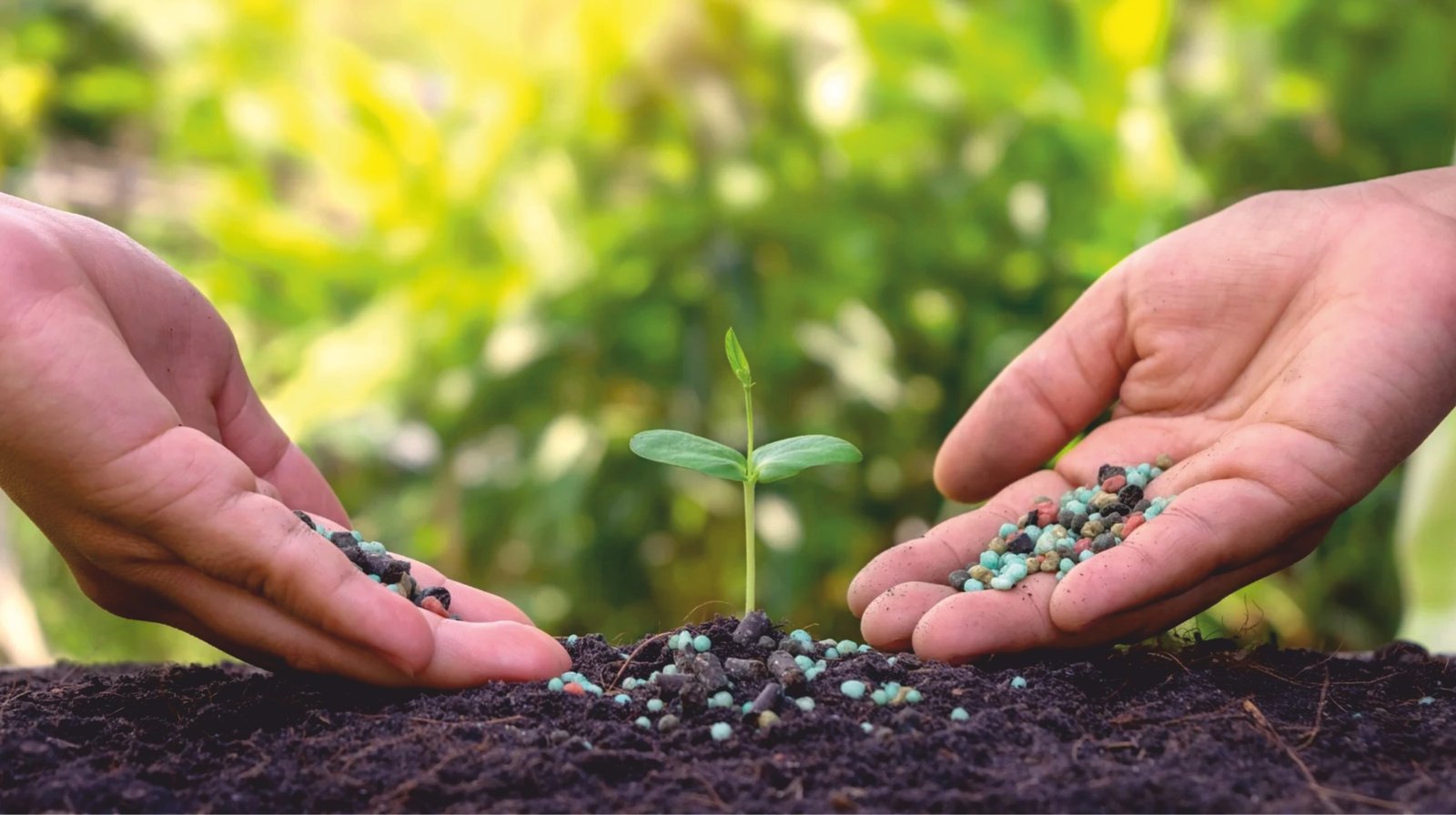
In the field of gardening and agriculture, fertilizers are the key to providing nutrients to the plants that they thrive for. However, every fertilizer is distinct from each other. Among the varieties of fertilizers which are available, slow-release fertilizer has gained everyone’s attention. It is because of its skill to provide the nutrients slowly over time, which makes it a user’s first choice. As it keeps the plants healthy for the long term and contributes to sustaining the environment. This article will provide you with an overview of these fertilizer benefits, types, and usage which will be just the thing you need to enhance your gardening or farming efforts.
