In the world of cardiology, diagnostic tools are essential for accurately assessing heart health. One such tool is the stress echocardiogram, a test that combines echocardiography and exercise to evaluate how well the heart functions under stress. This article delves into the intricacies of stress echo, their importance, procedure, benefits, risks, and how they compares to other cardiac tests.
What is a Stress Echocardiogram?
It is a non-invasive test that uses ultrasound imaging to visualize the heart while it is subjected to physical stress. The primary goal is to assess the heart’s function and structure during increased physical activity, which can reveal conditions that may not be apparent during a resting echocardiogram.
Importance of Stress Echo
It plays a crucial role in diagnosing various heart conditions. They are particularly useful for detecting coronary artery disease (CAD), assessing the severity of heart valve diseases, and evaluating the effectiveness of cardiac treatments. By comparing images of the heart at rest and during stress, doctors can identify areas with poor blood flow or damage.
The Procedure of a Stress Echocardiogram
Understanding the procedure of a stress echo can help alleviate any anxiety associated with the test. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
1. Preparation
Before the test, patients are advised to avoid eating or drinking for a few hours and to wear comfortable clothing and shoes suitable for exercise. Certain medications may need to be paused, but this should always be done under a doctor’s guidance.
2. Resting Echocardiogram
The test begins with a resting echocardiogram. Patients lie on an examination table while a technician applies a special gel to the chest. A transducer, a device that sends and receives sound waves, is moved across the chest to capture images of the heart at rest.
3. Exercise Phase
After the resting images are taken, patients begin the exercise phase. This typically involves walking on a treadmill or pedaling a stationary bike. The intensity of the exercise gradually increases to elevate the heart rate. The goal is to reach a target heart rate that provides meaningful diagnostic information.
4. Stress Echocardiogram
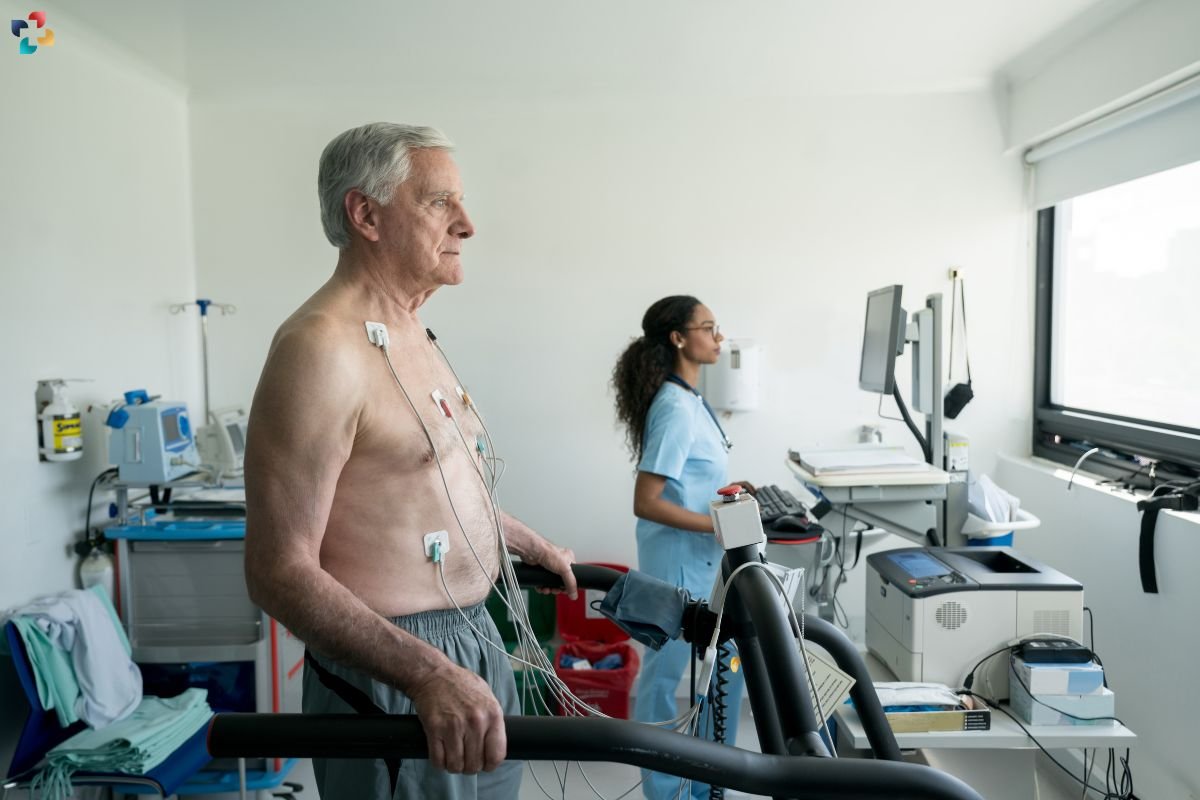
Once the target heart rate is achieved, the patient quickly returns to the examination table. The technician promptly repeats the echocardiogram to capture images of the heart under stress. These images are then compared to the resting images.
