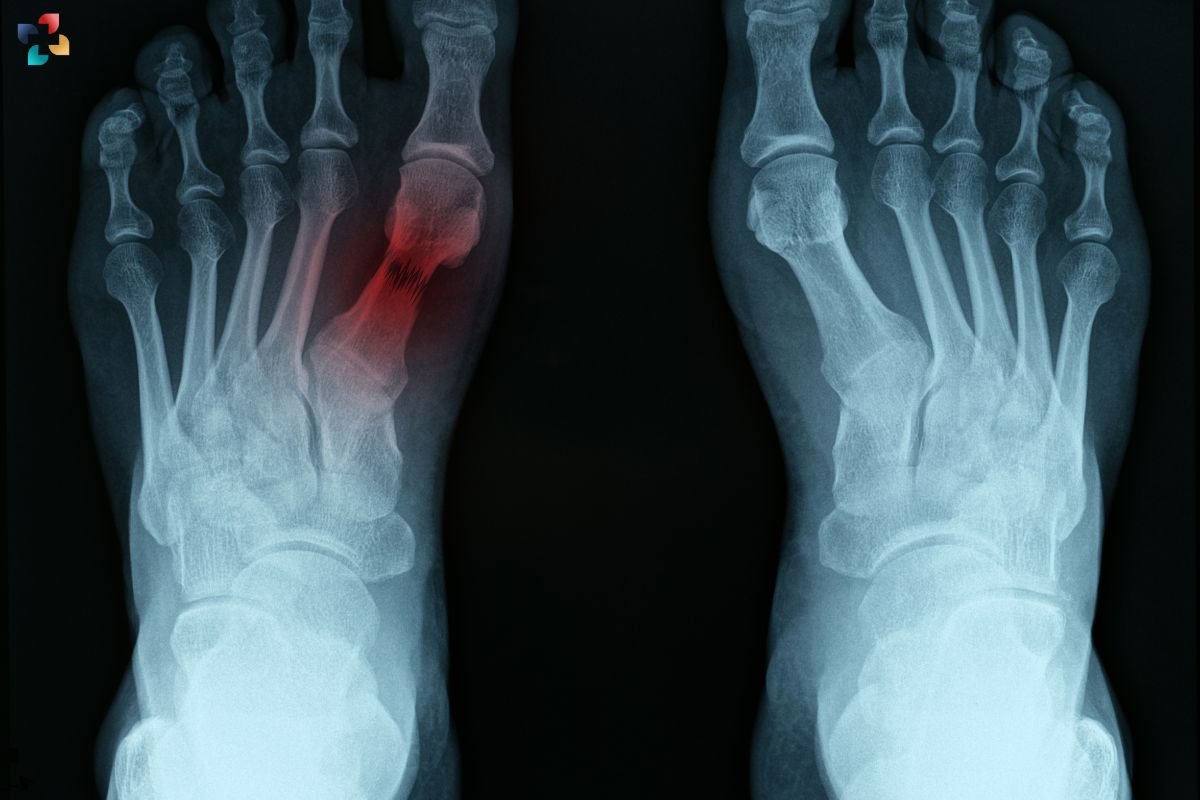
A navicular stress fracture is a common injury among athletes and active individuals, particularly those involved in high-impact sports. This condition affects the navicular bone, a small but crucial bone in the foot that plays a vital role in its structural integrity and function. In this article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for a navicular stress fracture, providing a comprehensive guide to understanding and managing this condition effectively.
What is a Navicular Stress Fracture?
A navicular stress fracture occurs when the navicular bone, located in the midfoot, experiences a small crack or break due to repetitive stress or overuse. Unlike acute fractures caused by sudden trauma, stress fractures develop gradually over time, often as a result of increased activity or changes in physical demand.
