Cancer is one of the most severe health conditions. It can affect the patient’s health drastically. So detection of cancer in an early stage can give us an upper hand in improving health and result in successful treatment. Medical science has made a lot of progress, among which are the most remarkable advancements in using tumor biomarkers for diagnosis. These biomarkers help identify cancer cells at an early stage. This article will give an insight into these tumor biomarkers and their importance in cancer diagnosis.
What Are Tumor Biomarkers?
Tumor biomarkers for diagnosis are biological molecules used to detect the presence of cancer cells in the body. These biomarkers are substances, usually proteins, which are made by cancer cells or other cells in response to cancer. These biomarkers are found in the blood, urine, tissues, or other bodily fluids. These biomarkers can consist of various substances such as proteins, DNA, RNA, and hormones that transform in quantity or structure when cancer is present.
There are two main types of tumor biomarkers:
- Prognostic Biomarkers: These biomarkers give information about a patient’s overall cancer prognosis, such as how aggressive the cancer is and how likely it is to spread.
- Predictive Biomarkers: These provide insights into how well a patient will respond to a specific treatment.
When used correctly, tumor biomarkers for diagnosis can help doctors make informed decisions about treatment plans and early interventions.
Indicators of Tumor Biomarkers
There are several indicators of tumor biomarkers commonly used in cancer diagnosis, each with its unique role:
1. Genetic Markers:
Some cancers are associated with specific genetic mutations. For example, BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations are linked to breast and ovarian cancer. Detecting these mutations early can lead to a more accurate diagnosis and preventive treatment.
2. Proteins:
Certain proteins are overproduced by cancer cells. For instance, Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) is a protein often elevated in men with prostate cancer. High levels of PSA can indicate the presence of the disease and lead to further testing.
3. Enzymes and Hormones:
Some cancers lead to increased production of specific enzymes and hormones. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG), for example, is a hormone found at elevated levels in some cancers, such as testicular cancer.
4. Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs):
These are cancer cells that have broken away from the primary tumor and circulate in the bloodstream. Detecting Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) can be a sign of metastasis or recurrence.
By identifying these biomarkers, clinicians can often detect cancer at an earlier stage, which is crucial for successful treatment.
The Role of Tumor Biomarkers in Cancer Diagnosis
The use of tumor biomarkers for diagnosis has revolutionized the field of oncology. Previously, cancer diagnosis relied heavily on imaging techniques like X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs, which often detected cancer at a more advanced stage. However, with tumor biomarkers, it is now possible to detect cancer long before visible signs appear on imaging scans.
1. Early Detection
The most critical advantage of using tumor biomarkers for diagnosis is the potential for early detection. In some cases, biomarkers can indicate the presence of cancer even before a tumor is detectable through imaging or physical exams. For example, a rise in levels of PSA in the blood can signal the early stages of prostate cancer, even when there are no noticeable symptoms.
2. Monitoring Treatment
Tumor biomarkers also play a vital role in monitoring the effectiveness of cancer treatment. By measuring the levels of certain biomarkers, doctors can see how well a patient is responding to chemotherapy, radiation, or other forms of treatment. A decline in biomarker levels often indicates that the treatment is working, while stable or rising levels may suggest that the cancer is resistant to the current treatment plan.
3. Predicting Recurrence
One of the biggest fears for cancer patients is the possibility of recurrence after treatment. Tumor biomarkers for diagnosis can be used to monitor patients who are in remission, providing an early warning if cancer returns. Regular testing for biomarkers such as Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA) in colorectal cancer patients, for instance, can help detect a recurrence at an early and more treatable stage.