Benefits of Stress Echocardiograms
It offers several benefits over other diagnostic tests:
1. Non-Invasive
Unlike angiograms, which require the insertion of a catheter, stress echo are non-invasive, making them safer and more comfortable for patients.
2. Real-Time Results
The images captured during a stress echocardiogram provide real-time information about the heart’s function and structure, allowing for immediate analysis and diagnosis.
3. Versatility
It can detect a range of heart conditions, including CAD, heart valve disease, and cardiomyopathy, making it a versatile diagnostic tool.
Risks and Considerations
While stress echo are generally safe, there are some risks and considerations to be aware of:
1. Exercise-Induced Complications
For some patients, especially those with severe heart conditions, the physical stress of exercise can lead to complications such as chest pain, dizziness, or, in rare cases, a heart attack.
2. Allergic Reactions
Although rare, some patients may have allergic reactions to the gel used during the echocardiogram or to certain medications that might be administered during the test.
3. False Positives/Negatives
Like any diagnostic test, stress echo are not infallible. There is a possibility of false positives, where the test indicates a problem that doesn’t exist, or false negatives, where an existing condition goes undetected.
Comparing Stress Echocardiograms to Other Cardiac Tests
It is one of several tools available for diagnosing heart conditions. Here’s how they compare to other common tests:
1. Stress Electrocardiogram (ECG)
A stress ECG monitors the heart’s electrical activity during exercise. While useful, it doesn’t provide visual images of the heart, which limits its ability to detect structural abnormalities.
2. Nuclear Stress Test
A nuclear stress test involves injecting a small amount of radioactive material into the bloodstream to visualize blood flow to the heart. This test can be more accurate than a stress echo but involves radiation exposure.
3. Cardiac MRI
Cardiac MRI provides detailed images of the heart and is excellent for assessing complex heart conditions. However, it is more expensive and less widely available than stress echo.
When to Consider a Stress Echocardiogram
Doctors may recommend a stress echocardiogram in several scenarios:
1. Symptoms of Heart Disease
If a patient presents symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or unexplained fatigue, a stress echo can help determine if these are related to heart disease.
