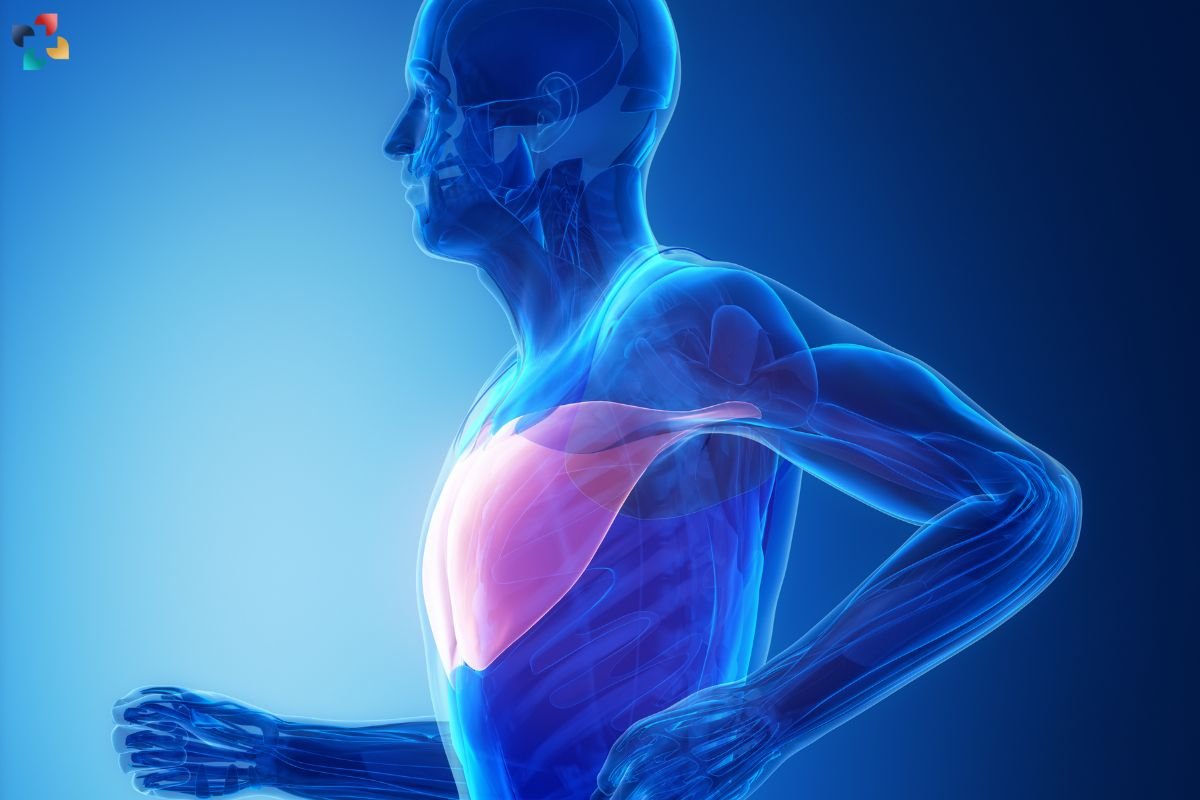
The pectoralis major, a thick, fan-shaped muscle situated at the chest, plays a crucial role in the movement of the shoulder and upper arm. Engaging in activities that involve pushing, lifting, or swinging can sometimes lead to a condition known as a pectoralis major strain. This injury, characterized by a tear or overstretching of the muscle fibers, can range from mild discomfort to severe pain, significantly impacting daily activities and athletic performance. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures for pectoralis main strain, providing valuable insights to help you manage and prevent this common injury.
Anatomy of the Pectoralis Major
The pectoralis major muscle is divided into two parts: the clavicular head and the sternocostal head. The clavicular head originates from the clavicle (collarbone), while the sternocostal head originates from the sternum and the upper six ribs. Both heads converge to attach to the humerus (upper arm bone). This muscle is responsible for various movements, including adduction, flexion, and internal rotation of the arm. Understanding its anatomy helps in identifying the exact location and extent of a pectoralis major strain.
Causes of Pectoralis Major Strain
- Overuse: Repetitive movements that engage the pectoralis major, such as weightlifting, swimming, or throwing sports, can lead to muscle fatigue and strain.
- Acute Trauma: Sudden, forceful movements or heavy lifting can cause a pectoralis major strain. This is common in activities like bench pressing or wrestling.
- Improper Technique: Incorrect form during exercises, particularly weightlifting, can place undue stress on the pectoralis major, increasing the risk of strain.
- Inadequate Warm-Up: Failing to properly warm up the muscles before engaging in intense physical activity can make the pectoralis major more susceptible to injury.
- Muscle Imbalance: Imbalances between the pectoralis major and other muscles of the shoulder girdle can lead to overcompensation and strain.
Symptoms of Pectoralis Major Strain

