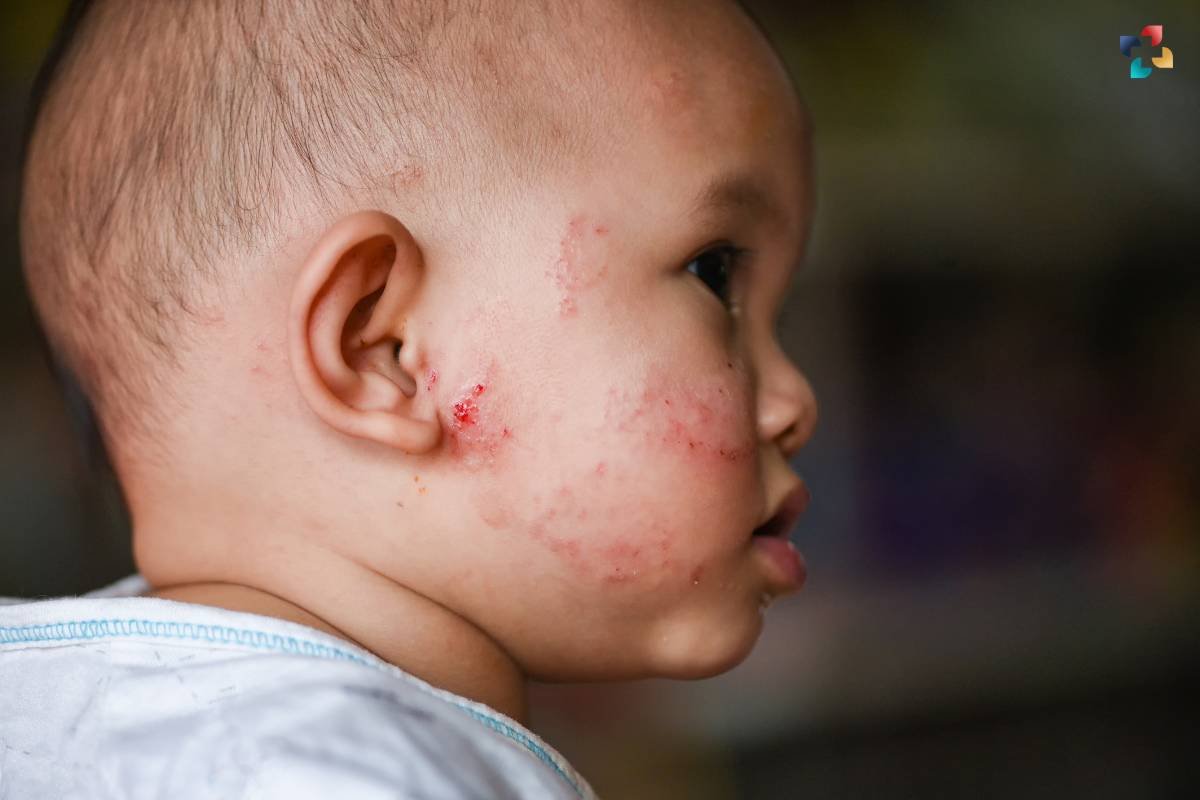
- Redness: The affected areas of the face may appear red or inflamed, particularly around the cheeks, forehead, and chin.
- Itching: Itching is a common symptom of eczema on the face and can range from mild to severe, leading to discomfort and irritation.
- Dryness: The skin affected by eczema on the face may become dry, rough, and scaly, with patches of flaky or cracked skin.
- Swelling: In some cases, eczema on the face may cause swelling, particularly around the eyes and lips.
- Crusting: Eczema flare-ups on the face may result in the formation of crusts or oozing lesions, especially if the skin is scratched or irritated.
Causes of Eczema on Face:
Eczema on the face can be triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. People with a family history of eczema, asthma, or allergies are at increased risk of developing eczema on the face. Environmental factors such as harsh weather conditions, exposure to irritants or allergens, and stress can also contribute to flare-ups of facial eczema.
Additionally, certain skincare products, cosmetics, and fragrances may contain ingredients that irritate sensitive facial skin, exacerbating eczema symptoms. Hormonal changes, such as those occurring during puberty or pregnancy, can also influence the development or worsening of eczema on the face. Furthermore, individuals with compromised immune systems or underlying health conditions may be more susceptible to experiencing facial eczema flare-ups. Understanding the various triggers and causes of eczema on the face is crucial for effectively managing the condition and minimizing its impact on daily life.
