Diagnostic imaging is an essential component of modern medicine that helps recognize and comprehend a wide range of medical disorders. The development of diagnostic imaging has completely changed how medical professionals see and diagnose illnesses, from fractures to abnormalities of the internal organs. The goal of this article is to examine the various kinds of diagnostic imaging methods that are now considered to be essential instruments in the toolbox of medical professionals. Patients should be aware of the variety of these approaches since they help to demystify medical procedures and give people the confidence to take an active role in their treatment.
Here are 10 Types of Diagnostic Imaging:
1. X-Ray Imaging: Unveiling the Skeletal Structure
Among the most well-known types of diagnostic imaging is X-ray imaging. This method utilizes electromagnetic radiation to capture images of the body’s internal structures. X-rays are commonly employed to examine the skeletal system, identifying fractures, dislocations, or abnormalities in bones. This non-invasive technique is rapid and widely accessible, making it a foundational tool in medical diagnostics.
2. Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: A 3D View Inside the Body
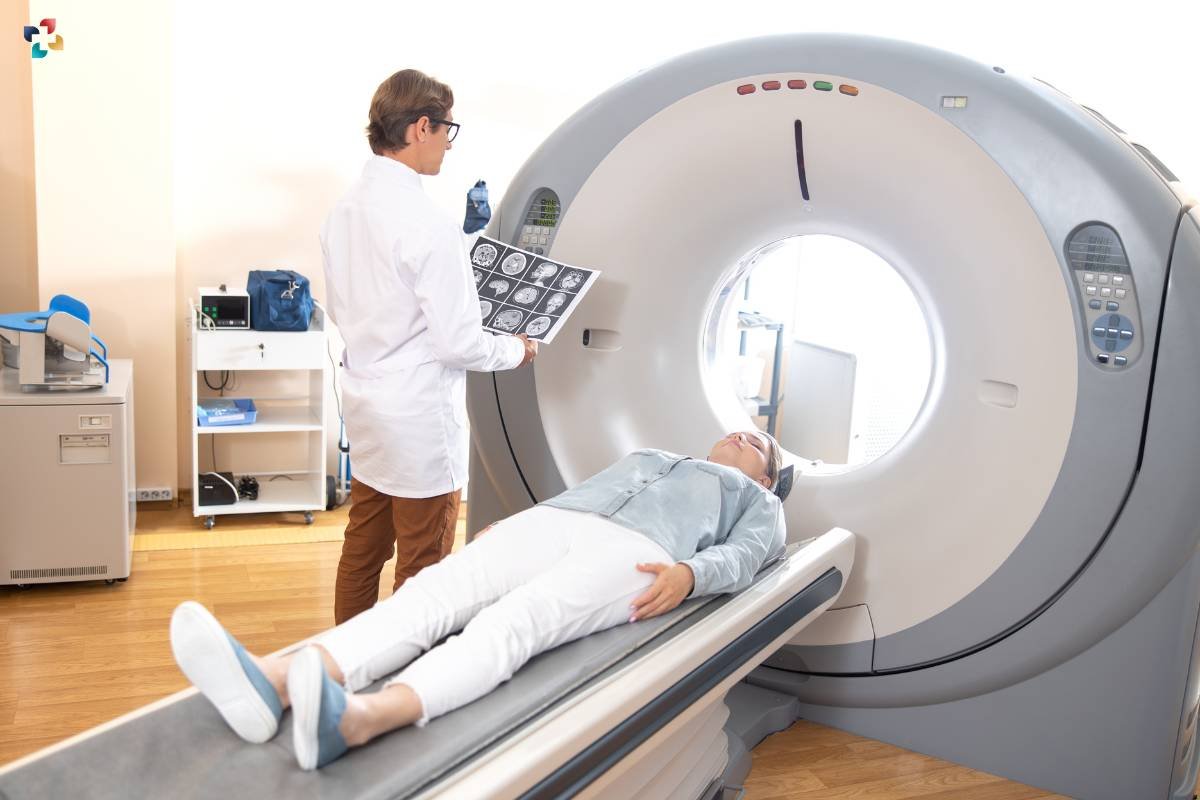
CT scans, also known as CAT scans, offer a more comprehensive view of internal organs and structures. This type of diagnostic imaging involves combining a series of X-ray images taken from different angles to create detailed cross-sectional images. CT scans are instrumental in detecting conditions such as tumors, blood clots, and internal injuries. The ability to generate 3D images enhances the precision of diagnosis and treatment planning.
3. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Mapping Soft Tissues
MRI is a non-invasive imaging technique that utilizes powerful magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of soft tissues, such as organs and muscles. This type of diagnostic imaging is particularly valuable in neurological and musculoskeletal examinations. MRI provides superior contrast for visualizing soft tissues, making it an essential tool for detecting conditions like brain tumors, spinal cord injuries, and joint abnormalities.
4. Ultrasound: Visualizing in Real-Time
Ultrasound, or sonography, is a dynamic type of diagnostic imaging that uses high-frequency sound waves to generate real-time images of the body’s internal structures. It is commonly associated with monitoring pregnancies, but its applications extend to various medical fields. Ultrasound is utilized to examine organs, blood vessels, and soft tissues, providing valuable insights into conditions like gallstones, vascular abnormalities, and abdominal issues.
5. Nuclear Medicine: Tracing Radioactive Tracers
Nuclear medicine involves introducing small amounts of radioactive substances, known as radiotracers, into the body. By detecting the emitted radiation, medical professionals can visualize the function and structure of organs and tissues. Techniques such as positron emission tomography (PET) and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) are common in nuclear medicine, enabling the assessment of metabolic activity and identifying conditions like cancer and cardiovascular diseases.
6. Fluoroscopy: Real-Time X-Ray Imaging
Fluoroscopy is a dynamic type of diagnostic imaging that involves continuous X-ray imaging to capture real-time moving images of the body’s internal structures. This technique is commonly used during medical procedures such as angiography (visualizing blood vessels) and gastrointestinal studies (examining the digestive system). Fluoroscopy aids in diagnosing conditions related to the functioning and movement of organs and structures.
7. Mammography: Screening for Breast Health
Mammography is a specialized type of diagnostic imaging focused on breast health. Using low-dose X-rays, mammograms help detect and diagnose breast abnormalities, including tumors and cysts. Regular mammography screenings play a pivotal role in early detection of breast cancer, contributing to improved treatment outcomes.
8. Bone Densitometry: Assessing Bone Density
Bone densitometry, or dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), is a diagnostic imaging technique specifically designed to assess bone density. This non-invasive test is crucial for diagnosing conditions like osteoporosis, helping to evaluate the risk of fractures. By measuring bone mineral density, healthcare professionals can initiate preventive measures and tailor treatment plans to enhance bone health.
9. Angiography: Visualizing Blood Vessels
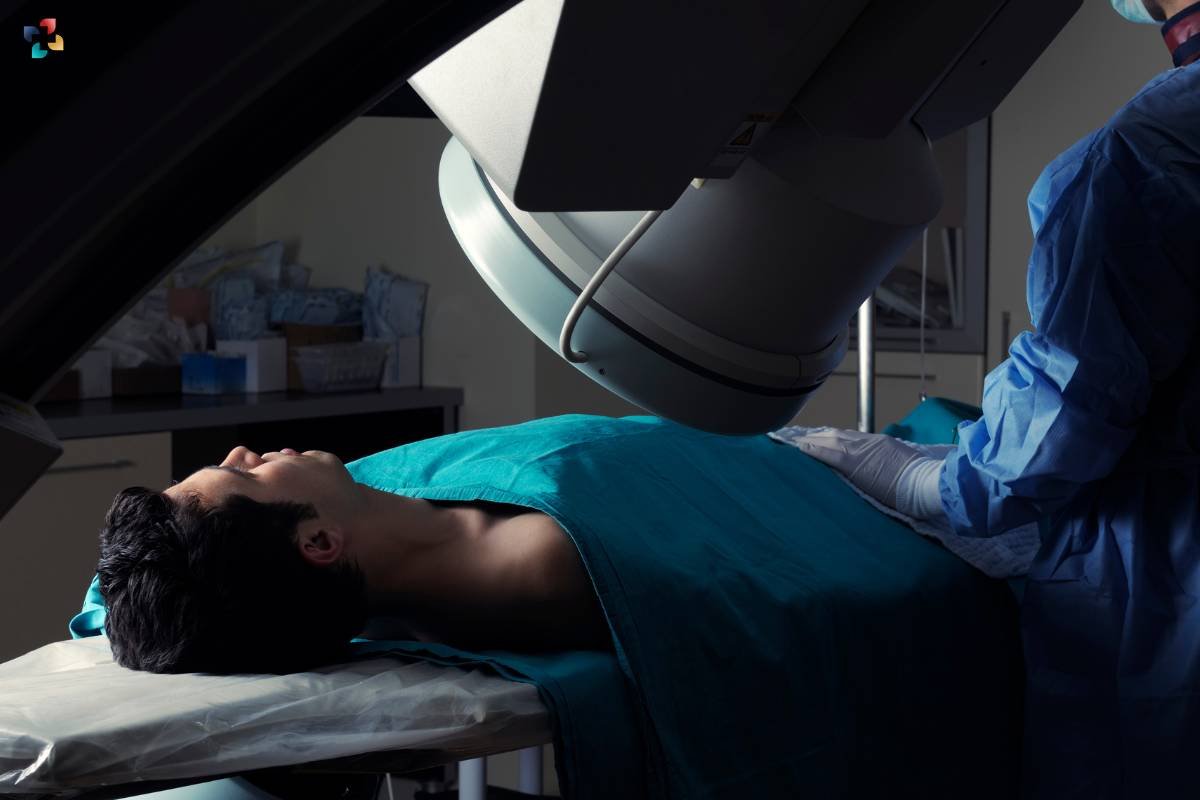
Angiography is a diagnostic imaging technique focused on visualizing blood vessels. It involves injecting a contrast dye into the blood vessels, making them visible on X-ray or fluoroscopy. Angiography is commonly used to diagnose conditions affecting the cardiovascular system, such as blockages, aneurysms, and vascular malformations.