Limitations of Tumor Biomarkers
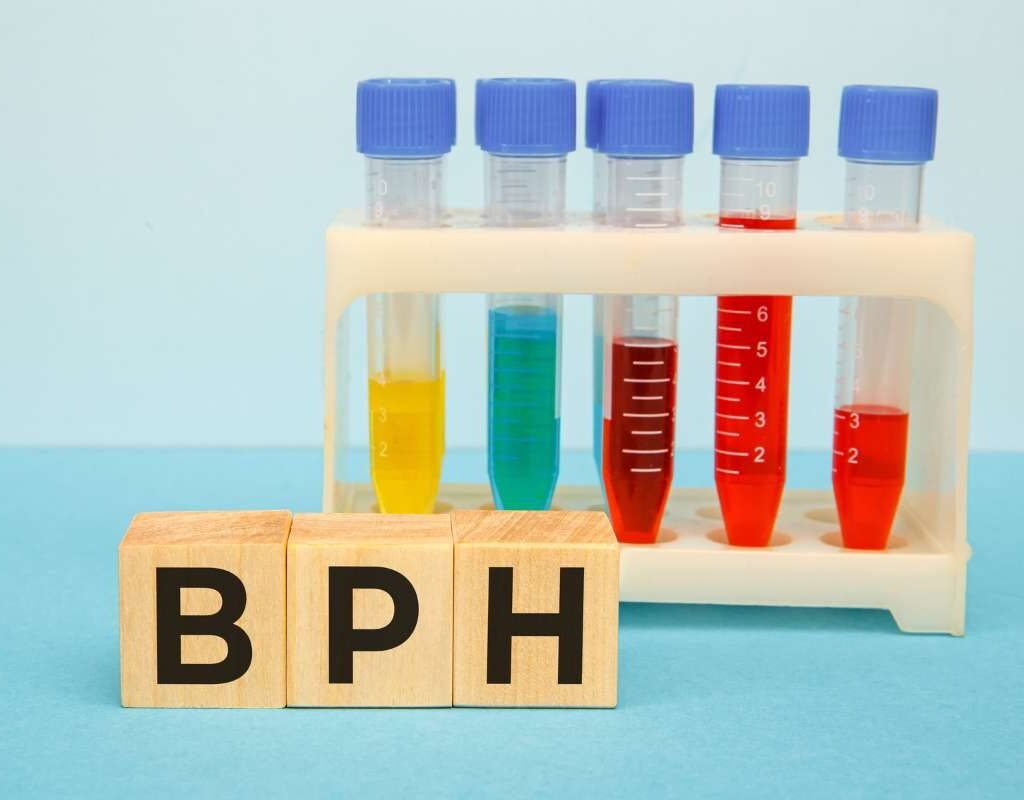

While tumor biomarkers for diagnosis are an invaluable tool, they do have limitations. One challenge is that some biomarkers may be elevated due to non-cancerous conditions. For example, PSA levels can also rise due to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostate infections, leading to false-positive results. This can cause unnecessary stress for patients and may result in further invasive testing, such as biopsies.
Moreover, not all cancers produce detectable biomarkers. In some cases, cancer cells may not release enough of a particular biomarker to be picked up by current tests. As a result, a cancer diagnosis might still be missed.
The Future of Tumor Biomarkers in Cancer Diagnosis
Advances in technology and genetic research are continually improving the field of biomarker-based cancer detection. The future holds promise for more personalized cancer treatments, where a patient’s unique biomarker profile can guide therapy choices. For instance, researchers are investigating the use of liquid biopsies, a non-invasive test that can detect multiple tumor biomarkers from a single blood sample. This approach could revolutionize cancer screening and diagnosis by providing more comprehensive and less invasive testing options.
Conclusion
Tumor biomarkers for diagnosis have come in as a boon in the medical field. Using these biomarkers, we are taking a step towards early detection and management of cancer. By recognizing biomarkers that indicate the presence of cancer, doctors can now diagnose earlier, also observe the course of treatment, and predict the risk of recurrence. Though some challenges can be overcome with time, it seem very promising from a futuristic perspective.
Including tumor biomarkers in routine diagnostic protocol could improve the way of cancer detection and treatment which could save many lives. As research continues, we can expect even more innovations in the field of biomarker-based cancer diagnosis, making it an indispensable tool in the fight against cancer.