2. Post-Heart Attack Assessment
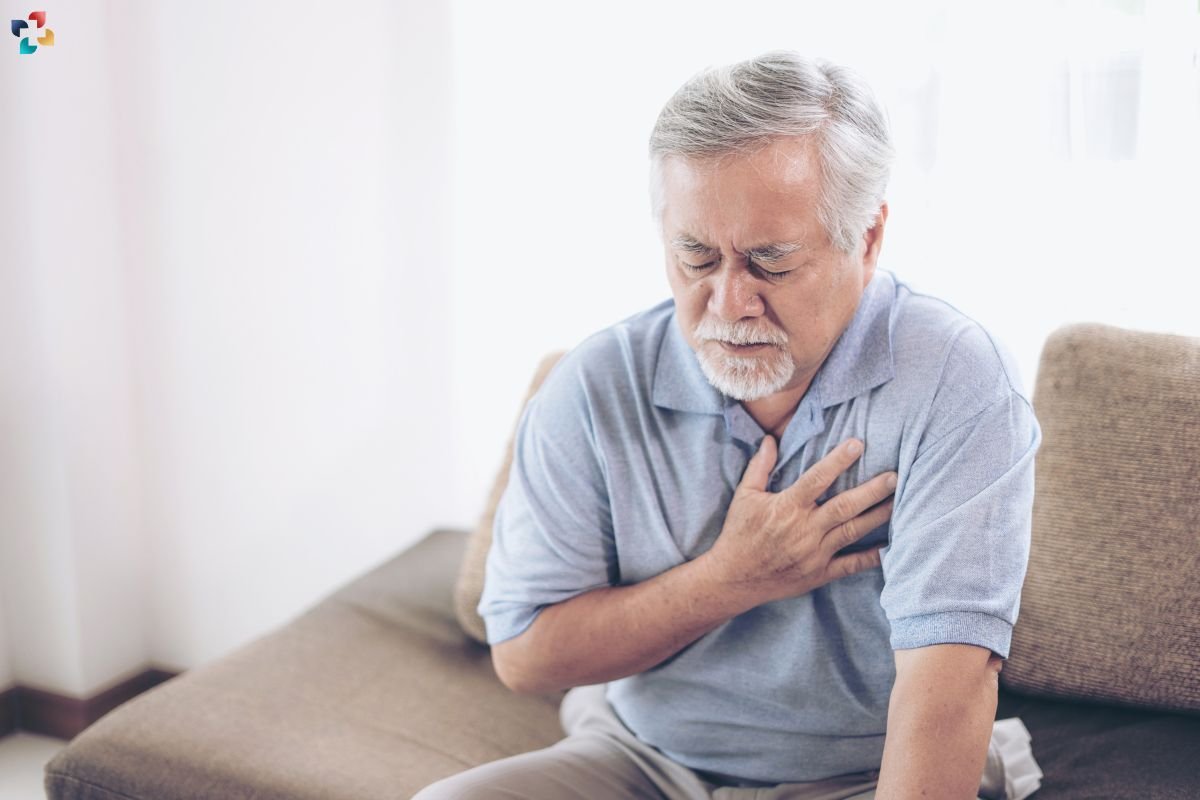

After a heart attack, it can evaluate the extent of damage to the heart and guide further treatment decisions.
3. Monitoring Heart Valve Disease
For patients with known heart valve disease, regular echocardiograms can monitor the progression of the condition and the effectiveness of treatments.
Preparing for a Stress Echocardiogram
Proper preparation can enhance the accuracy of this:
1. Medication Management
Patients should discuss their current medications with their doctor, as some drugs can affect heart rate and interfere with the test results.
2. Fasting
Fasting for a few hours before the test helps prevent nausea that might occur during exercise.
3. Clothing
Wearing comfortable, loose-fitting clothing and appropriate footwear facilitates easier movement during the exercise phase.
What to Expect During and After the Test?
Knowing what to expect can help patients feel more comfortable during a stress echo:
1. During the Test
The test usually lasts about 60 minutes. Patients can expect to exercise for 7-12 minutes, depending on their fitness level and how quickly they reach the target heart rate.
2. After the Test

There are typically no restrictions following a stress echocardiogram. Patients can resume normal activities immediately unless instructed otherwise by their doctor.
Interpreting the Results
The results of this can provide valuable insights into heart health:
1. Normal Results
Normal results indicate that the heart functions well during exercise, with no significant blockages in the coronary arteries and no abnormal heart rhythms.
2. Abnormal Results
Abnormal results can reveal areas of the heart with poor blood flow, indicating potential blockages or other issues. Further testing, such as coronary angiography, may be recommended to pinpoint the exact problem.
Conclusion
Stress echo are a vital tool in the diagnosis and management of heart conditions. By combining the benefits of echocardiography and exercise, they provide a comprehensive view of how the heart performs under stress. While the procedure carries some risks, its benefits in detecting and monitoring heart disease make it an invaluable resource for cardiologists and patients alike. Understanding the process, preparation, and interpretation of stress echocardiograms can help patients approach the test with confidence and peace of mind.