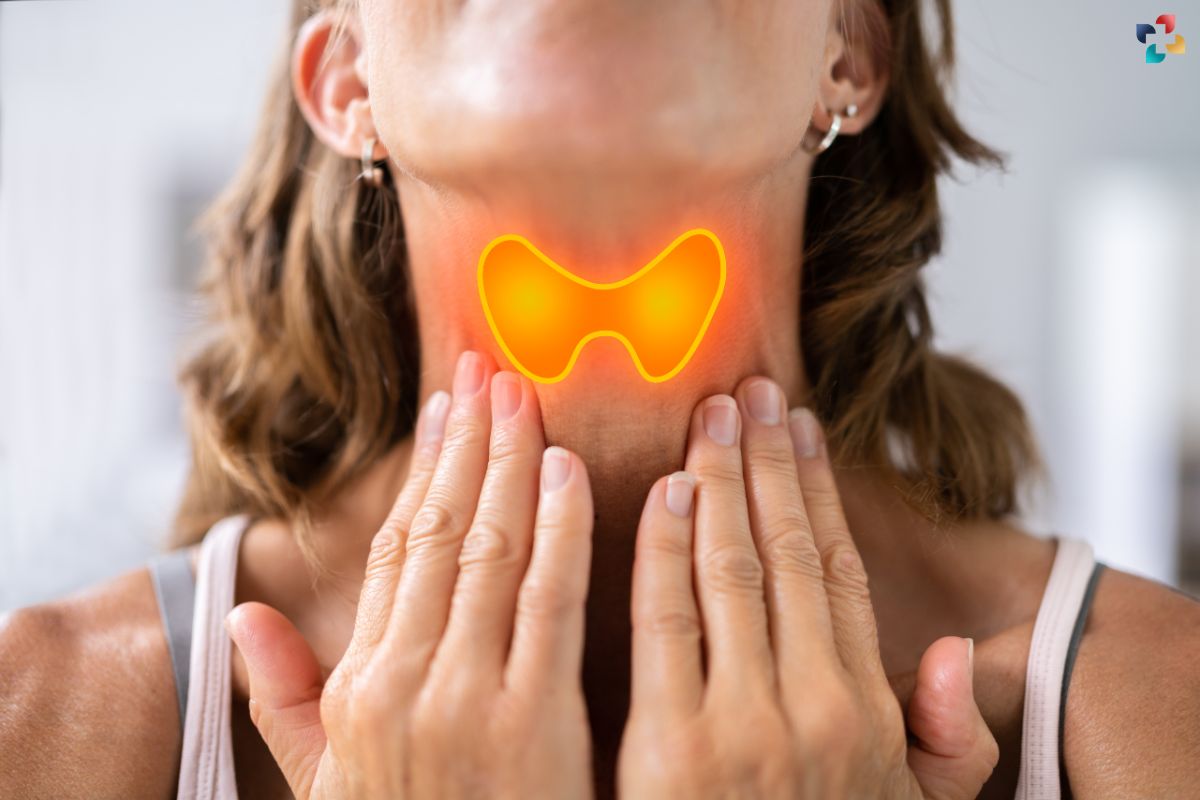
The thyroid, a small butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s metabolism through the production of thyroid hormones. When the thyroid gland fails to produce sufficient hormones, a condition known as underactive thyroid or hypothyroidism occurs. This condition can lead to a variety of symptoms and health issues if left untreated. This article delves into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of an underactive thyroid, offering a comprehensive understanding of this common but often misunderstood condition.
What is an Underactive Thyroid?
An underactive thyroid, or hypothyroidism, is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones to meet the body’s needs. These hormones, primarily thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), are critical for maintaining the body’s metabolic rate, heart function, digestive health, muscle control, brain development, and bone maintenance. When these hormones are in short supply, the body’s processes slow down, leading to various symptoms and health complications.
Causes of Underactive Thyroid
Several factors can contribute to the development of an underactive thyroid:
- Autoimmune Disease: The most common cause is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system attacks the thyroid gland.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, such as lithium, used to treat psychiatric disorders, can affect thyroid function.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation treatment for cancers of the head and neck can impair thyroid function.
- Thyroid Surgery: Removing all or a large portion of the thyroid gland can diminish hormone production.
- Iodine Deficiency: Iodine is essential for thyroid hormone production, and a deficiency can lead to hypothyroidism.
- Congenital Hypothyroidism: Some babies are born with a defective or absent thyroid gland.