Treatment Options for Eczema on Face:
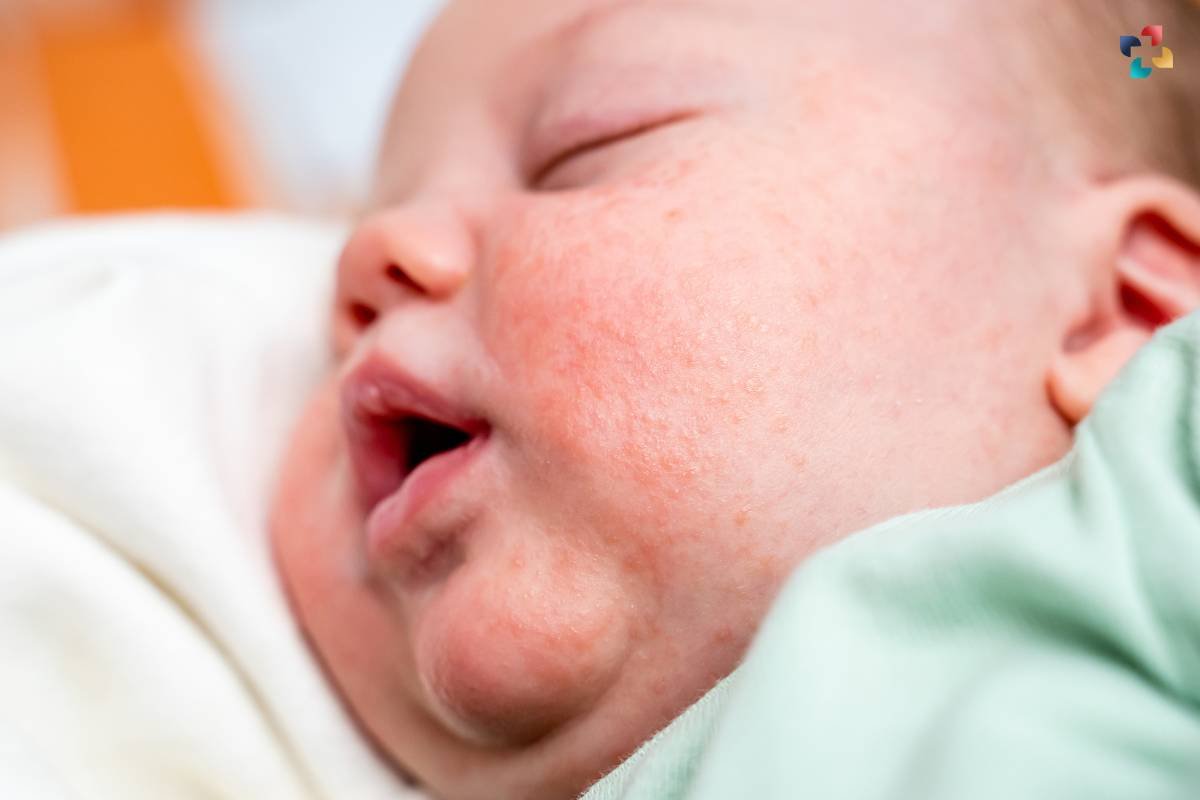

Treatment for eczema on the face focuses on relieving symptoms, reducing inflammation, and preventing flare-ups. Depending on the severity of the condition, treatment options may include:
1. Topical Steroids
Topical corticosteroids are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and itching associated with eczema on the face. These medications come in various strengths and formulations and should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
2. Moisturizers
Regular application of moisturizers helps to hydrate the skin, improve its barrier function, and reduce dryness associated with eczema on the face. Choose fragrance-free, hypoallergenic moisturizers and apply them liberally to the affected areas after bathing or showering.
3. Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors
In cases where topical steroids are not suitable or effective, topical calcineurin inhibitors such as tacrolimus or pimecrolimus may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and itching.
4. Antihistamines
Oral antihistamines may be recommended to relieve itching and promote better sleep, particularly if itching is interfering with daily activities or causing significant discomfort.
5. Avoidance of Triggers
Identifying and avoiding triggers such as harsh soaps, fragrances, and certain foods can help prevent flare-ups of eczema on the face. Keep a journal to track potential triggers and make necessary lifestyle changes to minimize exposure.
