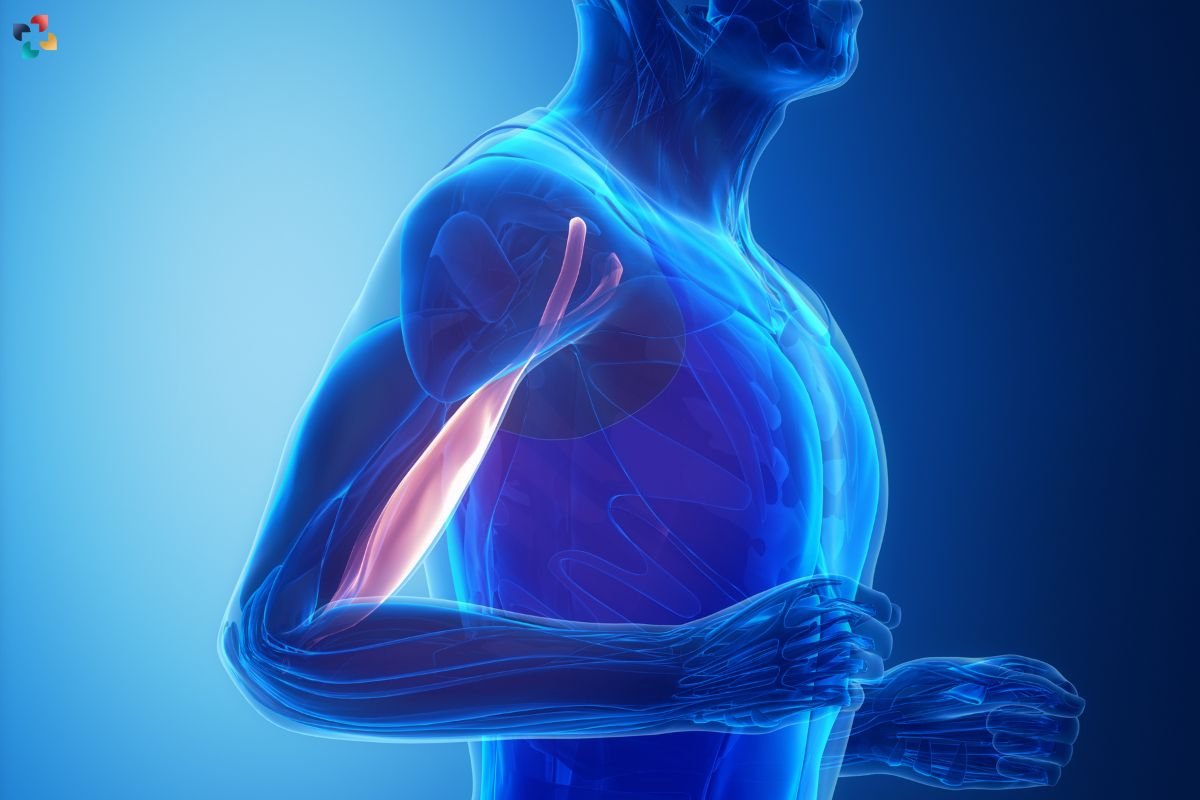
Distal biceps tendonitis is a common yet often misunderstood condition affecting the biceps tendon. This article provides a comprehensive overview of distal biceps tendonitis, covering its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. By understanding this condition in depth, individuals can better manage and prevent it.
What is Distal Biceps Tendonitis?
It is an inflammation of the biceps tendon which attaches to the radius bone in the forearm, known as the distal end. The biceps tendon is crucial for the functioning of the arm, as it helps with elbow flexion and forearm supination. When this tendon becomes irritated or inflamed, it leads to pain and reduced functionality, which can significantly impact daily activities.