Anatomy of the Navicular Bone
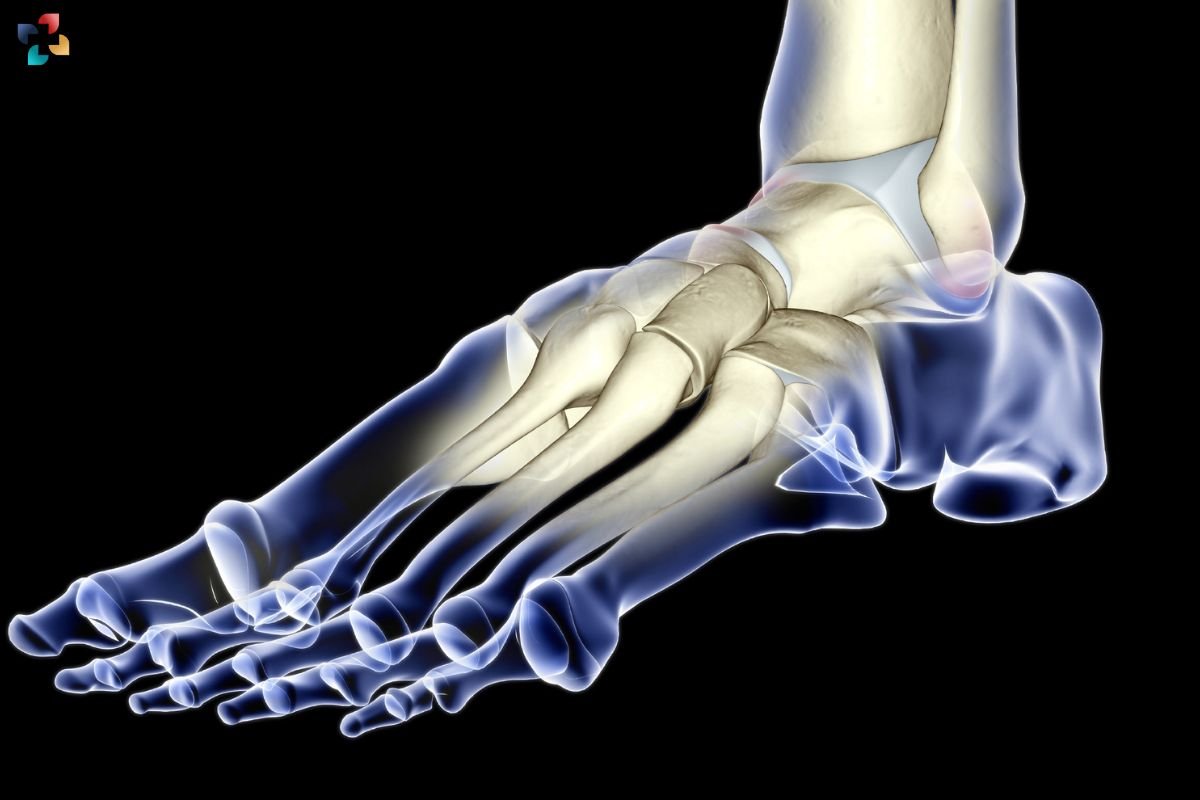
The navicular bone is situated in the midfoot and is integral to the formation of the arch. It serves as a keystone for the medial longitudinal arch and provides essential support for the foot’s overall structure. The navicular bone’s location makes it susceptible to stress fractures, particularly when subjected to excessive or repetitive forces.
Causes of Navicular Stress Fracture
Understanding the causes of this is crucial for prevention and effective treatment. Several factors contribute to the development of this injury:
1. Overuse and Repetitive Stress
The most common cause of a navicular stress fracture is repetitive stress on the foot. Athletes engaged in activities like running, jumping, or high-impact sports are at higher risk. The repetitive strain on the navicular bone can lead to microtears, eventually resulting in a stress fracture.
2. Sudden Increase in Activity
A sudden increase in activity level or intensity, such as starting a new training regimen or increasing mileage, can place excessive stress on the navicular bone. This abrupt change can overwhelm the bone’s ability to adapt, leading to a stress fracture.
3. Biomechanical Abnormalities
Biomechanical issues, such as flat feet or high arches, can contribute to abnormal stress distribution across the foot. These abnormalities may lead to increased pressure on the navicular bone, making it more susceptible to stress fractures.
4. Inadequate Footwear
Wearing inappropriate or worn-out footwear can impact the distribution of forces on the foot. Proper support and cushioning are essential to absorb shock and reduce the risk of a navicular stress fracture.
5. Poor Training Techniques
Improper training techniques, such as inadequate warm-ups or improper running form, can also contribute to the development of a navicular stress fracture. Ensuring proper technique and gradually increasing activity levels can help mitigate the risk.