Home Remedies for Eczema on Face:
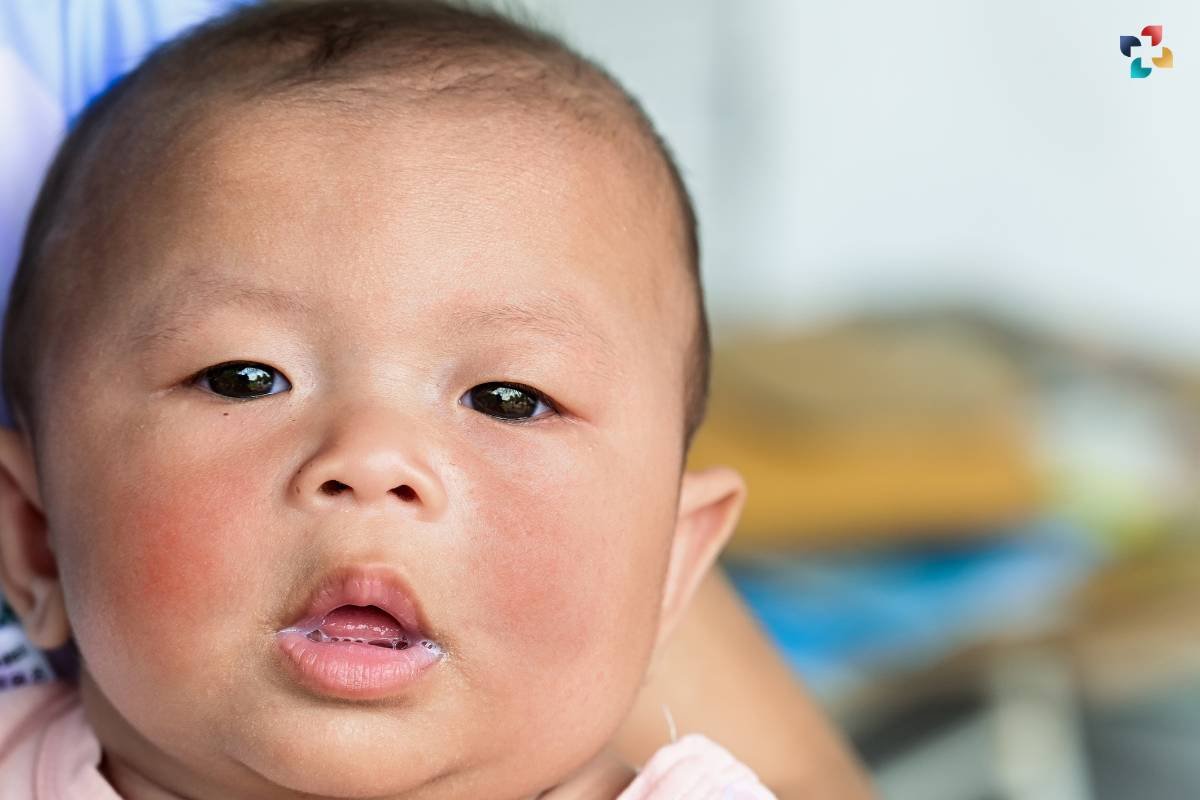

In addition to medical treatments, several home remedies may help alleviate symptoms and support skin health in eczema on the face. These include:
1. Warm Compresses
Apply a warm, damp cloth to the affected areas of the face to soothe itching, reduce inflammation, and promote relaxation.
2. Oatmeal Baths:
Taking an oatmeal bath can help soothe irritated skin and relieve itching associated with eczema on the face. Add colloidal oatmeal to lukewarm bathwater and soak for 15-20 minutes.
3. Coconut Oil
Coconut oil has moisturizing and anti-inflammatory properties that can help hydrate the skin and reduce inflammation. Apply virgin coconut oil to the affected areas of the face as needed.
4. Aloe Vera Gel
Aloe vera gel has soothing and healing properties that can help calm inflamed skin and promote healing. Apply pure aloe vera gel to the affected areas of the face and leave it on for 10-15 minutes before rinsing off with water.
5. Proper Skincare
Use gentle, fragrance-free skincare products designed for sensitive skin to cleanse and moisturize the face. Avoid harsh soaps, alcohol-based products, and exfoliants that can irritate the skin and exacerbate eczema symptoms.
Conclusion:
Eczema on the face can be a challenging condition to manage, but with proper treatment and care, most individuals can find relief from symptoms and improve their skin health. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for eczema on the face, along with incorporating practical tips and home remedies into their skincare routine, individuals can effectively manage their condition and enjoy clearer, healthier skin. If symptoms persist or worsen despite home remedies and over-the-counter treatments, consult a dermatologist for further evaluation and personalized treatment recommendations.