Causes of Distal Biceps Tendonitis
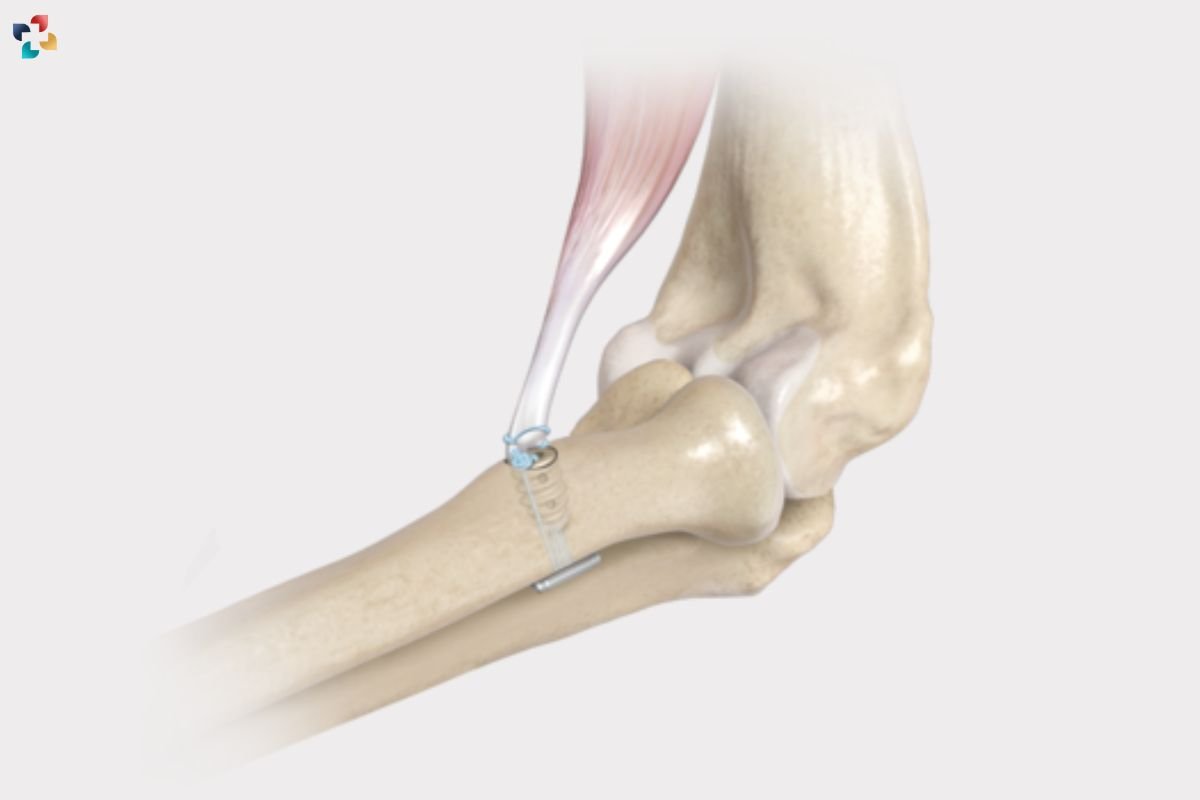
Several factors can contribute to distal biceps tendonitis. Understanding these causes is crucial for effective management and prevention.
- Repetitive Stress: Engaging in activities that involve repetitive motion, such as weightlifting, rowing, or other sports, can place excessive stress on the biceps tendon. Over time, this repetitive strain can lead to inflammation of the distal biceps of the Tendon.
- Aging: As people age, tendons naturally lose their elasticity and strength. This degeneration makes them more susceptible to inflammation and injuries like Inflammation of the Distal Biceps Tendon.
- Trauma: Direct trauma or sudden injury to the elbow or forearm can result in Inflammation of the Distal Biceps Tendon. This is often seen in cases where an individual experiences a sudden, forceful contraction of the biceps muscle.
- Improper Technique: Using improper techniques during physical activities, particularly those involving heavy lifting or strenuous movements, can contribute to the development of inflammation of the distal biceps tendon.
- Genetic Factors: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to tendon issues, making them more likely to develop conditions like Inflammation of the Distal Biceps Tendon.