10. Functional MRI (fMRI): Mapping Brain Activity
Functional MRI (fMRI) is an advanced imaging technique that not only captures detailed images of the brain’s structure but also maps its functional activities. By measuring changes in blood flow, fMRI enables the visualization of brain regions activated during specific tasks or stimuli. This type of diagnostic imaging is invaluable in neuroscience, helping researchers and clinicians understand brain function and detect abnormalities associated with neurological conditions.
The Role of Types of Diagnostic Imaging in Healthcare
The diverse array of diagnostic imaging techniques plays a pivotal role in healthcare by enabling precise and non-invasive visualization of the body’s internal structures and functions. These tools empower healthcare professionals to diagnose a wide range of conditions, from the most common to the most complex and life-threatening. Early detection facilitated by diagnostic imaging is often instrumental in initiating timely and effective treatments, contributing to improved patient outcomes.
Benefits and Considerations of Diagnostic Imaging
- Early Detection: Diagnostic imaging facilitates the early detection of abnormalities and conditions, allowing for prompt intervention and treatment.
- Non-Invasive Evaluation: Many types of diagnostic imaging are non-invasive, minimizing the need for surgical procedures and reducing patient discomfort.
- Treatment Planning: Detailed imaging helps healthcare professionals plan and execute surgical procedures with precision, enhancing the effectiveness of treatments.
- Monitoring Disease Progression: Diagnostic imaging allows for the ongoing monitoring of disease progression and the effectiveness of treatment regimens.
- Patient Education: Visual representations provided by diagnostic imaging empower patients to better understand their conditions, participate in treatment decisions, and take an active role in their healthcare.
- Despite the numerous advantages, it’s essential to consider certain factors associated with diagnostic imaging:
- Radiation Exposure: X-ray-based imaging techniques involve exposure to ionizing radiation, and repeated scans may accumulate radiation doses. Healthcare providers must balance the benefits of imaging against potential risks, especially in cases where alternative techniques with lower radiation exposure are available.
- Cost and Accessibility: Some advanced imaging techniques, such as MRI and CT scans, can be expensive, and accessibility may vary based on geographic location and healthcare resources.
- Contrast Agents: Certain imaging procedures, like angiography and CT scans, may require the use of contrast agents. While generally safe, individuals with allergies or kidney issues may experience adverse reactions.
- Pregnancy Concerns: Radiation exposure from certain imaging techniques, such as X-rays and CT scans, raises concerns during pregnancy. Healthcare providers must weigh the risks and benefits, considering alternative methods or delaying non-urgent imaging during pregnancy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, by offering a window into the complex structures and activities of the human body, the various forms of diagnostic imaging technology have revolutionized healthcare. Healthcare practitioners can diagnose, monitor, and treat a wide range of medical disorders with the help of these instruments, which range from basic X-ray imaging to the sophisticated capabilities of functional MRI. Further developments in precision medicine and personalized healthcare appear possible given the ongoing breakthroughs in diagnostic imaging technologies.
Patients, too, benefit from a better understanding of the various types of diagnostic imaging available to them. Informed participation in healthcare decisions, coupled with the guidance of knowledgeable healthcare professionals, contributes to a collaborative approach to diagnosis and treatment. As technology continues to advance, the field of diagnostic imaging remains at the forefront of medical innovation, shaping the future of healthcare and enhancing the quality of patient care.
Also Read: Emerging Trends in Regenerative Medicine