What Is Slow-Release Fertilizer?
It is a type of fertilizer designed to release nutrients steadily over a prolonged period. Unlike quick-release fertilizers that dissolve rapidly and deliver nutrients all at once, slow-release options are engineered to break down slowly, providing a consistent supply of nutrients to plants over weeks or even months. This gradual nutrient release minimizes the risk of nutrient runoff, which is not only better for the environment but also ensures plants receive a steady stream of essential nutrients.
Typically, fertilizers that are slow-released come in granulated, pellet, or coated forms, which are specially treated to control the rate at which nutrients are released into the soil. They are particularly popular among gardeners, landscapers, and agricultural professionals who seek a low-maintenance yet effective solution for nourishing plants.
Why Use Slow-Release Fertilizer?
They offer several key advantages over traditional quick-release options, making them a preferred choice for many gardeners and agriculturalists. One of the main benefits is their ability to provide a sustained nutrient supply. Unlike quick-release fertilizers that lead to sudden nutrient spikes, slow-release fertilizers deliver nutrients gradually, allowing plants to receive a steady, consistent supply. This promotes healthy, sustained growth without the nutrient highs and lows that can stress plants.
Another major advantage is the reduced environmental impact. Quick-release fertilizers are often associated with nutrient runoff, which can lead to the contamination of nearby water sources and negatively impact local ecosystems. These fertilizers, on the other hand, are absorbed more effectively by plants, which minimizes the risk of pollution and supports environmental sustainability.
Slow-release fertilizers also require lower maintenance. Because they release nutrients over an extended period, gardeners and farmers don’t need to apply them as frequently. This is especially useful for those with busy schedules or large agricultural operations, as it reduces labor and time costs significantly.