Symptoms of Distal Biceps Tendonitis
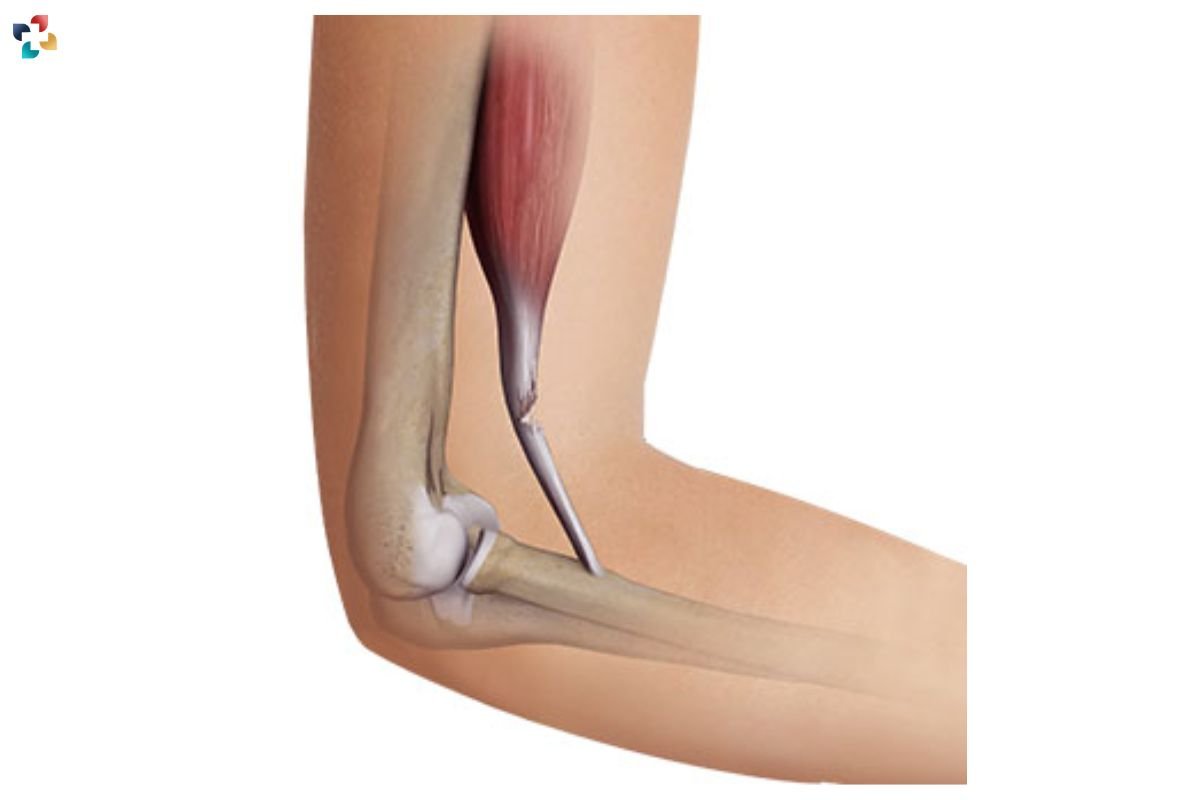
Identifying it early can help in managing the condition effectively. Common symptoms include:
- Pain: The primary symptom of this is pain in the front of the elbow. This pain may worsen with activities involving elbow flexion or forearm rotation.
- Tenderness: There is often tenderness in the area where the biceps tendon attaches to the radius bone.
- Swelling: Inflammation of the tendon can lead to swelling around the elbow joint.
- Weakness: Individuals may experience weakness in the arm, particularly when trying to lift objects or perform tasks that require elbow flexion.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Distal biceps tendonitis can limit the range of motion in the elbow and forearm, making it difficult to perform certain movements.
Diagnosing Distal Biceps Tendonitis
Accurate diagnosis of distal biceps tendonitis involves a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging studies.
- Physical Examination: A healthcare provider will perform a physical examination, assessing the area of tenderness, range of motion, and strength of the affected arm. They may also conduct specific tests to determine if the pain is related to the biceps tendon.
- Imaging Studies: To confirm the diagnosis, imaging studies such as ultrasound or MRI may be used. These tests help visualize the biceps tendon and assess the extent of inflammation or damage.
- Patient History: Understanding the patient’s history of physical activities, previous injuries, and symptoms helps in making an accurate diagnosis.