Recognizing the symptoms of a pectoralis major strain is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Sudden Pain: Acute, sharp pain in the chest or upper arm, especially during activities that involve pushing or lifting.
- Swelling and Bruising: Visible swelling and bruising may occur around the chest and upper arm area.
- Weakness: A noticeable decrease in strength and the inability to perform certain movements, such as lifting the arm or pressing weight.
- Tenderness: The affected area may be tender to the touch, with localized pain upon palpation.
- Muscle Spasms: Involuntary muscle contractions or spasms may occur in the chest or upper arm.
Diagnosing Pectoralis Major Strain
Proper diagnosis of this involves a thorough physical examination and, in some cases, imaging studies. Here are the steps typically taken by healthcare professionals:
- Medical History: The doctor will inquire about the patient’s activity level, recent physical activities, and the onset of symptoms.
- Physical Examination: The affected area will be examined for swelling, bruising, and tenderness. The patient may be asked to perform specific movements to assess pain and weakness.
- Imaging Studies: In severe cases, an MRI or ultrasound may be ordered to determine the extent of the muscle tear and rule out other possible injuries.
Treatment Options for Pectoralis Major Strain

The treatment of a pectoralis major strain depends on the severity of the injury. Here are the common treatment options:
Conservative Treatment
- Rest: Avoiding activities that exacerbate the pain is crucial for healing. Rest allows the muscle fibers to repair themselves.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice to the affected area for 15-20 minutes every few hours can help reduce swelling and alleviate pain.
- Compression: Using an elastic bandage or compression garment can help control swelling and provide support.
- Elevation: Keeping the affected arm elevated can help reduce swelling.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage pain and inflammation.
Physical Therapy
- Stretching Exercises: Gentle stretching exercises can help maintain flexibility and prevent stiffness in the affected muscle.
- Strengthening Exercises: Gradual strengthening exercises, under the guidance of a physical therapist, can help restore muscle strength and function.
- Manual Therapy: Techniques such as massage and myofascial release can help reduce muscle tension and promote healing.
Surgical Intervention
In severe cases where the pectoralis major muscle is completely torn, surgical repair may be necessary. This involves reattaching the torn muscle to the bone using sutures or anchors. Post-surgery, a comprehensive rehabilitation program is essential for restoring full function.
Rehabilitation and Recovery

Rehabilitation is a critical component of the recovery process for a pectoralis major strain. A structured program tailored to the individual’s needs can help ensure a successful return to activity. Here are the key phases of rehabilitation:
- Acute Phase: Focuses on pain management, reducing swelling, and protecting the injured muscle. Activities include rest, ice therapy, and gentle range-of-motion exercises.
- Subacute Phase: Aims to restore flexibility and prevent muscle atrophy. Stretching and light strengthening exercises are gradually introduced.
- Strengthening Phase: Involves progressive resistance training to rebuild muscle strength and endurance. Exercises are tailored to mimic functional movements.
- Return to Activity: The final phase involves a gradual return to sports or daily activities, with an emphasis on proper technique and preventive measures.
Preventing Pectoralis Major Strain
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are some strategies to reduce the risk of pectoralis major strain:
- Proper Warm-Up: Engage in a thorough warm-up routine before any physical activity to prepare the muscles for exertion.
- Strengthening Exercises: Incorporate exercises that strengthen the pectoralis major and surrounding muscles to maintain balance and stability.
- Correct Technique: Focus on proper form and technique during exercises, especially weightlifting, to avoid undue stress on the muscles.
- Gradual Progression: Increase the intensity and volume of workouts gradually to allow the muscles to adapt and strengthen over time.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to signs of fatigue and discomfort. Rest and recover as needed to prevent overuse injuries.
Conclusion
Pectoralis major strain is a common injury that can significantly impact physical performance and daily activities. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for effective management and recovery. By following preventive measures and seeking prompt medical attention when needed, individuals can reduce the risk of pectoralis major strain and maintain optimal muscle health. Remember, proper care and attention to technique are key to preventing and recovering from this injury, ensuring a swift return to pain-free activity and enhanced physical performance.
Visit The Lifesciences Magazine For More.