Additionally, these fertilizers contribute to better plant health. The gradual nutrient release helps prevent issues like nutrient overload and root burn, both of which can harm plant growth. Instead, plants are fed in a controlled manner, allowing them to develop strong root systems and improved resilience.
Finally, these fertilizers enhance soil quality over time. By minimizing nutrient leaching, they help maintain a balanced ecosystem within the soil. This contributes to long-term soil fertility, creating a healthier foundation for plants to thrive in the future.
Types of Slow-Release Fertilizer
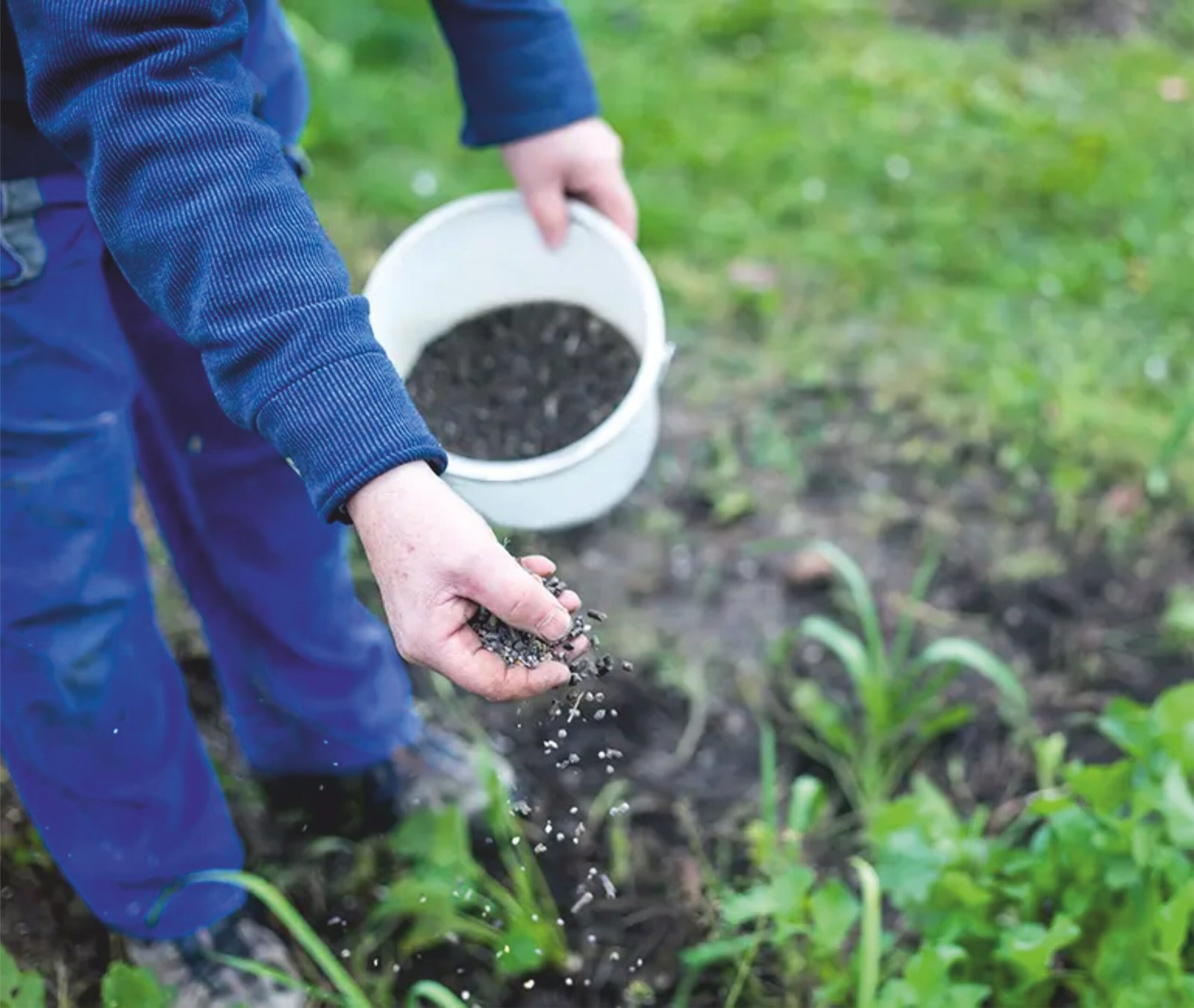

Several types of slow-release fertilizers are available, each suited to different applications and plant types. Here’s a look at some of the most common types:
- Organic Slow-Release Fertilizers: Organic options are derived from natural sources like bone meal, fish meal, compost, and manure. These fertilizers decompose slowly and enrich the soil over time, providing both macronutrients and micronutrients. Organic fertilizers which are slow-released are particularly popular among eco-conscious gardeners and sustainable farmers.
- Polymer-Coated Fertilizers: This type of fertilizers which are slow-released is encased in a polymer coating that regulates nutrient release. The coating controls the rate at which water penetrates the granule, affecting how fast nutrients are released. Polymer-coated fertilizers are ideal for use in gardens and potted plants where precise nutrient management is necessary.
- Sulfur-Coated Fertilizers: In sulfur-coated fertilizers which are slow-released, nutrients are encapsulated with a sulfur layer. This coating dissolves gradually, allowing nutrients to be released over time. Sulfur-coated fertilizers are often used in agriculture, where crops require a consistent nutrient supply to maximize yield.
- Urea-Formaldehyde Fertilizers: Urea-formaldehyde fertilizers release nitrogen slowly as soil microbes break down the formaldehyde component. This type of fertilizers which are slow-released is commonly used for lawns and turf, as it provides prolonged nitrogen availability essential for lush, green growth.