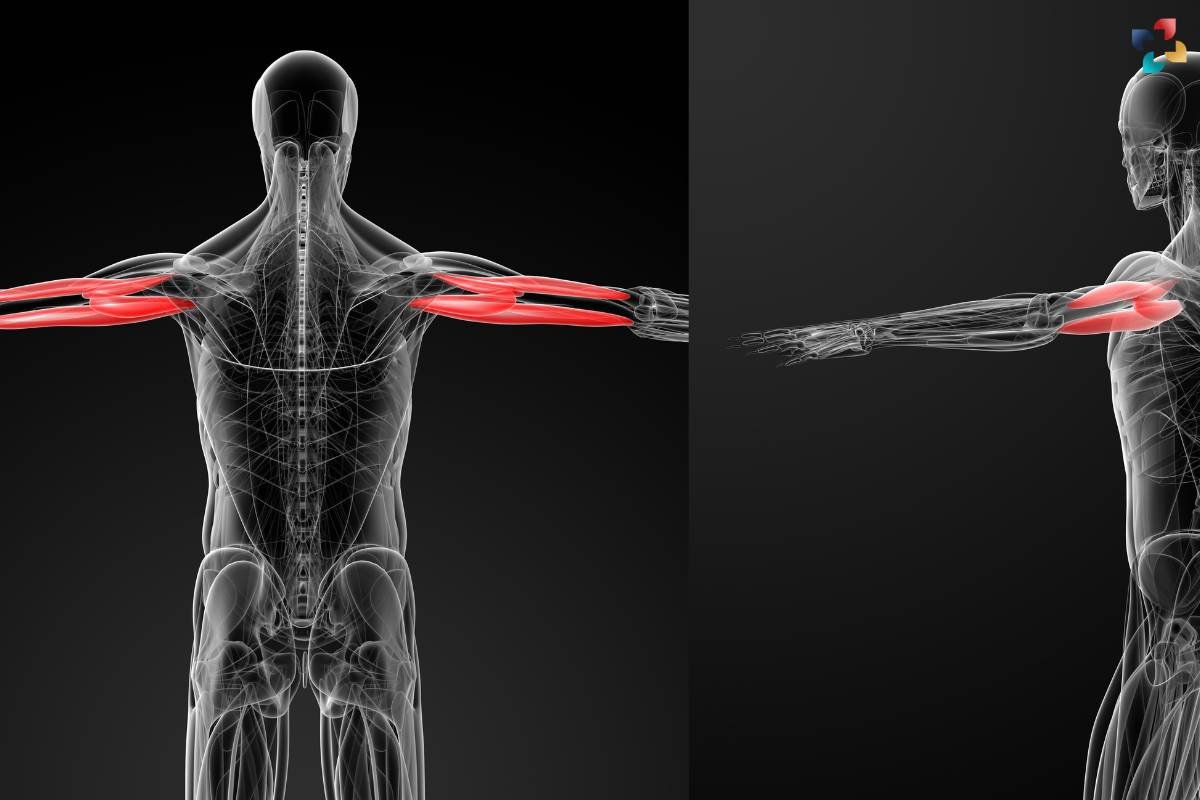
Unlocking the Power of Biceps Brachii: A Comprehensive Guide
The biceps brachii, often referred to simply as the biceps, is one of the most recognizable muscles in the human body. In this comprehensive guide, we delve deep into the anatomy, function, exercises, and common injuries associated with the biceps brachii.
Treatment Options for Distal Biceps Tendonitis
Treatment for distal biceps tendonitis aims to reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and restore normal function. The approach may vary based on the severity of the condition and individual needs.
- Rest and Activity Modification: Resting the affected arm and avoiding activities that exacerbate the pain is crucial. Modifying or temporarily stopping activities that place stress on the biceps tendon helps in reducing inflammation.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice to the affected area can help reduce swelling and alleviate pain. It is generally recommended to use ice for 15-20 minutes several times a day.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be used to reduce pain and inflammation. Medications like ibuprofen or naproxen may be recommended by a healthcare provider.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can design a rehabilitation program to strengthen the muscles around the elbow and improve flexibility. Therapy may include exercises to enhance the range of motion and prevent future injuries.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In cases of severe inflammation, corticosteroid injections may be used to provide temporary relief. These injections help reduce swelling and pain in the affected area.
- Surgery: If conservative treatments fail to provide relief or if there is significant tendon damage, surgical intervention may be considered. Surgical options may involve repairing or reattaching the biceps tendon.