- Pituitary Disorders: The pituitary gland controls the thyroid, and any malfunction can affect thyroid hormone production.
Common Signs and Symptoms
The symptoms of an underactive thyroid can be subtle and develop slowly, making it easy to overlook them initially. Common symptoms include:
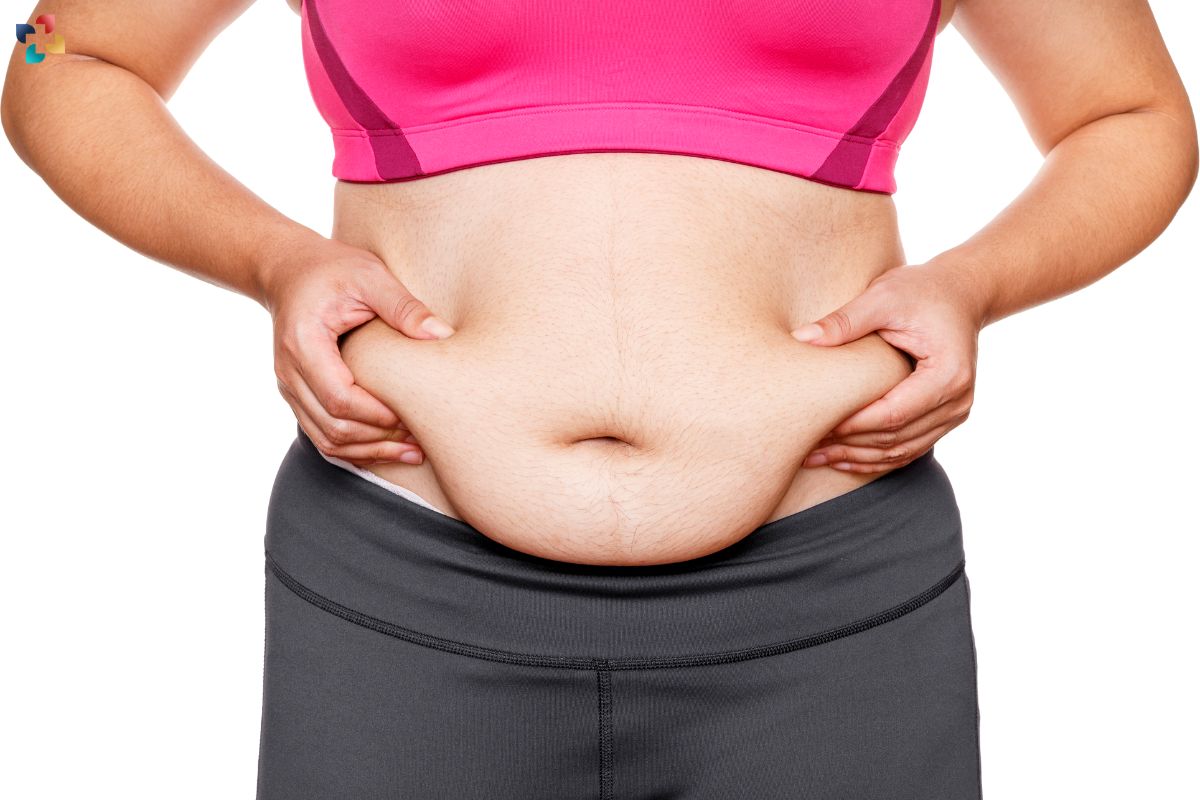

- Fatigue: A pervasive feeling of tiredness and lack of energy.
- Weight Gain: Unexplained weight gain despite no change in diet or activity level.
- Cold Intolerance: Increased sensitivity to cold temperatures.
- Dry Skin and Hair: Skin and hair can become dry and brittle.
- Muscle Weakness and Aches: Frequent muscle cramps and weakness.
- Constipation: Slowed digestive processes leading to constipation.
- Depression: Persistent low mood and depression.
- Memory Problems: Difficulty concentrating and memory lapses.
- Menstrual Changes: Irregular or heavy menstrual periods in women.
In men, symptoms can sometimes be more subtle and might include changes in libido, erectile dysfunction, and fertility issues. For a detailed list of signs specific to men, refer to the article from Southwest General Health Center .
Diagnosis of Underactive Thyroid
Diagnosing an underactive thyroid typically involves a combination of a physical examination, a review of medical history, and specific blood tests. Key tests include:
- TSH Test: The thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) test measures the level of TSH in the blood. Elevated TSH levels indicate that the pituitary gland is working harder to stimulate the thyroid, suggesting hypothyroidism.
