One of the fascinating branches of science that is known for explaining the nature of the universe has changed drastically over time. It can describe everything starting from the mobility of planets along with the behavior of subatomic particles, and that branch is called physics. With time, there has been a subdivision within it that is classical physics and quantum physics, the two sides of one coin. On one hand, the classical physics offer a well-organised and foreseeable explanation of natural occurrences. On the other hand, quantum physics challenges the same principles by offering uncertainty, probability, and strange behavior at a microscopic scale.
In this article, we will explore the concept of physics vs quantum physics and understand the major difference between these two terms. We will also explore how physics has changed over the years by referencing Newtonian mechanics and Schrödinger’s quantum theory.
What is Physics and Quantum Physics?
Physics is the branch of science that studies matter, energy, motion, and forces, describing how the universe behaves. It is based on fundamental laws such as Newton’s Laws of Motion, thermodynamics, electromagnetism, and gravity. Classical physics primarily deals with macroscopic objects and follows deterministic laws, meaning outcomes can be precisely predicted.
The key areas of classical physics include:
- Mechanics: Motion of objects (e.g., Newtonian physics).
- Thermodynamics: Heat and energy transfer.
- Electromagnetism: Electric and magnetic fields.
- Optics: Behavior of light.
Quantum physics, or quantum mechanics, is the branch of physics that describes the strange and unpredictable behaviors of particles at the atomic and subatomic levels. Unlike classical physics, which relies on certainty, quantum physics introduces principles such as superposition, entanglement, and probability.
Key concepts in quantum physics include:
- Wave-Particle Duality: Particles can behave as both waves and particles.
- Quantum Superposition: A particle can exist in multiple states simultaneously.
- Quantum Entanglement: Particles can be instantaneously connected across vast distances.
- Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle: The position and momentum of a particle cannot be precisely determined at the same time.
Key Differences – Physics vs Quantum Physics
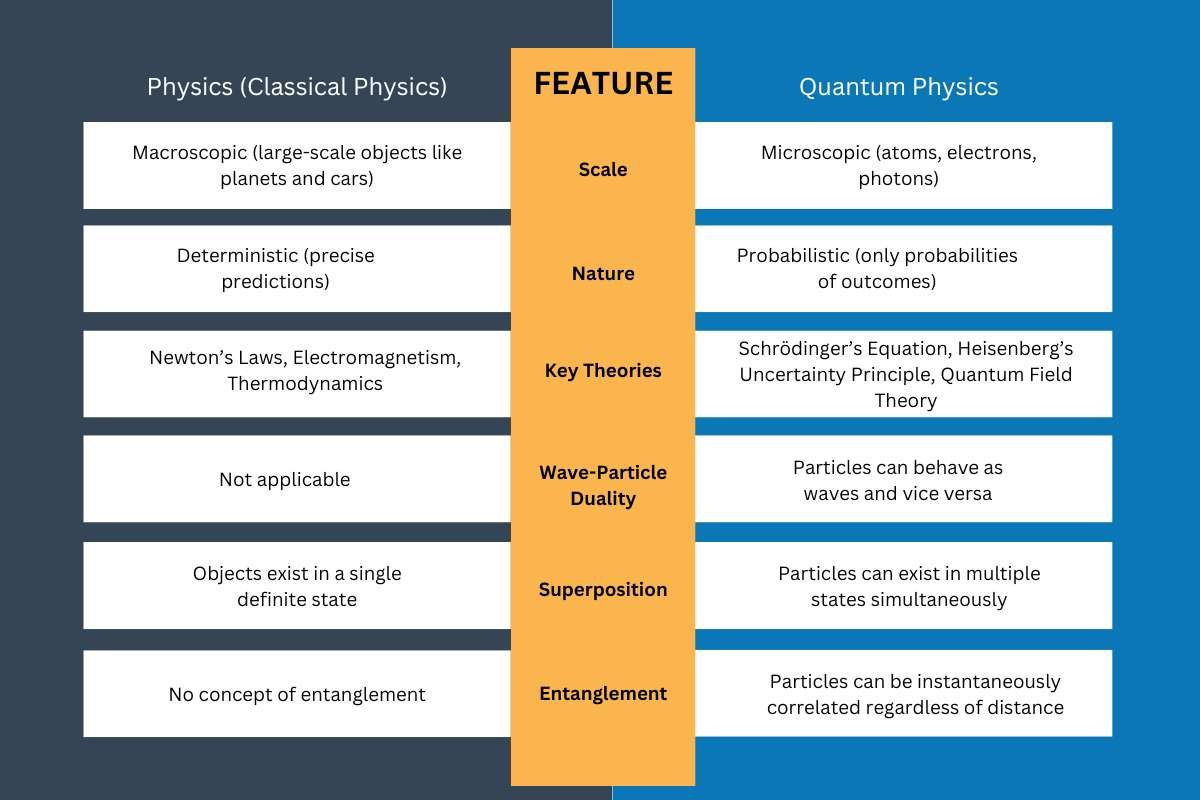
| Feature | Physics (Classical Physics) | Quantum Physics |
|---|---|---|
| Scale | Macroscopic (large-scale objects like planets and cars) | Microscopic (atoms, electrons, photons) |
| Nature | Deterministic (precise predictions) | Probabilistic (only probabilities of outcomes) |
| Key Theories | Newton’s Laws, Electromagnetism, Thermodynamics | Schrödinger’s Equation, Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle, Quantum Field Theory |
| Wave-Particle Duality | Not applicable | Particles can behave as waves and vice versa |
| Superposition | Objects exist in a single definite state | Particles can exist in multiple states simultaneously |
| Entanglement | No concept of entanglement | Particles can be instantaneously correlated regardless of distance |
These differences illustrate why Physics vs Quantum Physics is an important discussion in modern science. Classical physics explains everyday experiences, while quantum physics reveals the bizarre realities of the microscopic world.