Preventing Distal Biceps Tendonitis
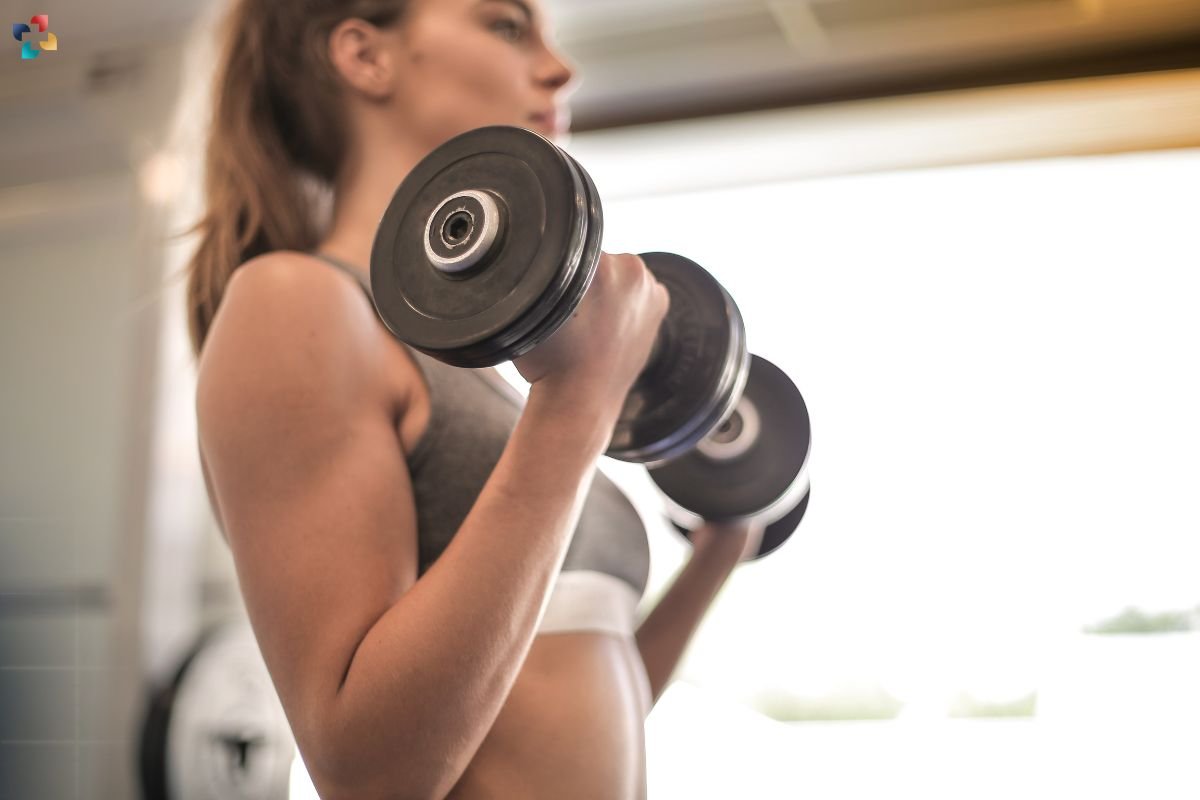

Preventing distal biceps tendonitis involves adopting strategies to reduce the risk of developing the condition. These strategies include:
- Proper Technique: Using proper technique during physical activities and exercises helps minimize stress on the biceps tendon. Seeking guidance from a fitness professional can ensure correct form.
- Strengthening Exercises: Engaging in exercises that strengthen the muscles around the elbow and shoulder can provide better support for the biceps tendon. Regular strength training helps prevent overuse injuries.
- Flexibility Training: Incorporating stretching exercises into your routine enhances flexibility and reduces the risk of tendonitis. Stretching the biceps and forearm muscles helps maintain their elasticity.
- Gradual Progression: Increasing the intensity of physical activities gradually allows the body to adapt and reduces the risk of overuse injuries. Avoid sudden increases in activity levels or weights.
- Rest and Recovery: Allowing adequate time for rest and recovery between strenuous activities is essential for tendon health. Overworking the biceps tendon without sufficient recovery can lead to inflammation and pain.
Conclusion
Distal biceps tendonitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the biceps tendon at its distal attachment. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition is crucial for effective management and prevention. By taking proactive measures such as proper technique, strengthening exercises, and gradual progression, individuals can reduce the risk of developing this and maintain optimal arm health.
If you experience symptoms of Inflammation of the Distal Biceps Tendon, seeking prompt medical attention is important for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. With the right approach, most individuals can recover from distal biceps tendonitis and return to their normal activities with improved strength and function.