- T4 Test: This test measures the level of thyroxine, the main hormone produced by the thyroid gland. Low levels of T4 confirm hypothyroidism.
- T3 Test: Although less commonly used, the T3 test measures triiodothyronine levels, providing additional information about thyroid function.
- Antibody Tests: Tests for thyroid antibodies can help diagnose autoimmune thyroid conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
Treatment Options
The primary treatment for an underactive thyroid is hormone replacement therapy, which aims to restore normal hormone levels. The most commonly prescribed medication is levothyroxine, a synthetic form of T4. Treatment involves:

- Medication: Levothyroxine is taken daily to normalize thyroid hormone levels. Dosage is carefully monitored and adjusted based on regular blood tests.
- Regular Monitoring: Periodic blood tests to check TSH and T4 levels ensure that the dosage is appropriate.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: A healthy diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being.
- Iodine Supplementation: In cases of iodine deficiency, dietary adjustments or supplements may be necessary.
Living with an Underactive Thyroid
Managing an underactive thyroid is a lifelong commitment that requires regular medical follow-up and adherence to treatment. However, with proper management, individuals with hypothyroidism can lead healthy, active lives. Here are some tips for living well with an underactive thyroid:
- Adhere to Medication: Take your medication exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Consistency is key to maintaining stable hormone levels.
- Monitor Symptoms: Keep track of any changes in symptoms and report them to your healthcare provider.
- Healthy Diet: Consume a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, including iodine, selenium, and zinc, which support thyroid function.
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in regular physical activity to boost energy levels and manage weight.
- Stay Informed: Educate yourself about hypothyroidism and stay updated on new research and treatment options.
How a Thyroid Gland Can Become Underactive?
Impact of Underactive Thyroid on Different Demographics
While an underactive thyroid can affect anyone, certain demographics are more prone to this condition. Understanding the impact on various groups can aid in early detection and management:
- Women: Hypothyroidism is more common in women, especially those over 60. Hormonal changes during pregnancy, menopause, or due to birth control can also trigger thyroid issues.
- Older Adults: Aging can affect thyroid function, and symptoms of hypothyroidism in older adults may be mistaken for normal aging signs.
- Infants and Children: Congenital hypothyroidism, if untreated, can lead to growth delays and intellectual disabilities. Newborn screening programs are essential for early detection.
- People with Autoimmune Diseases: Individuals with other autoimmune conditions, such as type 1 diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis, are at higher risk of developing hypothyroidism.
Complications of Untreated Underactive Thyroid
If left untreated, an underactive thyroid can lead to several serious health complications, including:
- Heart Problems: Hypothyroidism can raise cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart disease.
- Mental Health Issues: Severe, untreated hypothyroidism can lead to mental health issues, including depression and cognitive decline.
- Peripheral Neuropathy: Prolonged hypothyroidism can cause damage to the peripheral nerves, resulting in pain, numbness, or tingling in the limbs.
- Myxedema: This rare but life-threatening condition is characterized by severe hypothyroidism, leading to symptoms such as intense cold intolerance, drowsiness, and even coma.
- Infertility and Birth Defects: In women, untreated hypothyroidism can cause infertility and complications during pregnancy, including birth defects.

Preventive Measures
While not all cases of hypothyroidism can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk and aid in early detection:
- Regular Screening: Regular thyroid function tests, especially for those with risk factors, can help detect hypothyroidism early.
- Iodine Intake: Ensuring adequate iodine intake through diet or supplements can prevent iodine deficiency-related hypothyroidism.
- Managing Autoimmune Conditions: Proper management of autoimmune diseases can reduce the risk of developing thyroid issues.
- Avoiding Radiation Exposure: Limiting unnecessary radiation exposure, especially in the head and neck area, can protect thyroid health.
Conclusion
An underactive thyroid is a manageable condition with the right treatment and lifestyle adjustments. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain their thyroid health. Regular medical check-ups, adherence to prescribed medication, and a healthy lifestyle are key to living well with hypothyroidism. If you suspect you have an underactive thyroid, consult your healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation and appropriate management.
By staying informed and proactive, you can effectively manage your thyroid health and lead a vibrant, healthy life. Remember, early detection and treatment are crucial in preventing the complications associated with hypothyroidism. Stay vigilant, stay healthy, and take control of your thyroid health today.

8 Rare Symptoms of Thyroid to Watch Out
If you have any worries about your thyroid gland, you should discuss them with your primary care physician so that they can devise a strategy to help you get your health back on track.