Symptoms of Navicular Stress Fracture
Recognizing the symptoms of this is vital for prompt diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms include:
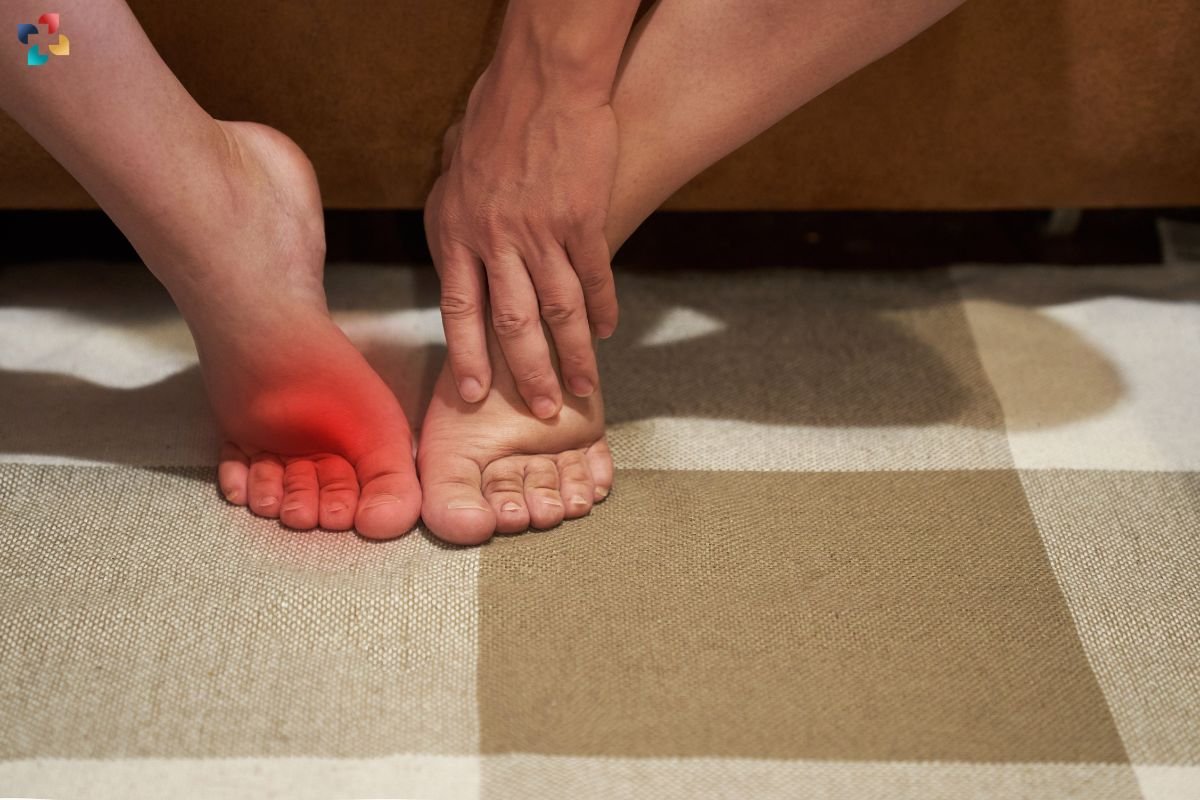
1. Foot Pain
Pain is the most prominent symptom of a navicular stress fracture. It is often localized to the midfoot, particularly around the navicular bone. The pain typically worsens with activity and improves with rest.
2. Swelling and Tenderness
Swelling and tenderness in the midfoot area are common signs of a stress fracture. The affected area may feel sore to the touch, and swelling may become noticeable as the condition progresses.
3. Difficulty Weight-Bearing
Individuals with it may experience difficulty bearing weight on the affected foot. Walking or participating in weight-bearing activities can exacerbate the pain and discomfort.
4. Persistent Discomfort
Unlike acute injuries, it often causes persistent discomfort that doesn’t subside with rest. The pain may gradually intensify, making it crucial to seek medical attention if symptoms persist.
Diagnosis of Navicular Stress Fracture
Accurate diagnosis of a navicular stress fracture involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies. Healthcare professionals use the following methods to diagnose the condition:
1. Medical History and Physical Examination
A thorough medical history and physical examination help identify symptoms and potential risk factors associated with a navicular stress fracture. The healthcare provider will assess the patient’s activity level, footwear, and any recent changes in training.
2. Imaging Studies
Imaging studies are essential for confirming a diagnosis of this. X-rays may not always reveal stress fractures in the early stages, so additional imaging techniques, such as MRI or CT scans, may be necessary for accurate diagnosis. MRI is particularly useful in detecting stress fractures before they become apparent on X-rays.
Treatment Options for Navicular Stress Fracture
Effective treatment for this focuses on alleviating pain, promoting healing, and preventing recurrence. Treatment options typically include:
1. Rest and Activity Modification
Rest is crucial for allowing the navicular bone to heal. Patients are advised to avoid activities that exacerbate the pain and engage in low-impact exercises that do not strain the foot.
