The world is facing an increasing threat from new infectious diseases, which are emerging rapidly across different regions. With climate change, rapid urbanization, and global changes, these diseases are more likely to spread and affect populations worldwide. Letting people know about these new infectious diseases has become a key focus for global health organizations, scientists, and governments to mitigate their impact.
In this blog, we will explore the rising concern of new infectious diseases, their causes, impacts, and the preventive strategies necessary to combat them.
The Rise of New Infectious Diseases
New infectious diseases refer to diseases that have recently been discovered or have been newly born to affect humans. Over the past decades, numerous new infectious diseases have emerged, such as the Zika virus, Ebola, and most recently, COVID-19. These diseases are often caused by pathogens that previously did not affect humans or were separated in certain regions. With the increasing interaction between humans, animals, and the environment, the chances of these diseases spilling over from animals to humans have risen significantly.
Pathogens like viruses, bacteria, and fungi that were once confined to animals are now leaping to humans, a process called zoonosis. This shift is responsible for many new infectious diseases and represents a growing health concern. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), nearly 60% of all infectious diseases that affect humans are zoonotic. This tells us the need for awareness of how changes in human behavior and the environment increase the risk of such diseases.
Factors Contributing to the Emergence of New Infectious Diseases

Several factors contribute to the rise of infectious diseases, which can make them difficult to control and prevent. Here are some of the key contributors:
- Global Travel and Trade: Increased international mobility means that diseases can spread across borders more easily than before. A person infected in one part of the world can unknowingly bring the disease to a different region, creating an outbreak. This interconnectedness makes it more challenging to contain infectious diseases.
- Urbanization: The rapid growth of cities has led to higher population density, inadequate sanitation, and increased interaction between humans and animals. Such conditions are breeding grounds for many infectious diseases.
- Climate Change: Changes in weather patterns and rising global temperatures are shifting the habitats of many disease vectors like mosquitoes. For example, diseases like malaria and dengue fever are now expanding to regions that were once considered safe. This increases the risk of infectious diseases becoming prevalent.
- Deforestation and Wildlife Trade: The destruction of natural habitats and the illegal wildlife trade bring humans into closer contact with wild animals, raising the risk of zoonotic diseases spilling over. This is particularly concerning as new infectious diseases like Ebola and the Marburg virus have emerged from animal hosts.
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR): As bacteria evolve to resist antibiotics, new infectious diseases are becoming harder to treat. AMR is making it increasingly difficult to manage infections that were once easily treatable, leading to a rise in mortality rates.
Notable New Infectious Diseases
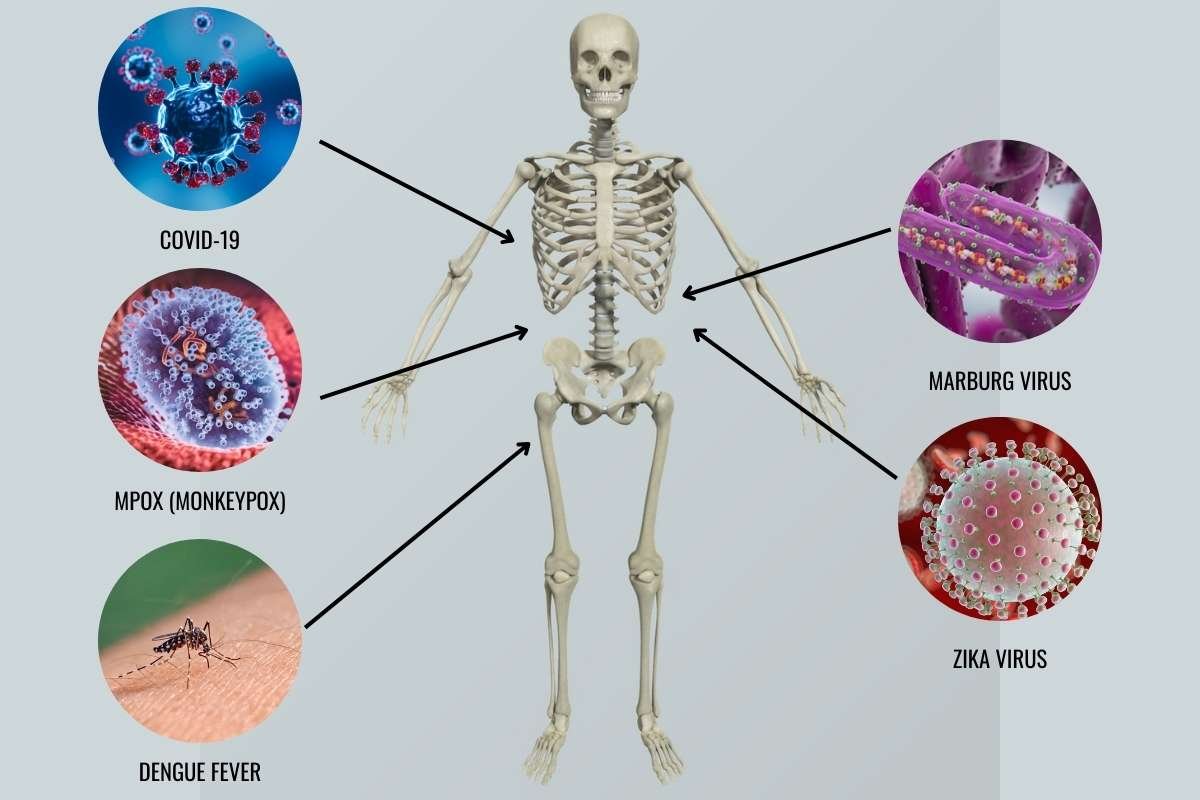
The world has already witnessed the devastating impact of several new infectious diseases in recent years. These diseases not only cause widespread illness but can also have severe economic, social, and political consequences. Some notable examples include:
- COVID-19: The novel coronavirus that emerged in late 2019 wreaked havoc on global health, with millions of lives lost and economies crippled. As the world continues to grapple with the aftermath, new variants of the virus continue to emerge, underscoring the ongoing threat posed by new infectious diseases.