Learn More: Hot Water Freezes Faster Than Cold: The Mpemba Effect Explained
From Newton to Schrödinger: The Evolution of Physics
Newtonian Physics: The Foundation of Classical Mechanics
Sir Isaac Newton’s laws of motion and universal gravitation laid the foundation for classical physics in the 17th century. His principles explained how objects move and interact under the influence of forces. These laws worked well for most practical applications, such as engineering, astronomy, and mechanical systems.
However, as scientists began exploring extremely fast-moving objects (close to the speed of light) and incredibly small particles (like electrons), classical physics started showing limitations.
Einstein’s Relativity: A Step Beyond Classical Physics
Albert Einstein revolutionized physics in the early 20th century with his Theory of Relativity. He introduced:
- Special Relativity (1905): Time and space are relative, and nothing can travel faster than light.
- General Relativity (1915): Gravity is the warping of space-time by mass.
Einstein’s theories explained phenomena that Newtonian physics couldn’t, such as black holes and the bending of light by gravity. However, these theories still didn’t fully address the mysteries of atomic and subatomic particles.
Learn More: Are quantum tunnels the future of advanced computing technology?
The Birth of Quantum Physics
At the same time Einstein was developing relativity, other scientists were uncovering the mysteries of quantum mechanics:
- Max Planck (1900): Proposed that energy is quantized, introducing the concept of quantum mechanics.
- Niels Bohr (1913): Developed the Bohr model of the atom, where electrons exist in discrete energy levels.
- Werner Heisenberg (1927): Introduced the Uncertainty Principle, stating we cannot simultaneously determine a particle’s position and velocity.
- Erwin Schrödinger (1926): Developed Schrödinger’s wave equation, describing the probabilistic nature of quantum particles.
By the mid-20th century, quantum physics had emerged as the most accurate way to describe atomic and subatomic behavior, leading to technologies such as semiconductors, quantum computing, and MRI scans.
Conclusion
The never-ending debate of physics vs quantum physics helps highlight two essential methods of understanding reality. Classical physics offers deterministic laws that rule the macro concept in objects. Whereas quantum physics uncovers a probabilistic world in the microscopic scale. Regardless of their differences, both are these concepts are primary for science. Newtonian physics explains the everyday mechanics, and quantum mechanics takes modern technologies to a higher scale.
Many physicists have continued exploring the quantum world in the hope of making discoveries that will change the world and bridge the gap between these two branches. Which will result in uncovering a deeper truth about the universe as we know it. The implications of physics and quantum physics are boundless in space exploration, medical technology, and even artificial intelligence, it is shaping our future in a way that is beyond our comprehension.
FAQ:
1. Is quantum physics the same as physics?
Classical Physics applies to macroscopic particles. Quantum Physics applies to microscopic particles. Here’s a simple analogy.
2. What is the difference between modern physics and quantum physics?
Modern physics is a survey of relativity, quantum mechanics, and a little particle physics. Quantum physics is a specific course in quantum mechanics and goes into much greater detail and more math.
3. Did Einstein like quantum physics?
Einstein famously rejected quantum mechanics, observing that God does not play dice. But he thought more about the nature of atoms, molecules, and the emission and absorption of light—the core of what we now know as quantum theory—than he did about relativity.