2. Footwear and Orthotics
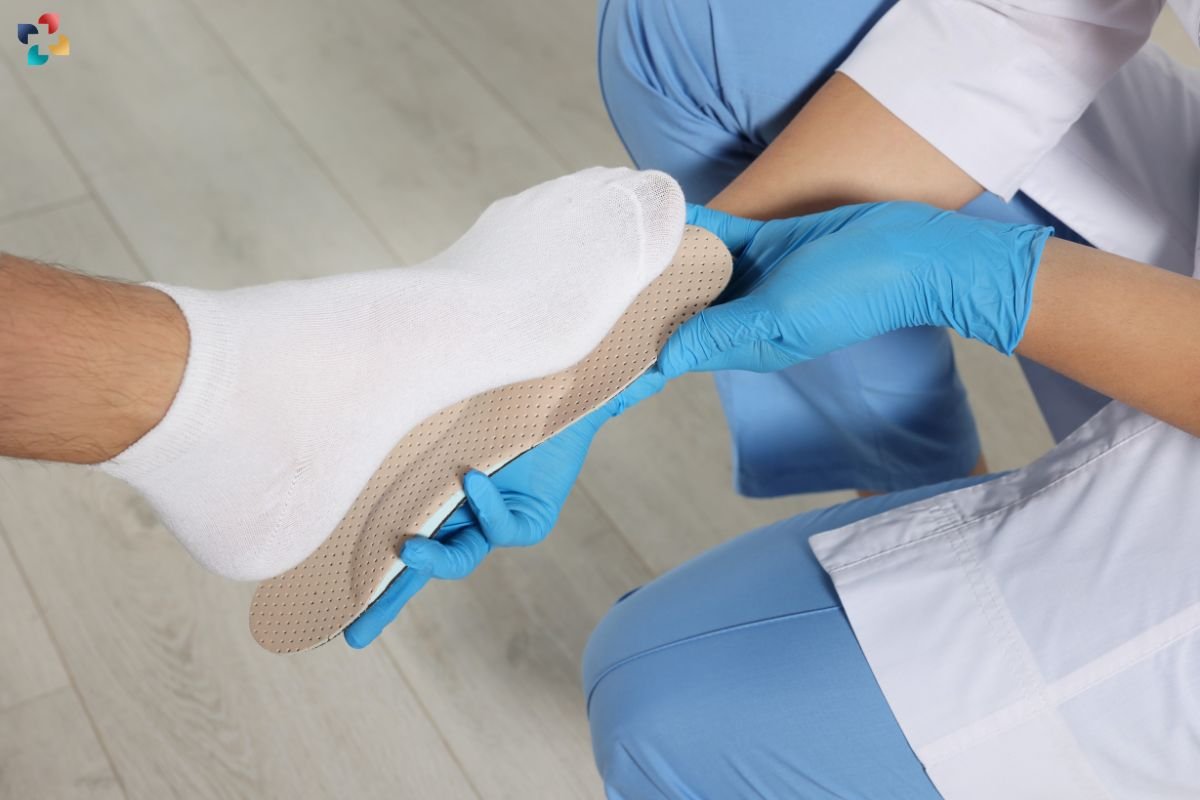
Wearing appropriate footwear with adequate support and cushioning is essential for managing a navicular stress fracture. Orthotic devices, such as custom insoles, may help distribute forces more evenly and reduce stress on the navicular bone.
3. Pain Management
Pain management strategies, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), may be recommended to alleviate discomfort and reduce inflammation. However, it’s essential to use medications as directed by a healthcare professional.
4. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can aid in the rehabilitation process by improving strength, flexibility, and overall foot function. A physical therapist may design a personalized exercise program to facilitate recovery and prevent future injuries.
5. Surgical Intervention
In rare cases, when conservative treatments fail to provide relief or when the stress fracture progresses, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgery may involve procedures to stabilize the bone or address any underlying biomechanical issues contributing to the stress fracture.
Prevention of Navicular Stress Fracture
Preventing this involves adopting strategies to minimize risk factors and promote overall foot health:
1. Gradual Increase in Activity
Avoid sudden increases in activity levels. Gradually increase training intensity and duration to allow the bones and muscles to adapt to new demands.
2. Proper Footwear
Invest in well-fitting, supportive footwear designed for your specific activity. Replace worn-out shoes to ensure adequate cushioning and support.
3. Strengthening and Flexibility Exercises
Incorporate strengthening and flexibility exercises into your routine to enhance foot and lower leg strength. Exercises targeting the foot and calf muscles can help improve biomechanics and reduce the risk of stress fractures.
4. Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider or sports medicine specialist can help identify potential issues early and provide guidance on maintaining foot health.
Conclusion
A navicular stress fracture is a significant concern for athletes and active individuals, but with proper understanding and management, it is possible to recover fully and prevent future injuries. Recognizing the causes and symptoms of a navicular stress fracture allows for timely diagnosis and effective treatment. By adopting preventive measures and following recommended treatment protocols, individuals can maintain their foot health and continue enjoying their favorite activities without the fear of recurring stress fractures.