- Mpox (Monkeypox): While initially a disease confined to specific regions in Africa, monkeypox has spread globally in recent years, leading to outbreaks in countries like the United States and Europe. The rapid spread of the virus and its ability to adapt to human hosts have raised alarms about future outbreaks of new infectious diseases.
- Dengue Fever: Once limited to tropical regions, dengue fever has spread to parts of the U.S. and other temperate areas due to changes in climate and the migration of disease vectors like mosquitoes. The emergence of new infectious diseases like dengue is directly tied to the shifting environmental conditions.
- Marburg Virus: Similar to Ebola, the Marburg virus is a deadly hemorrhagic fever that has caused sporadic outbreaks in Africa. As the virus adapts and spreads, it highlights the potential for new infectious diseases to create a global health emergency.
- Zika Virus: The Zika virus, known for causing birth defects when pregnant women are infected, was declared a global health emergency in 2016. The rapid spread of the virus demonstrated how new infectious diseases can quickly impact populations worldwide.
The Impact of New Infectious Diseases on Public Health
The emergence of new infectious diseases poses several challenges for public health systems worldwide. From limited knowledge about the disease to inadequate infrastructure to respond effectively, healthcare systems are often caught off guard. The impact of these diseases is not only seen in terms of the number of cases and fatalities but also in terms of the strain they put on healthcare systems, economies, and social structures.
Preventive Measures and Strategies
While new infectious diseases pose a significant threat, various strategies can help prevent and control outbreaks:
- Surveillance and Early Detection: Global health organizations like the WHO and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) are investing heavily in improving surveillance systems to detect new infectious diseases early. Early identification of pathogens is key to containing outbreaks before they spread.
- Global Collaboration: International cooperation is essential to tackling infectious diseases. Collaborations between governments, researchers, healthcare providers, and pharmaceutical companies are vital to developing vaccines, treatments, and diagnostic tools to address emerging health threats.
- Public Health Campaigns and Education: Misinformation and vaccine hesitancy have played significant roles in the spread of new infectious diseases. Public health campaigns aimed at educating people about the importance of vaccination, hygiene, and preventive measures are critical in controlling the spread of diseases.
- Research and Innovation: Investment in research to understand the causes, transmission, and potential treatments for new infectious diseases is essential. This includes developing more effective vaccines, antivirals, and diagnostic tests that can help mitigate the impact of future outbreaks.
- Strengthening Healthcare Infrastructure: In many regions, healthcare systems are not well-equipped to handle the rise in cases caused by new infectious diseases. Strengthening healthcare infrastructure and ensuring adequate resources for healthcare workers are key to managing outbreaks effectively.
Stay informed and protect yourself : Infectious Disease Prevention Strategies: A Comprehensive Guide

Conclusion
The rise of new infectious diseases is a growing concern for global health, with factors like climate change, urbanization, and antimicrobial resistance due to the new pathogens. These issues require coordinated global efforts, including improved surveillance, faster response times, and better research and prevention measures. If we focus on such strategies, we can prepare for the next health crisis and reduce the impact of new infectious diseases on public health. With the right resources, collaboration, and awareness, we can protect our future generations from these infectious and deadly diseases. One must we must stay vigilant, informed, and ready to act.