Each type of slow-release fertilizer has its specific application and benefits, so it’s essential to choose the right one based on your plant’s needs and the growing environment.
How to Use Slow-Release Fertilizer Effectively?
To make the most out of these fertilizers, it’s essential to apply them correctly to ensure optimal plant health. First, selecting the right type of slow-release fertilizer is key. The specific fertilizer you choose should align with your plants’ needs. For instance, if you’re growing vegetables, organic fertilizers are often the best choice, while polymer-coated or sulfur-coated fertilizers might be more suitable for lawn care.
Next, calculate the correct amount of fertilizer needed. Even with slow-release varieties, over-fertilizing can damage plants. Always refer to the manufacturer’s dosage guidelines, or better yet, conduct a soil test to assess the current nutrient levels before application.
Timing also plays a critical role. Most of these fertilizers are best applied at the start of the growing season since they gradually release nutrients over time. For flowering plants and perennials, early spring is generally an ideal time for application.
Proper watering is another important step, as it helps activate the fertilizer. This is especially true for polymer or sulfur-coated fertilizers, which require adequate moisture to begin releasing nutrients. Be sure to water the plants sufficiently right after applying the fertilizer.
Lastly, keep an eye on plant health over time. Although slow-release fertilizers are meant to last for an extended period, observe your plants for signs of nutrient deficiencies, such as yellowing leaves. If you notice such indicators, an additional application might be necessary to support ongoing plant growth.
Choosing the Best Slow-Release Fertilizer for Your Needs
With numerous brands and formulations available, selecting the best slow-release fertilizer can feel overwhelming. Here are a few factors to consider:
- Plant Type: Different plants have unique nutrient requirements. For example, vegetables typically need higher nitrogen levels, while flowering plants benefit from fertilizers rich in phosphorus.
- Soil Condition: Before applying any fertilizer, it’s a good idea to test your soil to see which nutrients are already present. This helps avoid excess nutrient application, which can be wasteful and detrimental to plant health.
- Environmental Considerations: Opting for organic fertilizers which are slow-released can be a good choice if you’re aiming for sustainable gardening. Organic fertilizers not only provide nutrients but also improve soil health and encourage beneficial microorganisms.
- Cost and Longevity: While these fertilizers tend to be more expensive upfront than quick-release options, they require fewer applications, making them cost-effective in the long run.
- Application Method: Some of these fertilizers are easier to spread than others. Choose one that matches your garden setup and the plants you’re tending to ensure convenience and effectiveness.
The Environmental Impact of Slow-Release Fertilizer
One of the main reasons slow-release fertilizers are recommended over quick-release versions is their positive impact on the environment. Quick-release fertilizers can lead to nutrient leaching, where excess nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus seep into waterways, causing issues like algae blooms that disrupt aquatic ecosystems. This fertilizer, on the other hand, delivers nutrients more efficiently, reducing the likelihood of nutrient runoff and helping protect water quality.
By using these fertilizers, gardeners, and farmers contribute to a more sustainable approach to plant care. The controlled nutrient delivery not only benefits plants but also minimizes the amount of chemical runoff that reaches rivers, lakes, and oceans.
Final Thoughts on Slow-Release Fertilizer
Incorporating fertilizers that are slow-released into your gardening or farming routine is an effective way to promote healthy, vigorous plant growth while reducing environmental impact. With its sustained nutrient release, low-maintenance application, and positive influence on soil quality, fertilizers which are slow-released are an invaluable tool for both amateur gardeners and professional growers. By choosing the right type and applying it correctly, you can enjoy lush, thriving plants with minimal effort and greater environmental responsibility.
Whether you’re growing flowers, vegetables, or managing a large agricultural operation, slow-release fertilizer offers a reliable and eco-friendly solution for ensuring that your plants receive the nutrients they need to flourish.